Sequelae of Preterm Birth - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 46
Title:
Sequelae of Preterm Birth
Description:
1. Multiple births 2 assisted reproductive techniques. ... of metronidazole 48 hours apart, on two occasions did not reduce preterm birth. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:171
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Sequelae of Preterm Birth
1
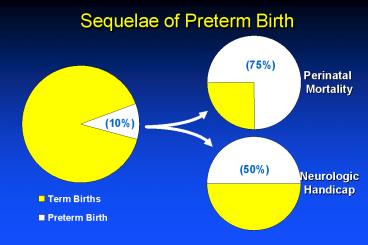
Sequelae of Preterm Birth
(75)
Perinatal Mortality
(10)
(50)
Neurologic Handicap
2
Incidence of Preterm Birth in The
U.S.A.1981-1994
3
Time Trends in Low Birth Weight (lt1,500 g) by
Race/Ethnicity - United States, 1970-1990
4
Increase in Preterm Birth
- 1. Multiple births 2 assisted reproductive
techniques. - 2. Increased indicated preterm deliveries.
- 3. Increased spontaneous preterm births ?
chorioamnionitis.
5
UAB Infants with Birthweights 1000 Grams
- Mean BW Survival
- 1975 900 gms 17
- 1980 860 gms 48
- 1985 820 gms 56
- 1990 804 gms 74
6
Distribution of Neonatal Mortality
- BWT (gms) Distribution
- lt1000 60
- 1000-2500 20
- gt2500 20
Majority associated with congenital anomalies
7
Preterm Birth
- Success Reduction in mortality
- Failures No reduction in SPB
- Little or no reduction in long-term handicap
among smallest survivors
8
What Outcomes Do We Really Care About?
- Living or dying (mother or fetus/infant)
- Long-term handicap (cerebral palsy)
- Severe neonatal morbidity (high cost)
9
Etiology of Preterm Birth
Preterm Birth for Maternal or Fetal Indications
Spontaneous Preterm Labor
20
50
30
Premature Rupture of Membranes
10
Two Possible Strategies to Improve Low
Birthweight Outcomes
- Prevent low birthweight
- Prevent morbidity and mortality in low
birthweight fetuses and newborns
11
REVIEW OF INTERVENTIONS TO PREVENT PRETERM BIRTH
Commonly used interventions which have not been
shown to reduce preterm birth include
- Prenatal care
- Risk screening
- Nutrition counseling
- Caloric supplementation
- Protein supplementation
- Iron supplementation
- Most labor inhibiting agents
- Drug, alcohol and tobacco cessation programs
- Bed rest
- Hydration
- Home uterine activity monitoring
12
PRENATAL CARE
- In general,
- 1) the provision of prenatal care to a population
which had none, - 2) more prenatal care where there was little, or,
- 3) advanced prenatal care where only routine care
was available - has not resulted in a reduction in prematurity
13
VALUE OF PRENATAL CARE
- Substantial decrease in stillbirths
- Substantial decrease in term neonatal mortality
- No or marginal effect on preterm birth rate
- No or marginal effect on very low birthweight
survival
14
Screening for Risk of Preterm Delivery
- Do the demographic/historical scoring systems
have any use?
15
Risk Scoring Systems and Preterm Delivery
- Low sensitivity and high false positive rates.
- Most of those who eventually have a preterm birth
are from the low-risk group, I.e., many false
negatives. - Identification of the high-risk status has not
led to a uniform improvement in outcome.
16
Predicting Preterm Birth
- When formal risk scoring for preterm birth is
part of standard antenatal care, a large number
of interventions are applied with a frequency
that is considerably higher than that found
elsewhere. - Chalmers Kierse
17
Bed Rest
- Recommended for
- Treatment of first trimester bleeding
- Treatment of second and third trimester bleeding
- Prevention of PTL in singletons
- Prevention of PTL in twins
- Treatment of PTL
- Prevention of preeclampsia
- Treatment of preeclampsia
- Treatment of non-proteinuric hypertension
- Treatment of edema
- Treatment of growth retardation
18
Bed Rest
- Randomized studies show no improvement in outcome
associated with bed rest in these conditions - First trimester bleeding
- Prematurity in twins
- Preeclampsia
- Non-proteinuric hypertension
- Growth retardation
- There are no studies showing benefits of bed rest
associated with preterm labor.
19
Four randomized studies of bed rest in hospital
in twin gestation to prevent preterm delivery
- Reference Hosp. (wk) Outcome
- Hartikainen-Sorri et al 30 No change
- 1984 (N 146)
- Saunders et al. 32 30 PTD in study subjects
- vs. 19 in controls (p lt 0.05)
- Crowther et al. 34 No change
- 1989 (N139)
- MacLennan et al 26-30 PTD before 32 wk,
- 16 in study subjects
- vs 8 in controls
20
Preterm Labor
- There were no significant differences in the
outcomes of women randomized in observation,
hydration, or one dose of subcutaneous
terbutaline.
