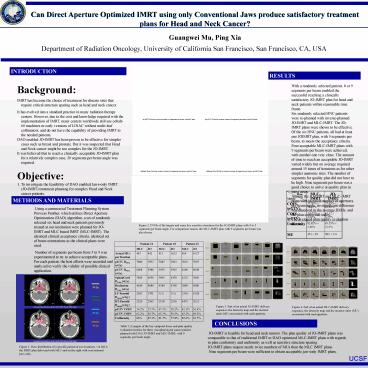
Aucun titre de diapositive - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 1
Title:
Aucun titre de diapositive
Description:
It has evolved into a standard practice in many radiation therapy centers. ... Department of Radiation Oncology, University of California San Francisco, San ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:44
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Aucun titre de diapositive
1
Can Direct Aperture Optimized IMRT using only
Conventional Jaws produce satisfactory treatment
plans for Head and Neck Cancer?
Guangwei Mu, Ping Xia Department of Radiation
Oncology, University of California San Francisco,
San Francisco, CA, USA
INTRODUCTION
RESULTS
- Background
- IMRT has become the choice of treatment for
disease sites that require critical structure
sparing such as head and neck cancer. - It has evolved into a standard practice in many
radiation therapy centers. However, due to the
cost and knowledge required with the
implementation of IMRT, many centers worldwide
still use cobalt-60 machines or early versions of
LINAC without multi-leaf collimators, and do not
have the capability of providing IMRT to the
needed patients. - DAO enabled JO-IMRT has been proven to be
effective for simpler cases such as breast and
prostate. But it was suspected that Head and Neck
cancer might be too complex for the JO-IMRT. - It was believed that to reach a clinically
acceptable JO-IMRT plan for a relatively complex
case, 20 segments per beam angle was required. - Objective
- To investigate the feasibility of DAO enabled
Jaws-only IMRT (JO-IMRT) treatment planning for
complex Head and Neck cancer patients. - To determine the proper number of segments needed
for a clinically acceptable plan for JO-IMRT.
- With a randomly selected patient, 8 or 9 segments
per beam enabled the successful reaching a
clinically satisfactory JO-IMRT plan for head and
neck patients within reasonable time frame. - Six randomly selected HNC patients were
re-planned with inverse-planned JO-IMRT and
MLC-IMRT. The JO-IMRT plans were shown to be
effective. Of the six HNC patients, all had at
least one JOIMRT plan, with 9 segments per beam,
to meets the acceptance criteria. Four acceptable
MLC-IMRT plans with 9 segments per beam were
achieved, with another one very close. The amount
of time to reach an acceptable JO-IMRT varied
widely but on average required around 15 times of
iterations as for other simpler anatomic sites.
The number of segments for quality plan did not
have to be high. Nine segments per beam was a
good choice to arrive at quality plan in most
cases. - Among the JO-IMRT and MLC-IMRT plans with
identical number of apertures per beam angle, no
significant difference was observed in the
average DVHs, and the plan conformal index. - The averaged plan quality evaluation metrics
METHODS AND MATERIALS
- Using a commercial Treatment Planning System
Prowess Panther, which utilizes Direct Aperture
Optimization (DAO) algorithm, a set of randomly
selected six head and neck patients previously
treated at our institution were planned for
JO-IMRT and MLC based IMRT (MLC-IMRT). The
identical clinical acceptance criteria, identical
set of beam orientations as the clinical plans
were used. - Number of segments per beam from 5 to 9 was
experimented to try to achieve acceptable plans.
For each patient, the best efforts were recorded
and analyzed to verify the validity of possible
clinical application. - The plan acceptance criteria were established
according to the RTOG-0225 protocol.
Figure 2. DVHs of the targets and some key
sensitive structures for the JO-IMRT plans with 9
to 5 segments per beam angle. For comparison
reason, the MLC-IMRT plan with 9 segments per
beam was also shown.
Figure 3. Part of an actual JO-IMRT delivery
sequence, the intensity map and the monitor units
(MU) associated with each aperture.
Figure 4. Part of an actual MLC-IMRT delivery
sequence, the intensity map and the monitor units
(MU) associated with each aperture.
CONCLUSIONS
Table 1. Example of the key endpoint doses and
plan quality evaluation metrics for three
nasopharyngeal cancer patient planned with DAO
JO-IMRT and MLC-IMRT, with 9 segments per beam
angle.
- JO-IMRT is feasible for head and neck tumors.
The plan quality of JO-IMRT plans was comparable
to that of traditional IMRT or DAO optimized
MLC-IMRT plans with regards to plan conformity
and uniformity as well as sensitive structure
sparing. - JO-IMRT plans require nearly twice numbers of MUs
than the MLC IMRT plans. - Nine segments per beam were sufficient to obtain
acceptable jaw-only IMRT plans.
Figure 1. Dose distribution of a specific patient
at two locations. On left is the IMRT plan
delivered with MLC and on the right with
conventional jaws only.
UCSF
.