Chapter 21' Derivatives of Carboxylic Acids - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 36
Title:
Chapter 21' Derivatives of Carboxylic Acids
Description:
acetyl chloride. 3-methyl-4-pentenyl bromide. Chapter 21. 6. 7. Anhydrides - for symmetrical ... acetyl propionyl anhydride. Chapter 21. 7. B. Spectroscopy. 1. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:128
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Chapter 21' Derivatives of Carboxylic Acids
1
Chapter 21. Derivatives of Carboxylic Acids
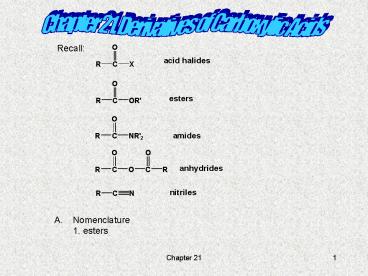
Recall
- Nomenclature
- 1. esters
2
Drop ol, add yl
Drop oic, add oate
Alcohol part of name goes before acid part of
name.
Common name n-propyl acetate IUPAC name
n-propylethanoate
trans-1-bromopropyl-2-butenoate
3
2. lactones - cyclic esters - add word lactone
to acid part of name, a number indicates
where the alcohol oxygen is joined to the
carbon
3,3-dimethyl-3-propanoic acid lactone
3. amides
4
Drop oic acid or ic acid from carboxylic acid
name, add amide. For groups on nitrogen name
as N-alkyl.
N-ethyl-N-methyl-3-phenyl- butanamide
Common N-phenylacetamide IUPAC
N-phenylethanamide
4. lactams - cyclic amides - name same as
lactones
5-amino-N,2-dimethyl-pent-3-enoic lactam
5
5. nitirles - as a group cyano - as the parent
name add nitrile to the alkane name.
Recall priority ordering 1. Acid 6. Ketone 2.
Ester 7. Alcohol 3. Amide 8. Amine 4. Nitrile 9.
Alkene 5. Aldehyde 10. Alkyne
2-methyl-4-pentanonenitrile
methyl 4- cyanopentanoate
6. acid halides - drop ic acid and yl halide
acetyl chloride
3-methyl-4-pentenyl bromide
6
7. Anhydrides - for symmetrical -
Drop acid add anhydride
For mixed anhydrides -
Drop ic acid name each acid portion and add
yl along with anhydride
acetyl propionyl anhydride
benzoic anhydride
7
B. Spectroscopy 1. IR
1710 cm-1
2500 - 3500 cm-1
1735 cm-1
3200 - 3500 cm-1
two peaks
1650 cm-1
one peak
1800 cm-1
1800 and 1750 cm-1
two peaks
2200 cm-1
8
2. 1H NMR
? 10-13 ppm, broad disappears with added D2O
X OH, OR, NH2, etc.
? 8 ppm
? 5-8 ppm, broad disappears with added D2O
? 60 ppm
3. 13C NMR
? 50 ppm
X OH, OR, NH2, etc.
? 170 ppm
? 120 ppm
9
4. special consideration - amides
Two different methyl groups!!
C. Uses - nitriles, acid halides and anhydrides
are really only used to make other
compounds, but esters and amides
10
mating pheromone for elephant several kinds of
moths
aspirin - Bayer C. Gerhardt (1853)
jasmine oder
banana oder
11
caffeine
piperine major component in pepper
capsaicin - peppers
Melatonin-natures sleeping
pill NOT Melanin
valium
12
Proteins and peptides!!
many polymers of amides (nylon, etc.) and
esters - see book
13
D. General reactivity patterns
14
The reactivity at CO depends on the amount of
resonance
And the leaving group ability of X- in RC(O)X
Cl- gt - OC(O)R gt -OR gt -NH2
15
So reactivity goes
Most reactive
Least reactive
16
E. Reactions of acid chlorides 1. General cases
and mechanism of substitution
17
2. reduction a. LiAlH4
b. LiHAlOC(CH3)33
18
c. Rosenmund reduction
3. addition of organometallics a. R-Li or R-MgX
19
b. organocuprates - recall
20
This is just an analog of the Gillman reaction
21
4. Friedal Crafts acylation
22
F. Reactions of anhydrides 1. substitution
reactions
23
2. Friedal-Crafts acylation
G. Reactions of esters 1. saponification - basic
conditions
24
2. hydrolysis - acid catalyzed
Notice that this is reversible.
Synthetically we always make esters by acid
chlorides or anhydrides!
25
Related to this is a series of reactions called
transesterification which is either acid or base
catalyzed
Work out the mechanism for each!!
26
3. addition of organometallics
27
4. reduction of esters
NOTE - NaBH4 does not react!!
28
F. Reactions of amides 1. acid and base
catalyzed hydrolysis
29
2. alkylation
30
3. reduction - remember esters ? alcohols.
4. dehydration
31
G. Reactions of nitriles 1. hydrolysis a. acid
catalyzed
(reverse of reaction before!!)
32
b. base catalyzed
33
c. addition of organometallics
34
d. reduction
35
We are skipping sections 21.15 21.16!!
H. Summary 1. Nomenclature - IUPAC common 2.
Spectroscopy - general features 3. Reactions of
acid chlorieds/ anhydrides a. additions of
nucleophiles b. reduction i. LiAlH4 ii.
LiHAlOC(CH3)33 c. addition of
organometallics i. R-Li/ Grignard
reagents ii. Gillman coupling d. acylation
reactions
36
4. Reactions of esters/ amides/ nitriles a.
hydrolysis i. base catalyzed ii. acid
catalyzed b. reduction c. addition of
organometallics