Anura frogs - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 33
Title:
Anura frogs
Description:
lipophilic alkaloids. dietary origin. Dendrobates. tinctorious. Anura (frogs) ... Mantella with skin alkaloids. and aposematic coloration. Buergeria japanicus ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:320
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Anura frogs
1
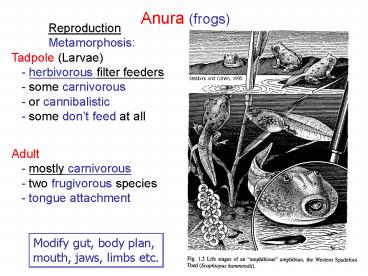
Anura (frogs)
Reproduction Metamorphosis Tadpole (Larvae)
- herbivorous filter feeders - some
carnivorous - or cannibalistic - some
dont feed at all
Stebbins and Cohen, 1995
Adult - mostly carnivorous - two
frugivorous species - tongue attachment
Modify gut, body plan, mouth, jaws, limbs etc.
2
Lissamphibia Anura (frogs) 28 families, 310
genera, gt 4,300 spp.
Fig. 3-20 Pough et al. 2001
3
Anura (frogs)
Larvae
Surface film
Internal Gills
Stebbins and Cohen, 1995
Suctorial scraper
Carnivore
Use to ID
Stebbins and Cohen, 1995
4
Anura (frogs)
Larvae General types based on morphology and
diet
Keratinous mouth parts
1
2
3
4
spiracles
spiracle
Pough et al., 2001
5
Anura (frogs) Sound Most important
anuran communication tool
- Most anurans vocalize - Usually male -
Inflate throat sacs
- species specific calls - mate
attraction - territoriality - alarm calls
- more later...
6
Anura (frogs) Skin Specialized for
multiple functions - hydration, defense,
locomotion, thermoregulation, reproduction,
respiration etc.
1
2
glands - mucus (2 types) - poison
granular pigmentation
Fig 2.1 Stebbins and Cohen, 1995
7
Anura (frogs) Skin Specialized glands A.
mucus -1 moist coating prevent dehydration
-2 sexual dimorphism nuptial pads
Nuptial pads
Pough et al., 2001
B. poison granular -defensive secretions
(sticky, antibiotics, toxic, etc.)
Dendrobates tinctorious
8
Anura (frogs) Skin Pigmentation
(Chromatophores) Xanthophores Iridophores
Melanophores
-reflectance -infrared -aposematic
Stebbins and Cohen, 1995
Pigmentation under hormonal control
9
Anura (frogs)
Skin Respiration - blood vessels
- epidermal thickness
- versus hydration gas transfer requires
solution
Stebbins and Cohen, 1995
10
Lissamphibia Anura (frogs) 28 families, 310
genera, 4,300 spp.
Fig. 3-20 Pough et al. 2001
11
Anura (frogs) Ascaphidae (1 species NW U.S.,
into Canada) - monotypic Family and Genus -
tailed frog - tail is extension of cloaca -
internal fertilization (1 of 3 spp.) - do not
call - no tympana - highly turbulent aquatic
habitat
Ascaphus truei
12
Anura (frogs) Leiopelmatidae (1 genus, 3
species New Zealand) - only amphibians native
to NZ - ribs embedded in ventral musculature
- lack ear components and vocal sac - direct
development - male parental care in 2/3 species
Leiopelma hamiltoni
Leiopelma hochstetteri
13
Anura (frogs) Bombinatoridae (2 genera, 8
species Europe, E Asia) - Bombina toxic
skin secretions aposematic coloration (orange
yellow) unken reflex
Bombina orientalis
14
Lissamphibia Anura (frogs) 28 families, 310
genera, 4,300 spp.
Fig. 3-20 Pough et al. 2001
15
Anura (frogs) Pelobatidae (3 genera, 11
species N America, Eurasia) - include spade
foots - well-developed keratinous, spade-like
metatarsal tubercle on hind feet - fossorial
- often with enlarged parotoid glands on dorsum
- desert adapted aestivate explosive
breeders egg to metamorph in 8 days
16
Anura (frogs) Pelobatidae (cont)
Scaphiopus couchii
spade
17
Anura (frogs) Rhinophrynidae (1 species Texas
to Costa Rica) - monotypic family and genus -
ultra fossorial spade tubercles pointed
head with cornified skin small eyes no
tympanum reinforced skull - feed on ants and
termites underground - unique tongue
Rhinophrynus dorsalis
18
Anura (frogs) Pipidae (5 genera, 30 species
Panama, S America, sub-Saharan Africa) - no
tongue - keratinous claws - aquatic -
modified ears and calling - Xenopus laevis
research polyploids - Pipa spp. eggs
in dorsal skin of female
X. tropicalis
19
Lissamphibia Anura (frogs) 28 families, 310
genera, 4,300 spp.
