Auditory System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 20
Title: Auditory System
1
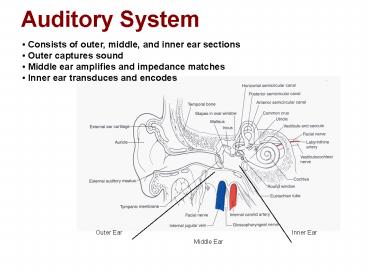
Auditory System
- Consists of outer, middle, and inner ear
sections - Outer captures sound
- Middle ear amplifies and impedance matches
- Inner ear transduces and encodes
Outer Ear
Inner Ear
Middle Ear
2
Sound waves
3
The middle ear...
- Ossicles act as levers to
- transform air borne vibrations
- into fluid borne vibrations.
- Cochlea is a closed system, with
incompressible fluid. - What goes in, must come out.
- Perilymph (high Na, low K - like CSF) in scala
vestibuli and scala tympani. - Endolymph (low Na, high K - like intracellular
fluid) in scala media.
- Conductive hearing loss
- Otitis media middle ear infection often due to
eustachian tube restriction - Otosclerosis tissue overgrowth restricting
ossicle (stapes) movement
4
Cochlear mechanics
- Basilar membrane
- In-out motion of stapes
- produces up-down motion of basilar membrane
- Resonant frequency varies
- along length
- Sharp frequency tuning
5
Frequency specificity on basilar membrane
- Resonant frequency varies
- along length
- Most sounds have complex waveforms
- In mammals, cochlea is not straight, but
coiled
6
The organ of Corti...
- has two groups of receptors (hair cells)
- Inner hair cells (single row) receive 95 of all
afferents - Outer hair cells (3 rows) receive few afferents,
but all efferents
7
Hair cells are mechanoreceptors
- Stereocilia gated channels that open/close as
stereocilia displace
Tip link
8
Hair cells are mechanoreceptors that are
spatially tuned
9
Hair cells are frequency selective
- Each cell responds with lowest threshold to a
characteristic or best frequency (CF) - Frequency tuning uses twomechanisms
- Basilar membrane vibration
- Resonant frequency of hair cell (membrane
channels)
Base
Apex
Hair cell tuning curves Threshold vs. frequency
10
Outer hair cells function to amplify/protect
- Cochlear amplification/protection
- Mechanical response of hair cell to
- Membrane voltage change
- Increase sensitivity of inner hair cells
- Sharpen tuning
- Regulated by efferents
- Produces otoacoustic emissions
11
Hair cells are easily damaged
- Loud sounds (gt110db) explosions, gun shot
- Continuous exposure (gt95 db) lawn mower,
musical amplifier - Ototoxic antibiotics (aminoglycosides)
- Cancer treatment drugs (Cisplatnin)
12
Auditory afferents are frequency tuned
- Each afferent responds with lowest threshold to
a characteristic or best frequency (CF) - Place code array of CFs along tonotopic map
- Rate code fibers rate proportional to sound
frequency
13
Cochlear implants
- Implanted through mastoid into scala tympani
- Only covers basal 40 50 of cochlea
- Generally destroys basilar membrane, how then
does it work? - Hint stimulating contacts pointing toward the
spiral ganglion cells
14
Central auditory processing
Main goals first where, then what
Sound Localization (where it is) Based on
comparisons between ears Differences in timing,
intensity
Sound Identification (what it is) Emphasizes
species-specific vocalizations Poorly understood
for humans, monkeys, Best understood for bats,
songbirds
15
Central auditory pathway
Sound Localization Timing differences (low
frequencies, lt 1 kHz), good discrimination lt1
deg Intensity differences (high frequencies,
gt 3 kHz), good discrimination lt1 degBetween 1
3 kHz, both ITD and IID, poorer discrimination gt3
deg,
Auditory Cortex A1
Medial geniculate
Inferior colliculus
Cochlear nuclei
Dorsal CN
Ventral CN
Lateral lemniscus
Superior olivary complex
16
Brainstem auditory evoked response (BAER)
- Clinical neurophysiology diagnostic
- Evoked potentials elicited by repetitive clicks
- Peaks at regular latencies are correlated with
structures of auditory pathway - Shifts in latency or changes in amplitude
indicate lesion
17
Cochlear nuclei
- CN is tonotopically organized
- Bushy cells (ventral or ACN) project bilaterally
to SOC sound localization - Multipolar cells project only to contralateral
IC sound intensity - Octopus cells project to contralateral IC speech
frequency - Pyramidal cells project monaurally to
contralateral IC ?
18
Central auditory pathway - II
- Monaural path
- Binaural path
19
Auditory cortex
- Location mainly in Sylvian fissure superior
temporal gyrus - AI area 41, AII area 42 Tonotopy arranged in
isofrequency columns - Area 22 includes speech processing, damage
results in Wernickes aphasia - Areas 44 45 (Brocas aphasia) processes
expressive speech and language
20
Auditory cortex
- Wernickes area includes speech comprehension
processing - Brocas area processes expressive (production)
speech and language