The Central Nervous System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 21
Title:
The Central Nervous System
Description:
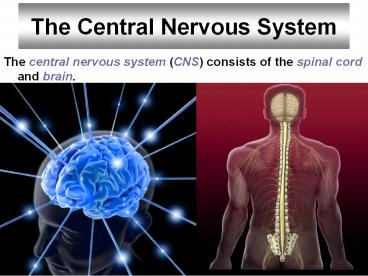
The Central Nervous System The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the spinal cord and brain. 17-* 17-* Organization of the Nervous System Both are protected by ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:118
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Central Nervous System
1
The Central Nervous System
- The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the
spinal cord and brain.
2
Organization of the Nervous System
3
- Both are protected by bone, wrapped in protective
membranes called meninges, and surrounded and
cushioned with cerebrospinal fluid that is
produced in the ventricles of the brain.
4
- The ventricles are interconnecting cavities that
produce and serve as a reservoir for
cerebrospinal fluid. - The CNS receives and integrates sensory input and
formulates motor output.
5
Gray matter contains cell bodies and short,
nonmyelinated fibers white matter contains
myelinated axons that run in tracts.
6
The Spinal Cord
- The spinal cord extends from the base of the
brain through the vertebral canal.
7
- Structure of the Spinal Cord
- A central canal holds cerebrospinal fluid.
- Gray matter of the spinal cord forms an H and
contains interneurons and portions of sensory and
motor neurons. - White matter consists of ascending tracts
(dorsally) taking sensory information to the
brain and descending tracts (ventrally) carrying
motor information from the brain. Tracts cross
just before entering the brain. So left ??right.
8
YOU NEED TO KNOW THIS ANATOMY
9
YES, EVEN IF IT IS SIDEWAYS OR UPSIDE DOWN !
10
Functions of the Spinal Cord
- The spinal cord is the center for many reflex
arcs. - It also sends sensory information to the brain
and receives motor output from the brain,
extending communication from the brain to the
peripheral nerves for both control of voluntary
skeletal muscles and involuntary internal organs.
- Severing the spinal cord produces paralysis.
11
The Brain
- The brain has four cavities called ventricles.
- The cerebrum has two lateral ventricles, the
diencephalon has the third ventricle, and the
brain stem and cerebellum have the fourth
ventricle.
12
The Cerebrum
- The cerebrum or telencephalon has two cerebral
hemispheres connected by the corpus callosum. - .
SEE THE C
13
Cerebral Lobes
Learning, memory, language and speech take place
in the cerebrum. Sulci divide each hemisphere
into lobes including the frontal, parietal,
occipital, and temporal lobes
14
I need some HELP here !
FAsT - FrontalPEOPLE - Parietal TAKE -
Temporal OUT - Occipital CHEESE -
Cerebellum BURGERS - Brain Stem
15
The Cerebral Cortex
- The cerebral cortex is a thin, highly convoluted
outer layer of gray matter covering both
hemispheres. - The primary motor area is in the frontal lobe
this commands skeletal muscle. - The primary somatosensory area is dorsal to the
central sulcus or groove. - The primary visual area is at the back occipital
lobe. - The temporal lobe has the primary auditory area.
16
(No Transcript)
17
Language and Speech
- Language and speech are dependent upon Brocas
area (a motor speech area) and Wernickes area (a
sensory speech area) that are involved in
communication. - These two areas are located only in the left
hemisphere the left hemisphere functions in
language in general and not just in speech.
18
The Diencephalon (Two in the Head)
- The hypothalamus and thalamus are in the
diencephalon that encircles the third ventricle.
- The hypothalamus controls homeostasis and the
pituitary gland, and the thalamus receives all
sensory input except smell and integrates it and
sends it to the cerebrum.
19
The Cerebellum little brain
- The cerebellum receives sensory input from eyes,
ears, joints and muscles and receives motor input
from the cerebral cortex. - It integrates this information to maintain
posture, coordination and balance. - The cerebellum is involved in learning of new
motor skills, such as playing the piano or
hitting a golf ball.
20
The Brain Stem
- The brain stem contains the medulla oblongata,
pons, and midbrain. - The medulla oblongata and pons have centers for
vital functions such as breathing, heartbeat, and
vasoconstriction. - The medulla also coordinates swallowing and some
other automatic reactions (many reflex centers
for heartbeat, breathing and BP) - The midbrain acts as a relay station between the
cerebrum and spinal cord or cerebellum.
21
The Reticular Formation
- The reticular formation is a complex network of
nuclei and fibers that extend the length of the
brain stem. - One portion of the reticular formation, called
the reticular activating system, arouses the
cerebrum via the thalamus causing alertness. - It is believed to act as a filter for incoming
sensory impulses.