Technologies for the Data Grid - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 6
Title:
Technologies for the Data Grid
Description:
(GUMS SAZ ...) Fat Client. 1. 2. 3. Periodic. Updates. Identity & Attribute. Management (VOMS) ... (ESG Security Service Shib-ACEGI/SSO, MyProxy) B,D,E use ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:20
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Technologies for the Data Grid
1
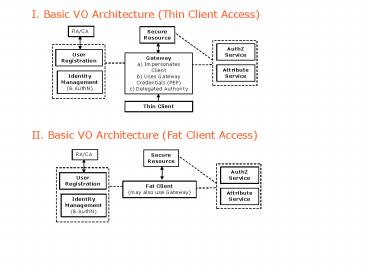
I. Basic VO Architecture (Thin Client Access)
RA/CA
SecureResource
AuthZ Service
UserRegistration
Gatewaya) ImpersonatesClientb) Uses
GatewayCredentials (PEP)c) Delegated Authority
AttributeService
Identity Management( AuthN)
Thin Client
II. Basic VO Architecture (Fat Client Access)
RA/CA
SecureResource
AuthZ Service
UserRegistration
Fat Client(may also use Gateway)
AttributeService
Identity Management( AuthN)
2
OSG VO Architecture
RA/CA
UserRegistration(VOMS-RS)
3
SecureResource
AuthZ Service(GUMSSAZ)
2
4
PeriodicUpdates
Identity AttributeManagement(VOMS)
Fat Client
1
2
3
TeraGrid VO Architecture (Fat Client)
RA/CA
CentralizedAccountingSystem
UserRegistration(Create cert, accounts, Gridmap
files)
AuthZ(local accounting system)
3
SecureResource
2
4
Identity AttributeManagement(My-Proxy)
1
Fat Client
3
4
TeraGrid VO Architecture (Gateway)
CentralizedAccountingSystem
RA/CA
AuthZ (local accounting system)
UserRegistration(Create cert, accounts, Gridmap
files)
4
Secure Resource
3
5
Gateway (Local AuthN,Community account)
1
6
Identity AttributeManagement(My-Proxy)
2
Thin Client
4
5
ESG VO Architecture Plan
RA/CA
C. SecureResource
D. AuthZ Service(TBD)
4
A. UserRegistration(Purse/Relational db)
3
0
Gatewaya) Impersonates ClientShib/ACEGI-SSO
2
B.E. Identity/AttributeManagement (ESG Security
Service Shib-ACEGI/SSO, MyProxy)
1
Thin Client
B,D,E use same database
6
caBIG VO Architecture
CA
Trust Root Provisioning(Grid Trust Service)
D. AuthZ Service(Common Security Module)
B. Grid Identity Management (Dorian)
4
C. SecureResource
5
2
E. Attribute Service(Grid Grouper)
6
3
B. Local Identity Management (Institution
Identity/RA)
Fat Client
1