Continuous Flow Method - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Continuous Flow Method
Description:
Syringes are filled with A and B solution and compressed at constant rate ... to same pattern of activated complexes are not kinetically distinguishable. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1091
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Continuous Flow Method
1
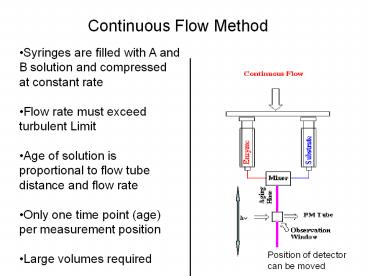
Continuous Flow Method
Syringes are filled with A and B solution and
compressed at constant rate Flow rate must
exceed turbulent Limit Age of solution is
proportional to flow tube distance and flow
rate Only one time point (age) per measurement
position Large volumes required
Position of detector can be moved
2
Stopped Flow Method
- Syringes are filled with A and B solution and
compressed to small amounts (50-200µl) then
stopped - Once the flow is stopped, solution ages with
time (can be controlled) - Detector sees more than one age
- Low dead times (1 ms)
- Expensive detection system
3
Relaxation methods
4
Relaxation Methods
5
Relaxation Methods
6
Determining Mechanism from Rate Law
- If the rate law is
, the total composition of the reactants
in the rate limiting step is aAbB.. - If the rate law is
, the total composition
of the reactants in the rate limiting step is
aAbB..-?M-nN.. - A rate law, to be properly interpreted according
to rule 1, must be written in terms of the
predominate species in the reaction medium.
7
Determining Mechanism from Rate Law
- The number of positive terms in the rate law is
the number of independent, parallel pathways.
Negative terms represent the reverse reaction. - A summation of n terms in the denominator implies
a succession of n steps, all but nth are
reversible. - Species whose concentrations appear in
single-term denominators are produced in the step
prior to rate controlling step.
8
Determining Mechanism from Rate Law
- Adding up the steps in a mechanism must yield the
net chemical reaction rapid reaction may follow
the rate-controlling step. - Alternative mechanisms leading to same pattern of
activated complexes are not kinetically
distinguishable. - The order increases with increasing concentration
when the reaction proceeds by parallel pathways
but decreases when a series of steps occur.