Tooth Fractures - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 10
Title:
Tooth Fractures
Description:
6. Cuspid (canine/eye tooth) 7. Lateral incisor. 8. Central ... 11. Cuspid (canine/eye tooth) 12. 1st Bicuspid (1st premolar) 13. 2nd Bicuspid (2nd premolar) ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1132
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Tooth Fractures
1
(No Transcript)
2
Tooth Fractures
3
Anatomy of Tooth
Cementum - the layer of hard bone-like tissue
covering the root of the tooth. Cemento-enamel
junction - the line where the enamel and cementum
meet. Dentin - the hard yellow tissue underlying
the enamel and cementum, making up the main bulk
of the tooth. Enamel - the hard, white outer
layer of the tooth. Gingiva - the gum tissue
surrounding the tooth. Ligament - the connective
tissue that surrounds the tooth and connects it
to bone. Nerves - relay signals such as pain to
and from your brain. Pulp - located in the center
of the tooth, it contains the arteries, veins and
nerves. Root canal - canal in the root of the
tooth where the nerves and blood vessels travel
through
4
Numbering
1. 3rd Molar (wisdom tooth)2. 2nd Molar (12-yr
molar)3. 1st Molar (6-yr molar)4. 2nd Bicuspid
(2nd premolar)5. 1st Bicuspid (1st premolar)6.
Cuspid (canine/eye tooth)7. Lateral incisor8.
Central incisor9. Central incisor10. Lateral
incisor11. Cuspid (canine/eye tooth)12. 1st
Bicuspid (1st premolar)13. 2nd Bicuspid (2nd
premolar)14. 1st Molar (6-yr molar)15. 2nd
Molar (12-yr molar)16. 3rd Molar (wisdom
tooth)17. 3rd Molar (wisdom tooth)18. 2nd Molar
(12-yr molar)19. 1st Molar (6-yr molar)20. 2nd
Bicuspid (2nd premolar)21. 1st Bicuspid (1st
premolar)22. Cuspid (canine/eye tooth)23.
Lateral incisor24. Central incisor25. Central
incisor26. Lateral incisor27. Cuspid
(canine/eye tooth)28. 1st Bicuspid (1st
premolar)29. 2nd Bicuspid (2nd premolar)30. 1st
Molar (6-yr molar)31. 2nd Molar (12-yr
molar)32. 3rd Molar (wisdom tooth)
primary teeth are designated by upper case
letters A through T, with A being the patient's
upper right second primary molar and T being the
lower right second primary molar.
5
Classification
- Ellis I enamel only
- White, chalky appearance
- Ellis II enamel dentin
- Dentin is pink /or yellow
- Hot/cold sensitivity
- More serious in childrenlt12 yrs old (less dentin)
- Ellis III to the pulp
- Exposed blood
- Severe pain 2/2 exposed nerve
- Risk for abscess formation
6
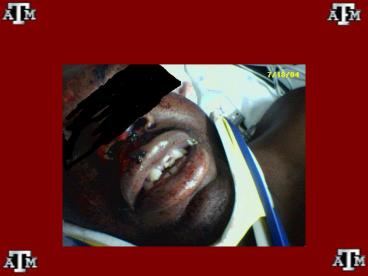
Ellis Type II
7
Evaluation
- PE
- Evaluate surrounding soft tissue area for
laceration, discoloration, ecchymosis and
embedded foreign bodies (eg, chipped
teeth?chronic infexn, fibrosis). - Evaluate if tooth is mobile or if an entire
segment is mobile (have pt bite down on tongue
blade) - Percuss with tongue blade to evaluate
sensitivity. - XR
- Panorex evaluate for mandibular/maxillary fx,
foreign body, displacement
8
Treatment
- Ellis Ismooth rough cornes with dental drill or
emery board - Immediate dentral referral w/I 24 hr when soft
tissue injury caused by sharp pieces of tooth - Ellis IICover exposed dentin with a layer of
zinc oxide or calcium hydroxide paste (Dycal). - Cover tooth with a small piece of dental or
aluminum foil. Exposure to humidity increases the
rate at which the Dycal will set. - In patients younger than 12 years, coverage is
especially important to prevent infection. - Refer to denist within 24 hours
- Ellis IIISame as type II BUT urgent Dental
Refferal - Risk for Abscess formation
- Abx pcn, amoxacillin
9
- Ellis II III
- Advise pts to not eat food to lessen chances of
loosing adhesive dressing - Root Fx
- Early reduction, immob, spliting
- Coe-Pak (stabilizin compund)
- Dental referral w/I 24 hours
- Complications
- Tooth loss
- Cosmetic Deformity
- Infection
10
Medical/Legal Pitfalls
- Failure to provide tetanus prophylaxis
- Failure to rule out aspiration of tooth chips if
unable to recover the tooth in the field - Failure to properly examine surrounding
traumatized tissue for tooth chips - Failure to recognize domestic and/or child abuse
- Failure to evaluate fully the temporomandibular
joint, maxilla, mandible, and occlusion - Failure to evaluate associated head and neck
injuries - Failure to recognize possible airway compromise
- Failure to warn patient that any trauma to teeth
can disrupt the neurovascular supply and lead to
long-term pulp necrosis or root resorption