General model for transcriptional regulation in higher eukaryotes - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 35
Title:
General model for transcriptional regulation in higher eukaryotes
Description:
TBP: TATA binding protein. TAF: TBP associated protein. BRE: TFIIB response element ... TATA(AT)AA(GA) YYAN(TA)YY. Y = C or T (pyrimidine) (AG)G(AT)(CT)(GAC) ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:125
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: General model for transcriptional regulation in higher eukaryotes
1
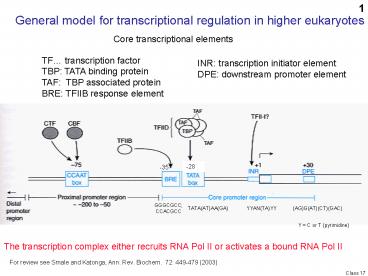
General model for transcriptional regulation in
higher eukaryotes
Core transcriptional elements
TF transcription factor TBP TATA binding
protein TAF TBP associated protein BRE TFIIB
response element
INR transcription initiator element DPE
downstream promoter element
-28
-35
GGGCGCC CCACGCC
TATA(AT)AA(GA)
YYAN(TA)YY
(AG)G(AT)(CT)(GAC)
Y C or T (pyrimidine)
The transcription complex either recruits RNA Pol
II or activates a bound RNA Pol II
For review see Smale and Katonga, Ann. Rev.
Biochem. 72 449-479 (2003)
2
Many enhancer elements often lie upstream of
promoters,allowing for many combinations of TF
binding
3
DNA regulatory region upstream of a reporter gene
to analyze elements
Space for res. enz. to bind
Reportergene
PCR
4
Popular reporters to study promoter/enhancers
- Beta-galactosidase (B-gal) detection by several
different assays - Luciferase (firefly, Renilla jellyfish)
detection, easy dual, sensitive luminescent
assay - Green fluorescent protein (GFP, BFP, YFP))
cytological, visible in living cells, fusion
proteins, FACS - Neomycin phosphotransferase (neo)selectable drug
resistance (G418R)
5
Testing for a cell-specific promoter
chloramphenicol acetyl transferase (CAT) reporter
assay
CAT cDNA is from a prokaryotic source. CAT is
not found in mammalian cells. Therefore low
backgrounds
diacetylated
B
A
Thin layer chromatography (TLC)
monoacetylated
6
Mapping transcriptional elements upstream of a
promoter Mapping with restrictionenzyme
mediated deletions
Conlcusion
7
Corticosteroids purified from adrenal gland
extracts ( then chemically synthesized and
chemical analogs made) as active ingredients with
many physiological responses, including
anti-inflammatory actions. Nobel Prize 1950 How
do they act? Bind receptors (one is GR), which
move to nucleus, bind DNA, activate or repress
specific transcriptional targets, depending on
exact binding site and partner co-activator or
co-repressors
8
(No Transcript)
9
(No Transcript)
10
(No Transcript)
11
(No Transcript)
12
(No Transcript)
13
(No Transcript)
14
Protein-DNA binding EMSA or gel shift
(EMSA electrophoretic mobility shift assay)
1 2 3 4 5
competitor
(supershift)
(shift)
DNA element
(Even though the hexagon looks like a protein
here)
U. Arizona
15
Gel shifts (EMSA
Protein DNA complexes migrate more slowly than
naked DNA
(competed only by specific probe)
(two molecules of protein bound)
(competed by NON-specific probe)
16
Footprinting detects sites on DNA to which
protein are bound
DNA DNA-binding protein
Naked DNA
Population of molecules
Population of molecules
missing
17
Note uneven cleavage of naked DNA by DNase
18
Methylation Interference
Partially modify bases (G, A) by methylation of
pure labeled DNA fragment
Bind DNA to protein and Separate DNA that is bound
Cleave DNA at methylated sites No bands for
positions where methylation Prevented protein
binding
19
(No Transcript)
20
(No Transcript)
21
(No Transcript)
22
(No Transcript)
23
(No Transcript)
24
(No Transcript)
25
(No Transcript)
26
(No Transcript)
27
(No Transcript)
28
(No Transcript)
29
ChIP-chip for protein DNA interactions
Isolate chromatin
Formaldehyde (HCHO) crosslinks amino groups on
proteins to functional groups on DNA bases
No-antibody background
Ab to the protein of interest
Using protein A beads
Gives total DNA signal for comparison
Formaldehyde crosslinks can be reversed by heat,
pH, or high salt
Cy5 and Cy3 are fluorescent labeling compounds of
different color
via linker ligation (ligate a constant DS
sequence to all fragments and then do PCR) or
random priming (using random hexamers, say)
30
ChIP-chip for protein DNA interactions
Isolate chromatin
Formaldehyde (HCHO) crosslinks amino groups on
proteins to functional groups on DNA bases
Ab to the protein of interest
No-antibody background
Using protein A beads
31
Gives total DNA signal for comparison
Formaldehyde crosslinks can be reversed by heat,
pH, or high salt
Cy5 and Cy3 are fluorescent labeling compounds of
different color
via linker ligation (ligate a constant DS
sequence to all fragments and then do PCR) or
random priming (using random hexamers, say)
32
(No Transcript)
33
Synthetic, range usually 6 to 40-mers
SELEX
(T7 RNA Pol from an embedded T7Pol promoter
(huge number)
(usually a protein)
by PCR
(re-iterate 3-10 times)
Binding to Protein, e.g.
Separate using nitrocellulose binding, gel
electrophoresis, etc.
sequences ? consensus
34
(No Transcript)
35
(No Transcript)