(Guinn et al, 1997)
21
Antibiotics in Women with Preterm Labor and
Intact Membranes
- Delayed Improved Infant Study Antibiotic
N Delivery OutcomeMacGregor, 1986 Erythromycin
17 Yes No - Morales, 1988 Erythromycin, Ampicillin 150 Yes
No - Winkler, 1988 Erythromycin 19 Yes -
- Newton, 1989 Erythromycin / Ampicillin 95
No No - MacGregor, 1991 Clindamycin 103 Yes No
- McCaul, 1992 Ampicillin 40 No No
- Romero, 1993 Ampicillin / Amoxicillin /
Erythromycin 275 No No - Cox, 1995 Ampicillin / Amoxicillin 78 No
No - Gordon, 1995 Ceftizoximine 117 No No
22
Antibiotics in Women with Preterm Labor and
Intact Membranes
- Meta-analysis of existing RCTs
- These results do not support the routine use of
antibiotics in women in preterm labor
Egarter et al, 1996
23
Antibiotics and Preterm BirthLabor with Intact
Membranes
Metronidazole and Ampicillin for 6 days at 30
weeks in a RCT
- Study Group Placebo GroupOutcome n43 n38
- BWT (x) (g) 2318 2093
- Days to delivery (median) 15 2.5
- Delivery lt7 days () 37 63
- NEC () 0 13 plt.05
- greater prolongation occurred in lt30 week
pregnancies
Norman et al (South Africa), Br J Obstet
Gynaecol, 1994
24
Antibiotics and Preterm Birth Labor with Intact
Membranes
Ampicillin and Metronidazole for 8 days at 30
weeks in a RCT
- Antibiotics Placebo
- Outcome (n59) (n51) P value
- Days to delivery (x) 48 27 .01
- GA at delivery (wks) (x) 37 34 .01
- Birth lt37 weeks () 42 65 .01
- BWT (g) (x) 2662 2370 .08
- NICU Admission () 40 63 .03
- Neonatal sepsis () 10 22 .18
Svare et al (Denmark), Br J Ob Gyn 1997
25
Survival Curves Cervical Fetal Fibronectin at
Week 24
Proportion not Delivered
1.0
0.9
negative FF
0.8
0.7
0.6
positive FF
30
25
35
Gestational Age
26
- In women with a short cervix, placement of a
cerclage has produced conflicting data in regard
to a reduction in preterm birth - Althuisius and Rust, SMFM 2001
27
FETAL FIBRONECTIN
- A marker for upper genital tract basement
membrane disruption
28
FFN AND PRETERM BIRTH
- Delivery (weeks) OR
- lt28 60
- lt30 42
- lt32 23
- lt35 11
- lt37 5
- Goldenberg AJOG 1995
29
Summary
- Whether this screening test will ultimately be of
value in reducing preterm births will depend on
the availability of an effective intervention.
30
Fetal Fibronectin
- Women in early preterm labor with a negative fFN
test have lt1 chance of delivering in the next 2
weeks. - Use of the test based on its negative predictive
value may result in fewer hospitalizations and
reduce cost.
31
Bacterial VaginosisandPreterm Birth
32
BV and Prematurity
- The odds ratio for preterm birth in association
with BV in nearly every study ranges from 1.5 to
3.0
33
BV and Prematurity
- Randomized trial of metronidazole and
erythromycin in women with BV and at high risk
for PTB - Rx 23 Placebo 37 p lt.001
Hauth 1994
34
BV and Preterm Birth
- Treating asymptomatic predominantly low-risk
women with BV with two doses of 2gm of
metronidazole 48 hours apart, on two occasions
did not reduce preterm birth.
35
- Advances in molecular biology make possible many
new predictive tests for preterm birth. - Predicting preterm birth without an effective
treatment results in an increase in use of
ineffective interventions and increased cost, and
potentially an increase in iatrogenic
complications.
36
Markers for SPBConsiderations
- The major reason to prospectively identify
markers of SPB is to identify women who may
benefit from a specific intervention determined
to prevent the SPB. - Before one introduces the use of markers into
practice, effective intervention in women
positive for that marker should be available.
37
COCHRANES APHORISM
- Before ordering a test, decide what you will do
if it is - 1. Positive 2. Negative
- If both answers are the same, dont do the test.
38
Preventing Prematurity
- Most strategies aimed at preventing preterm birth
have not been shown to be effective when applied
to defined populations. - It is therefore not surprising that the
prematurity rate has not declined.
39
Can the morbidity and mortality associated with
preterm delivery be reduced or eliminated?
- RDS
- NEC
- IVH
- PDA
- Sepsis
- SIDS
40
ANCS
- In this retrospective analysis, multiple courses
of antenatal corticosteroids did not improve
outcome and were associated with increased
mortality, decreased fetal growth, and prolonged
adrenal suppression. - Banks, AJOG 1999
41
- Weekly courses of ANCS did not improve any
pregnancy outcome compared to a single dose. - Guinn, SMFM 2001
42
- Everything is a poison.
- The only thing that distinguishes a poison from a
remedy is dose. - Alan Jobe
43
Maternal Health Care
- The premature use of new technology pervade
modern medical practice. Obstetrics, like the
rest of medicine, must adopt a sensible but
rigorous approach to the evaluation of new
technology. - Thacker
44
Summary
- When resources are limited during pregnancy,
interventions should be limited to those that
clearly work.
45
Prematurity
- The treatment of premature labor is identical
with that already described for term labor, and
does not require further mention. - Williams 1908
46
- The great obstacle to discovering the shape of
the earth, the continents, and the ocean was not
ignorance but the illusion of knowledge. - The Discoverers