Alcohols, Amines, and Carboxylic Acids - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 23
Title:
Alcohols, Amines, and Carboxylic Acids
Description:
Consist of three fatty acids linked to a single molecule of glycerol via a ... Fatty acids become linked to glycerol through an ester bond ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:51
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Alcohols, Amines, and Carboxylic Acids
1
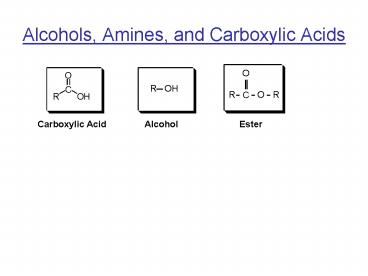
Alcohols, Amines, and Carboxylic Acids
O
R OH
C
R
O
H
Carboxylic Acid Alcohol
Ester
2
Reactions of Carboxylic Acids
- With Alcohols
- With Amines
3
Reactions of Alcohols
- With Carboxylic Acids
- With Other Alcohols
4
Reactions of Amines
- With Carboxylic Acids
5
Chapter 8Lipids
6
- Lipids
- are a class of organic molecules found in
nature, mostly from living things, that are - Soluble only in organic (non-polar) solvents
- Insoluble in water
7
- Lipids
- Hydrophobic molecules
- Consist of C, H, and O (note the proportion of O
is much lower in lipids than in carbohydrates) - Various classes of lipids
- 1. Triglycerides (neutral fats)
- Consist of three fatty acids linked to a single
molecule of glycerol via a condensation/dehydratio
n reaction - Fatty acids become linked to glycerol through an
ester bond - Fatty acids can be saturated or unsaturated
- Concentrated source of energy
- Stored in adipocytes or fat cells
8
Triglyceride Synthesis
9
Triglyceride Synthesis
10
O
11
(No Transcript)
12
f
a
t
t
y
a
c
i
d
s
t
h
a
t
c
o
n
t
a
i
n
a
t
l
e
a
s
t
o
n
e
C
-
C
d
o
u
b
l
e
b
o
n
d
13
Polyunsaturated Fatty acids
14
Some other examples of unsaturated fatty acids
15
Differences between saturated and unsaturated
fatty acids
Saturated Fatty Acids
16
Unsaturated Fatty acids
17
Fats and Oils
- A fat is a triacylglycerol that is solid at
room temperature
- An oil is a triacylglycerol that is liquid at
room temperature
- Usually fats come from animal sources and
contain more saturated fatty acids
- Oils come from plant sources and have a high
content of unsaturated fatty acids
18
- 2. Phospholipids
- Consist of two fatty acids and a phosphate head
group linked to a single molecule of glycerol - Main lipid component of the cell (plasma)
membrane - Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules they
have both polar and non-polar regions - Phosphate head group is polar (hydrophilic)
- Fatty acid groups are non-polar (hydrophobic)
19
(No Transcript)
20
- 3. Eicosanoids
- 20 carbon compounds synthesized from arachidonic
acid - Function predominantly as hormone-like substances
that allow communication between cells - Most diverse group are the prostaglandins
- Contain 5 carbon ring
- Produced by almost all tissues
- Involved in various processes, including
inflammation, blood clotting, labor contractions
and blood vessel diameter
21
(No Transcript)
22
- 4. Steroids
- Lipid containing 4 rings
- Cholesterol is the parent molecule for the
synthesis of all other steroids - Corticosteroids (prednisone, hydrocortisone,
aldosterone) - Progesterone
- Testosterone
- Estrogens
- Bile acids
- Vitamin D
- Cholesterol made only in animal cells
(hepatocytes) - Cholesterol is also a necessary component of cell
membranes
23
C
D
A
B
Steroid
Cholesterol