Coleus stem tip - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 39
Title:
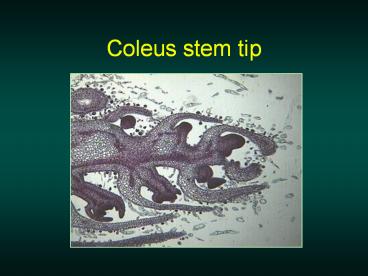
Coleus stem tip
Description:
Fungi can perform similar functions to root hairs in the more mature portion of the roots ... Monocot root close up. Dicot secondary growth in root ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:470
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Coleus stem tip
1
Coleus stem tip
2
Root systems
- Fibrous systems are characteristic of monocots
- Tap roots are typically found in dicots and
gymnosperms
Fibrous
Tap
3
- Examples of strong tap roots
4
Root cap apical meristem
- Notice the pattern of cells that have been laid
down by the apical meristem.
Wheat
5
Root tip
Protoderm
Root cap
Procambium
Ground meristem
Apical meristem
6
Root tip growth regions
7
(No Transcript)
8
Three zones of the root tip
9
(No Transcript)
10
Root hairs
11
Arabidopsis
12
Epidermal cells - root hairs
13
Mycorrhizae
- Fungi can perform similar functions to root hairs
in the more mature portion of the roots
14
(No Transcript)
15
Dicot (Buttercup) root x-section
- The vascular tissue is in the center of the root
epidermis
cortex
Endodermis
16
(No Transcript)
17
(No Transcript)
18
Vascular cylinder
- As in the stem, xylem is to the inside, phloem to
the outside - Endodermis surrounds the stele
cortex
xylem
phloem
endodermis
pericycle
19
Endodermis
20
Endodermis
- The Casparian strip blocks water and minerals
from moving through the exoplast to the vascular
tissues
Casparian strip
Cell wall
membrane
Plasmodesmata
21
(No Transcript)
22
Vascular cylinder
- Pericyle (one cell thick) surrounds the vascular
tissue
cortex
xylem
phloem
endodermis
pericycle
23
Lateral roots
- Lateral roots arise from the pericycle
- Vascular tissue in the new root is connected to
that tissue in the parent root.
24
Monocot root x-section
- Pith is
- found
- in the
- center
- of
- monocot
- roots
25
(No Transcript)
26
Monocot root close up
27
Dicot secondary growth in root
- Vascular cambium is between the xylem and phloem
extends to the pericycle
28
Dicot secondary growth in root
- Like in the stem, xylem is formed to the inside,
phloem to outside
29
Vascular cylinder
cortex
xylem
phloem
endodermis
pericycle
30
Root branching
- Note the grafting in the Beech roots
Ash
Beech
31
N fixing nodules
Rhizobium nodules
Actinomycete on Alnus
32
Prop roots
Banyan tree
Red Mangrove
33
Epiphyte roots
34
Specialty roots
- Manroot
- weighs 60 lbs. and stores water
35
Pathway of water movement
- The endodermis regulates what ions enter the
vascular tissues
36
Water movement
- Water movement into the tissues of the plant
follows the water potential gradient
37
Absorption lag
- Caused by resistance in the water path in the
root (water must pass through endodermis) - When roots are cut off under water in an actively
transpiring plant, absorption into the xylem
increases. - The lag may be great enough to cause mid-day
closure of the stomata until the absorption rate
catches up
38
Root pressure
- Minerals actively pumped into the xylem lower
water concentration - Water diffuses into the xylem causing a pressure
to build since the cells can not expand - Water is forced up the xylem
39
Leaf guttation
- Root pressure can cause guttation of water from
the leaf, especially in small plants
40
(No Transcript)