Land Use in the World - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
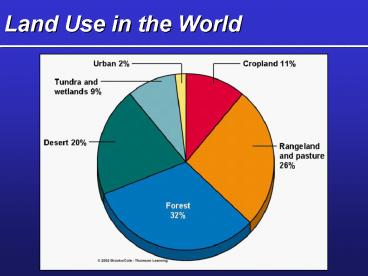
Land Use in the World
Description:
Developed to maximize use and profit. Sold to homesteaders, railroads, ... Aldo Leopold, WI conservationist. 1964: National Wilderness Act (4 ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:26
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Land Use in the World
1
Land Use in the World
2
Land Use in the United States
3
U.S. Public Lands
4
Managing U.S. Public Lands
- Management ethics
- Economic
- Balanced multiple use
- Ecological
- Preservationist
5
Changing Management
- Through late-1800s economic
- Developed to maximize use and profit
- Sold to homesteaders, railroads,
- timber and mining companies
6
Changing Management
- Late-1800s balanced multiple use
- Use in several ways, but manage
- properly so resource is not damaged
- Maximum sustained yield
- Set aside forest reserves to ensure
- adequate timber supply, protect
- river watersheds
7
Changing Management
- Also late-1800s ecological
- Use it, but emphasize maintaining
- natural aspects (plants, animals)
- 1872 lands set aside for eventual 1st
- national park - Yellowstone
- Ethic supported greatly by U.S.
- President Theodore Roosevelt
8
Changing Management
- Throughout 1900s preservationist
- No development, leave as is for future
- Aldo Leopold, WI conservationist
- 1964 National Wilderness Act (4)
- - lands set aside, retained in natural
- state, no development unless for the
- national good
9
Todays Management
- Most lands managed according to
- balanced multiple use or ecological
- ethics
- - e.g. U.S. Forest Service
- Bureau of Land Management
- Public lands still facing many problems
10
Conflicting Demands
Mineral Resources
11
Wilderness Problems
- Suffering from overuse
- Limited entry in many areas
- Timber, mining companies want
- access to resources
- For the national good
12
Park Problems
- Severe overuse
- Billions of visitors each year
- Cars, noise, pollution, litter, crime
- Conflicts between providing for
- visitor enjoyment and still
- conserving resources
13
Managing and Sustaining National Parks
- Most parks are too small to maintain biodiversity
- Invasion by exotic species
- Popularity a major problem
- Traffic jams and air pollution
- Visitor impact (noise)
- Natural regulation
- Better pay for park staff
14
Forest Problems
- Conflicting demands
- Timber, grazing, recreation, mining,
- ecology
- Ecological benefits air cleaning,
- erosion control, oxygen, soil fertility,
- water recycling, wildlife shelter
- Exceeding maximum sustained yield
- in many areas
15
Types of Forests
- Old-growth (frontier) forests
- Second-growth forests
- Tree farms/plantations
16
Rangeland Problems
- Overgrazing
- Too many on too little for too long
- Kills grass root systems
- When combined with drought,
- overgrazing can cause desertification
- - conversion to desert
17
The Fuelwood Crisis
- Planting fast-growing fuelwood plants
- Burning wood more efficiently
- Switching to other fuels
18
Degradation of Tropical Forests
19
Logging Roads
- Increased erosion and runoff
- Habitat fragmentation
- Pathways for exotic species
- Accessibility to humans
20
Tropical Deforestation
- Rapid and increasing
- Loss of biodiversity
- Cultural extinction
- Unsustainable agriculture and ranching
- Clearing for cash crop plantations
- Commercial logging
- Fuelwood
21
Reducing Tropical Deforestation
- Identification of critical ecosystems
- Reducing poverty and population growth
- Sustainable tropical agriculture
- Encourage protection of large tracts
- Debt-for-nature swaps
- Less destructive harvesting methods