The ten essential shared capabilities - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 11
Title:
The ten essential shared capabilities
Description:
Be able to engage the learner in a collaborative assessment process. ... Demonstrate ability to develop harmonious working relationships with learners ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:33
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The ten essential shared capabilities
1
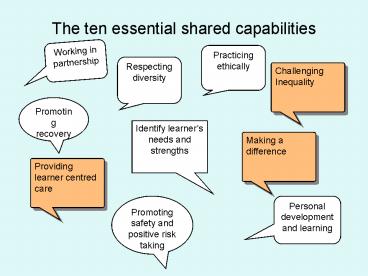
- The ten essential shared capabilities
Working in partnership
Practicing ethically
Respecting diversity
Challenging Inequality
Promoting recovery
Identify learners needs and strengths
Making a difference
Providing learner centred care
Promoting safety and positive risk taking
Personal development and learning
2
1. Working in Partnership
- Have the ability to explain in an understandable
way, their professional role and any parameters
they are working in. - Have the ability to communicate with all
stakeholders involved in an individuals care and
understand own role and that of others within
multidisciplinary setting - Be able to engage the learner in a collaborative
assessment process. - Communicate across professional and
organisational boundaries.
3
2. Respecting Diversity
- Provide a learning environment where existing
beliefs about age, race culture, disability,
gender, spirituality and sexuality can be
examined and challenged. - Understand the impact of discrimination and
prejudice in mental health and mental health
services. - Demonstrate the ability to promote peoples
rights and responsibilities and recognise the
learners rights to privacy, dignity, respect and
confidentiality.
4
3. Practising ethically
- Demonstrate an understanding of and commitment to
the legal and human rights of learners and their
carers. - Have the ability to respond to the needs of
people in an ethical, honest, non judgemental
manner. - Have the ability to encourage active choices and
participation in care and treatment (including
learning). - Have an understanding of the learners wider
social and support network and the contribution
made by carers, family and friends to the
recovery process. - Knowledge of policies, practices and procedures
concerning the local mental health services - and related legislation.
5
4. Challenging Inequality
- Understand the nature of stigma
- Understand the effects of exclusion and
discrimination - Understand the role that services have to play in
fighting inequality and discrimination. - Demonstrate the ability to challenge inequality
and discrimination within their role. - Demonstrate the ability to communicate their
concerns to others within the care - system.
6
5. Promoting Recovery
- Understand that recovery is a process that is
unique to each person. - Recovery is about recovering what was lost
rights, roles, responsibilities, decision making
capacity, potential and mental well being. - Understanding the essential role of hope in the
recovery process. - Understand that the planning, arrangements and
delivery of support should be determined by the
needs of the learner. - Ensure all efforts are made to present
non-stigmatizing and positive views of people who
experience - mental health problems.
7
6. Identifying peoples needs and strengths
- Help learners to describe their experience in
such a way as to identify their strengths and
formulate their needs. - Understand the impact that other parts of the
system may have on the individuals physical and
mental health. - Understand how the physical and mental health of
an individual can be promoted or demoted. - Understand the impact that an individuals health
needs, mental or physical, may have on other
parts of the system.
8
7. Providing Learner Centred care
- Negotiating achievable and meaningful goals from
the perspective of the learner. - Helping the learner to identify and use their
strength to achieve their goals and aspirations. - Ensure that any goals are achievable and
measurable. - Identify strengths and resources within the
learners wider network which may have a role to
play in supporting goal achievement.
9
8. Making a Difference
- Understand the impact of any particular problem
on the life of the learner. - Have the ability to design, or contribute to the
design, of programmes of learning (care) based on
best practice or the best available evidence. - Understand the role that others may play in such
a programme. - Communicate with all, including the learner, who
have a part to play in a programme of learning.
10
9. Promoting safety and positive risk taking
- Demonstrate ability to develop harmonious working
relationships with learners who may not wish to
engage with mental health services. - Contribute to accurate and effective risk
assessments, identifying specific risk factors
relevant to the individual. - Contribute to the development of risk management
strategies and plans which involve the learner
and clearly identify the agreed action to be
taken. - Working with the tension between promoting safety
and positive risk taking and dealing with
possible risks for the learner and the wider
community. - Demonstrate understanding of multi-agency working
in promoting safety and positive risk taking.
11
10. Personal development and learning
- Keeping up to date with changes in practice .
- Participate in life-long learning, personal and
professional development . - Access to education and training based on the
best available evidence. - To recognise the importance of supervision and
reflective practice and integrate both in
everyday practice.