Chapters 11,14, and 15 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 22
Title:
Chapters 11,14, and 15
Description:
A to P segmentation of the segmental plate. determine the ... (myotome) Cells transfected with Xenopus Noggin gene transplanted to chick lateral plate ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:49
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Chapters 11,14, and 15
1
(No Transcript)
2
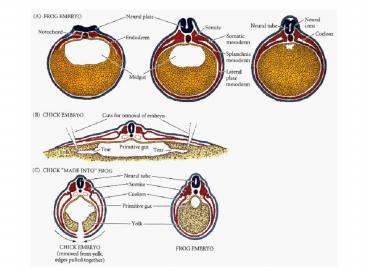
Amniote mesodermal derivatives
Page 191, 11.15 M
heart, blood
amnion chorion yolk sac allantois
blood vessels
tendons
3
Somites
- A to P segmentation of the segmental plate
- determine the migration path of NC cells
- differentiate
- dermis (dermatome)
- vertebrae and ribs (scleretome)
- muscles of back and ribs (myotome)
4
(No Transcript)
5
Cells transfected with Xenopus Noggin gene
transplanted to chick lateral plate
6
back dermis
back, rib, and limb muscles
vertebrae and ribs
Page 199, 11.25 P
7
Somites are formed periodically from A to P
somite
What would happen if segmental plate were
inverted along A-P axis?
segmental (paraxial) plate
8
Notch juxtacrine signaling
Notch Delta juxtacrine signaling (Fig. 6.26)
quail protein
9
(No Transcript)
10
(No Transcript)
11
Control Delta-like 3 knock out mouse
12
The Notch autonomous segmentation clock
From regressing Hensens node
Feedback loops establish periodicity
Retinoic acid keeps L and R clocks synchronized
13
Somite epithelialization mesenchyme to
epithelium transformation
14
(No Transcript)
15
Segmental plate is specified before the somites
form
16
Somite patterning
17
How are multinucleate skeletal muscle cells
(myotubes) formed?
18
Use of chimeric mice
19
Intermediate induced by paraxial mesoderm
8 day mouse. Lim1
Pax2
Pax2 and Lim1 are kidney specific TFs
20
Kidneys and gonads the urogenital system
13-day mouse
21
Reciprocal M-E inductionureteric bud
mesenchyme
22
(No Transcript)