Selection - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 18
Title:
Selection
Description:
Cognitive ability. Personality. Work ability & sample tests. Trade tests. Vocational interests ... Objectives & content carefully thought out. Two way process? ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:30
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Selection
1
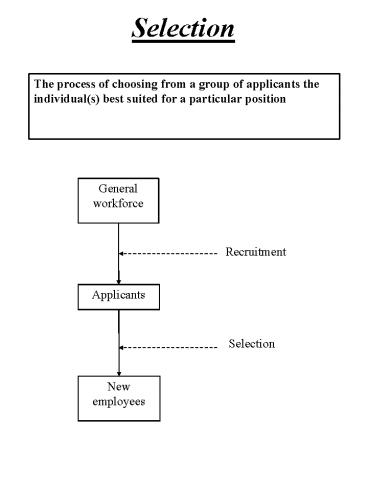
Selection
The process of choosing from a group of
applicants the individual(s) best suited for a
particular position
General workforce
Recruitment
Applicants
Selection
New employees
2
Pre-Requisites
- HR Corporate Strategy
- Job analysis
- HR Planning
- Recruitment
Cost of Poor Selection
- Productivity differential
- Cost of dismissal
- Cost of labour turnover
- Litigation?
3
Influencing Factors
Strategic types
- Strategy
- Legal considerations (esp. AA EE)
- Speed
- Hierarchy
- Applicant pool
Selection Ratio
No. of people hired into position No. of
available applicants
4
Selection Method Standards
Organisations could just hire randomly from
applicant pool, BUT you would get randomly
distributed performance too. Good selection
methods consistently choose highest performing
candidates, who make money for the organisation,
while remaining within the boundaries of the law.
Measurement not error ridden
- Note
- Consistency
- Chooses highest performers
- Money
- Legality
Generalisable between jobs
5
Selection Method Standards
RELIABILITY
Extent to which a measure is consistent, i.e.
gives same result every time you use it
- Assessing reliability through correlation
coefficients - Test-retest reliability
- Split-half reliability
- Inter-rater reliablity
6
Selection Method Standards
VALIDITY
Extent to which a performance on the measure is
related to performance on the job.
- Criterion-Related Validity
- Scores for selection measure vs. job performance
scores - Predictive validation (job applicant scores vs.
later performance) - Concurrent validation (current employee scores
vs. current performance)
- Advantages of predictive method
- Test motivation
- Current employees higher ability
- Range restriction
7
Content Validity Sample sizes small cant use
criterion-related method Content validation
looks at whether the selection measures
represents job conditions. Usually estimated
through judgmental method (i.e. experts assessing
content validity). Content validation ratio
(CVR)
ne no. of judges rating item essential to job N
no. of judges
8
Construct-Related Validity
Measures how well selection method measures a
trait which in turn is supposed to be related to
performance
Selection measure
Construct
Criterion / Content
Trait (e.g. IQ)
Actual performance
Thus if IQ is thought to predict performance for
a certain job, then you have construct validation
if the test measures IQ well.
9
Selection Method Standards
GENERALIZABILITY
Degree to which the validity of a selection
method established in one context extends to
other contexts.
- Contexts for generalizability
- Different situations
- Different people
- Different times
Validity generalization If a test used in one
situation is valid and generalizable, it can be
used elsewhere without new validity testing.
10
Selection Method Standards
UTILITY
Degree to which information provided by selection
methods results in an extra monetary payoff for
the organisation
Monetary payoff comes partly from systematically
hiring higher performers. Therefore more
reliable, valid general methods generally give
higher utility. However payoff also comes from
other factors
- Utility can further be improved by
- lower selection ratios
- higher economic consequences of failure
- lower no of people tested and costs
11
Selection Method Standards
LEGALITY
- Anti Discrimination
- Affirmative action
- EEA selection medical testing laws (later)
12
Selection Process
No set rules, no set progression
Pre-screening
Initial interview
Reference / other checks
Application forms / blanks
Testing
Interview
Job offer
Medical
13
Selection Testing
LEGALITY
- S8 of EEA
- Psychological testing is prohibited unless
- Scientifically shown to be valid reliable
- can be fairly applied to all employees
- is not biased against any employee or group
- Therefore make sure tests are assessed for
reliability and validity, and not culturally
biased.
14
Selection Tests
ADVANTAGES
Possible productivity gains Accurate
assessment Accuracy
DISADVANTAGES
Ability, not application / motivation Test
anxiety Possible bias
15
Selection Tests
CHARACTERISTICS OF PROPERLY DESIGNED TESTS
Standardisation Objectivity Norms Reliability
Validity
16
Selection Tests
TYPES OF TESTS
Psychomotor Cognitive ability Personality Work
ability sample tests Trade tests Vocational
interests Honesty Drug / substance abuse AIDS
17
Formal Interview
Objectives content carefully thought out. Two
way process? Structured vs. unstructured
interview Individual vs group for interviewers
or interviewees Reliability, validity, utility
18
Medical Testing
LEGALITY
- S7 of EEA
- Medical testing is prohibited unless
- Legislation permits or requires it
- it is justifiable in the light of medical facts,
employment conditions, social policy, the fair
distribution of benefits or the inherent
requirements of the job. - Testing for AIDS is furthermore prohibited
unless such testing is determined to be
justifiable by the Labour Court