Fig. 3-20 Pough et al. 2001
20
Anura (frogs) Bufonidae (33 genera, 400
species widespread, not in Australopapuan
region) - Bidders organ rudimentary ovary
on male testes (paedomorphic) - no teeth -
parotoid glands toxins - Bufo
marinus pest
21
Anura (frogs) Leptodactylidae (49 genera, gt
900 species Americas, West Indies) - not
monophyletic - variable - Eleutherodactylus
gt 500 species!! most species rich
genus of vertebrates some with direct dvpt.
2 spp. with internal fert.
Eleutherodactylus auriculatus
Ceratophrys cornuta
22
Miscellaneous
I. Anuran Calling -Protoamphibians with
developed ears and calling, some components lost
in some stream-dwelling and fossorial groups. -
Vocal Cords and other morphological structures...
- Calling linked to breathing See 1. Duellman
and Trueb. 1986. Biology of Amphibians. Johns
Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, Maryland. 2.
Ryan, M.J. (editor). 2001. Anuran Communication.
Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, D.C.
II. Pelobatidae (Spadefoots) Pelobates
(Eurasia), Spea, Scaphiopus III. Costal Grooves
(salamanders) equivalent to 1o Annuli
(caecilians) one per vertebrae
23
Anura (frogs) Myobatrachidae (21 genera, 120
species Australia, New Guinea, Tasmania) -
variable - one species with male inguinal
pouches for brood rearing - two species
with gastric brooding in female
Rheobatrachus (extinct?)
Rheobatrachus vitellinus
24
Anura (frogs) Rhinodermatidae (2 species
Argentina and Chile) - fleshy proboscis at
tip of snout - males carry larvae to
water, or brood in vocal pouch
Rhinoderma darwinii
25
Anura (frogs) Hylidae (38 genera, 760 species
Americas, W indies, Australopapuan region) (Hyla
in Americas, Eurasia, Japan, N Africa) -
arboreal generally - well-developed toe discs
- claw-shaped terminal phalanges - many spp.
with females that transport young dorsally
- Phyllomedusa toxin for native rituals
lipid glands in skin wiping behavior
Phyllomedusa sauvagi
26
Anura (frogs) Centrolenidae (3 genera, gt 130
species Mexico to S America) - medial process
on 3rd metacarpal - toe discs - terminal
phalanges T-shaped - eggs attended by males -
transparent venter glass frogs
Centrolenella fleischmanni
Centrolenella oyampiensis
27
Lissamphibia Anura (frogs) 28 families, 310
genera, 4,300 spp.
Fig. 3-20 Pough et al. 2001
28
(No Transcript)
29
Anura (frogs) Dendrobatidae (6 genera, 185
species Cent. America, N South America) - pair
of dermal scutes on dorsal surface of fingers -
generally diurnal and terrestrial - cephalic
amplexus (if amplex) - parental care move
larvae around - Dendrobates may feed
tadpoles eggs - Phyllobates terribilis
lipophilic alkaloids dietary origin
Dendrobates tinctorious
30
Anura (frogs) Arthroleptidae (7 genera, 75
species sub-Saharan Africa) - includes
Trichobatrachus robustus (hairy frog) male
sits on clutch and aids aeration?
Stebbins and Cohen, 1995
31
Anura (frogs) Ranidae (46 genera, gt 700
species most everywhere, except many islands)
- likely not monophyletic - variable - some
unique Rana esculenta hybrids both sexes
represented alternate generations
sexual lt---gt asexual
Rana pipiens
32
Anura (frogs) Hyperoliidae (19 genera, 230
species sub-Saharan Africa, Seychelles,
Madagascar) - many arboreal - toe discs -
brightly colored - Afrixalus eggs on leaf
then taco
Afrixalus osorioi congicus
33
Anura (frogs) Rhacophoridae (15 genera, 315
species Africa, Madagascar, Asia) - mostly
arboreal - enlarged toe discs - some with
foam nests - some communal nests -
Mantella with skin alkaloids and aposematic
coloration
Buergeria japanicus