Respiratory system - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 15
Title:
Respiratory system
Description:
The tiniest bronchioles branch to the alveoli (sing. = alveolus) which are tiny, multi-lobed air sacs made of simple squamous cells. A look at what we have seen so far ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:52
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Respiratory system
1
(No Transcript)
2
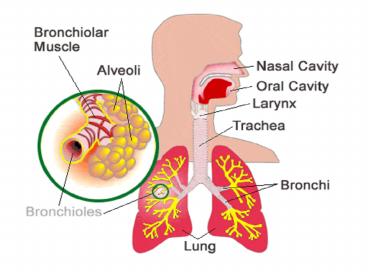
- The tiniest bronchioles branch to the alveoli
(sing. alveolus) which are tiny, multi-lobed
air sacs made of simple squamous cells.
3
A look at what we have seen so far
- http//www.mhhe.com/biosci/genbio/animation_quizze
s/graphics/abm3s8a.ram
4
And these put together allow us to breath.
- The process of breathing ventilation
- In order to understand the process it is
important to look at the physics involved. - http//www.mhhe.com/biosci/genbio/animation_quizze
s/graphics/abm3s3h.ram - Us.. McGraw-Hill Online Learning Center
TestltBLURTgt
5
- Tutorial 48.2 Airflow in Mammals ( good review )
6
The site of gas exchange is the alveoli
- The process of respiration
- McGraw-Hill Online Learning Center TestltBLURTgt
- Shape of alveoli increase surface area
7
- Having this thin wall enables air exchange with
the equally-thin-walled capillaries of the
circulatory system. - Animation Quizzes
8
Exchange of gases
- External respiration
- exchange of O2 CO2 between external environment
the cells of the body - efficient because alveoli and capillaries have
very thin walls are very abundant (your lungs
have about 300 million alveoli with a total
surface area of about 75 square meters) - Internal respiration - intracellular use of O2 to
make ATP - occurs by simple diffusion along
partial pressure gradients
9
Partial pressure
- In summary, gases move from a region of higher
partial pressure to a region of lower partial
pressure. - Animations partial pressure. Keep in mind above
summary.
10
Partial Pressures of O2 and CO2 in the body
(resting)
- Alveoli
- PO2 100 mm Hg
- PCO2 40 mm Hg
- Alveolar capillaries
- Entering the alveolar capillaries
- PO2 40 mm Hg (relatively low because this blood
has just returned from the systemic circulation
has lost much of its oxygen) - PCO2 45 mm Hg (relatively high because the
blood returning from the systemic circulation has
picked up carbon dioxide)
11
- Because of the differences in partial pressures
of oxygen carbon dioxide in the systemic
capillaries the body cells, oxygen diffuses
from the blood into the cells, while carbon
dioxide diffuses from the cells into the blood. - Leaving the systemic capillaries
- PO2 40 mm Hg
- PCO2 45 mm Hg
12
How are oxygen carbon dioxide transported in
the blood?
- Oxygen is carried in blood
- 1. bound to hemoglobin (98.5 of all oxygen in
the blood) - 2. dissolved in the plasma (1.5)
- Animation Quizzes hemoglobin
13
A look from the top of Everest
- A view from the summit of Everest _at_ National
Geographic Magazine
14
Gas exchhange
- Howstuffworks "Gas Exchange"
15
- Animation Quizzes gas exchange