Lect 18 The Urinary System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 29
Title:
Lect 18 The Urinary System
Description:
Lect 18 The Urinary System Kidneys Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra Hypertonic Hypotonic * * * * * * * * * * * What is Bowman's capsule = visceral & parietal layers of ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:165
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Lect 18 The Urinary System
1
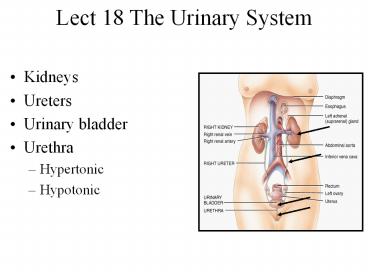
Lect 18 The Urinary System
- Kidneys
- Ureters
- Urinary bladder
- Urethra
- Hypertonic
- Hypotonic
2
- Functions of Urinary System
- Regulation of blood
- Volume
- Pressure
- pH
- Endocrine hormone release
- Calcitriol absorption of Ca
- Renin
- Erythropoietin
- Conservation of nutrients
- Role in toxin degradation
- Production and elimination of wastes in
hypertonic urine
3
- Location of Kidneys
- 4-5 in long, 2-3 in wide,1 in thick
- 4-5 in long, 2-3 in wide,1 in thick
- Retroperitoneal
- Protected by
- 11 12 ribs
- Perinephric and pararenal fat
- Anchored by
- Collagen fibers to fascia (renal fascia)
- Fascia continuous with deep fascia of muscles
4
- Fibrous capsule
- Renal fasacia
- Deep fascia
- Pararenal fat
- Perinephric fat
5
- Pelvis
- Hilum
- Renal sinus
- ureter
- Capsule
- Cortex
- Renal medulla
- Minor calyx
- Major calyx
- Renal pyramid
- Renal papilla
- Renal column
3
2
4
5
1
6
(No Transcript)
7
- Blood Vessel and Nerves Supply
- Abundantly supplied with blood vessels
- receive 25 of resting cardiac output via renal
arteries - Enter/leave at hilus
- Blood vessels divide giving rise to afferent
arterioles - Filtration and reabsorption of materials from
blood occurs at nephron - Nerve supply
- Sympathetic nerve supply regulation of
- Regul of blood flow/pressure
- Renin (endocrine hormone) release
- Stimul of Na/water reabsorption
8
- Renal artery
- Segmental artery
- Interlobar artery
- Arcuate artery
- Afferent arteriole
- Veins carry same names
9
The Nephron
- Kidney has over 1 million nephrons composed of a
corpuscle and tubule site of filtration/reabsorp
tion in kindey - Renal corpuscle site of plasma filtration
- glomerulus is capillaries where filtration occurs
- glomerular (Bowmans) capsule is double-walled
epithelial cup that collects filtrate - Renal tubule
- proximal convoluted tubule
- loop of Henle dips down into medulla
- distal convoluted tubule
- Collecting ducts and papillary ducts drain urine
to the renal pelvis and ureter
10
(No Transcript)
11
1 - renal corpuscle 2 - proximal convoluted
tubules 3 - distal convoluted tubules 4 -
Bowman's capsulae space
12
(No Transcript)
13
- Two types of nephrons
- Cortical nephron
- 80-85 of nephrons are cortical nephrons
- Renal corpuscles are in outer cortex and loops of
Henle lie mainly in cortex - Juxtamedullary nephrons
- 15-20 of nephrons are juxtamedullary nephrons
- Renal corpuscles close to medulla and long loops
of Henle extend into deepest medulla enabling
excretion of dilute or concentrated urine
14
Structure of Renal Corpuscle
- Bowmans capsule surrounds capsular space
- podocytes cover capillaries to form visceral
layer - simple squamous cells form parietal layer of
capsule - Glomerular capillaries arise from afferent
arteriole form a ball before emptying into
efferent arteriole
15
Cortical Nephron
16
Juxtamedullary Nephronhttp//www.lakemichigancoll
ege.edu/liberal/bio/anat/urin.html
17
Histology of the Nephron Collecting Duct
- Single layer of epithelial cells forms walls of
entire tube - Distinctive features due to function of each
region - microvilli
- cuboidal versus simple
- hormone receptors
18
- Juxtaglomerular Apparatus
- Involved in release of renin
- Endocrine release of renin and erythropoietin
- Renin increases blood pressure
- Erythropoietin stimulation of hemopoiesis
- Components
- macula densa ( dense spot) - specialized DCT
epithelial cells monitor electrolyte conc. -
chemoreceptors - juxtaglomerular cells modified smooth muscle
cells in wall of afferent arteriole respond to
changes in bp - granular cells contain and release renin
- Extraglomerular mesangial cells function?
19
(No Transcript)
20
Overview of Renal Physiology
- Nephrons and collecting ducts perform 3 basic
processes - glomerular filtration
- a portion of the blood plasma is filtered into
the kidney - tubular reabsorption
- water useful substances are reabsorbed into the
blood - tubular secretion
- wastes are removed from the blood secreted into
urine - Rate of excretion of any substance is its rate of
filtration, plus its rate of secretion, minus its
rate of reabsorption
21
Number of Nephrons
- Remains constant from birth
- any increase in size of kidney is size increase
of individual nephrons - If injured, no replacement occurs
- Dysfunction is not evident until function
declines by 25 of normal (other nephrons handle
the extra work) - Removal of one kidney causes enlargement of the
remaining until it can filter at 80 of normal
rate of 2 kidneys
22
Anatomy of Ureters
- 10 to 12 in long
- Varies in diameter from 1-10 mm
- Extends from renal pelvis to bladder
- Retroperitoneal
- Enters posterior wall of bladder
- Physiological valve only
- bladder wall compresses arterial opening as it
expands during filling - flow results from peristalsis, gravity
hydrostatic pressure
23
Location of Urinary Bladder
- Posterior to pubic symphysis
- In females is anterior to vagina inferior to
uterus - In males lies anterior to rectum
24
Anatomy of Urinary Bladder
- Hollow, distensible muscular organ with capacity
of 700 - 800 mL - Trigone is smooth flat area bordered by 2
ureteral openings and one urethral opening
25
Histology of Urinary Bladder
- 3 layers in wall
- mucosa is transitional epithelium lamina
propria - since organ must inflate deflate
- mucus prevents the cells from being contacted by
urine - muscularis (known as detrusor muscle)
- 3 layers of smooth muscle
- inner longitudinal, middle circular outer
longitudinal - circular smooth muscle fibers form internal
urethral sphincter - circular skeletal muscle forms external urethral
sphincter - adventitia layer of loose connective tissue
anchors in place - superior surface has serosal layer (visceral
peritoneum)
26
(No Transcript)
27
Anatomy of the Urethra
- Females
- length of 1.5 in., orifice between clitoris
vagina - histology
- transitional changing to nonkeratinized
stratified squamous epithelium, lamina propria
with elastic fibers circular smooth muscle - Males
- tube passes through prostate, UG diaphragm
penis - 3 regions of urethra
- prostatic urethra, membranous urethra spongy
urethra - circular smooth muscle forms internal urethral
sphincter UG diaphragm forms external urethral
sphincter
28
(No Transcript)
29
(No Transcript)