When Atoms Bond - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 69
Title:
When Atoms Bond
Description:
If it has a subscript of more than one, use a prefix to tell how many of that atom there are. ... Carbon likes to make 4 bonds. Hydrogens around the outside ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:225
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: When Atoms Bond
1
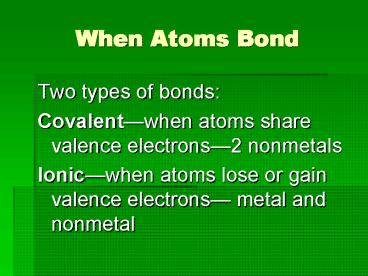
When Atoms Bond
- Two types of bonds
- Covalentwhen atoms share valence electrons2
nonmetals - Ionicwhen atoms lose or gain valence electrons
metal and nonmetal
2
Why do atoms bond?
- All atoms wannabe like the noble gasses with 8
valence electrons. (or with 2 like Helium) - Atoms will lose, gain, or share electrons to be
like a noble gas - This is called the octet rule!
3
IONIC BONDING
- Atoms will lose or gain electrons to achieve an
octet set of valence electrons. - Ionsatoms that have lost or gained electrons
- What determines if they will lose or gain??they
will do whatever is easiest. - Always made of a metal and a nonmetal!!!
4
How do IONS form?
- Remember how group numbers on the periodic table
tell you the number of valence electrons? - That helps you determine how many electrons an
atom will lose or gain. - Ex Na is in group 1, has 1 valence electron.
It will lose that electron to become more like
5
Valence electrons e- in outermost sub level
Number of valence electrons 1, 2, 3 in groups
3-12
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Group number
6
How Na become Na
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Na
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Na
-
-
-
-
-
When Na loses an electron, it has 10 total
electrons and 8 valence electrons just like the
noble gas Ne!!!
-
-
7
How Mg become Mg2
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Mg2
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Mg
-
-
-
-
-
When Mg loses 2 electrons, it has 10 total
electrons and 8 valence electrons just like the
noble gas Ne!!!
-
-
-
8
How Cl become Cl-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Cl-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Cl
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
When Cl gains 1 electron, it has 18 total
electrons and 8 valence electrons just like Ar
the noble gas !!!
-
-
-
-
-
9
How Li become Li--an exception to the octet
-
Li
-
-
Li
-
When Li loses 1 electron, it has 2 total
electrons and 2 valence electrons just like He
the noble gas !!!
-
10
Positive or Negative Ion?
- Atoms are neutral because they have the same
number of electrons(-) and protons(). - If an atom gains electrons, it becomes a negative
ion because it now has more electrons(-) that
protons(). - If an atom loses electrons, it becomes a positive
ion because it now has more protons() than
electrons(-).
11
Oxidation numbers
- Tell us what charge an ion will have from its
position on the periodic table!!
12
1 2 Oxidation Numbers 3 ?
3- 2- 1-
13
How do Ions form Ionic Bonds?
- Negative and positive charges attract.
- Negative and positive ions attract.
- This attraction is what forms an ionic bond to
make ionic compounds!!! - Ex Na and Cl- attract to make NaCl
- One ion of each, since they are of equal (1), but
opposite charges!
14
What about Ca2 and Cl-
- It takes 2 Cl- to equal 1 Ca2
- Soooooo the formula is
- CaCl2 and now we have a neutral molecule!!
15
What about Na and S2-?
- We must have 2 Na to equal 1 S2-
- So the formula is.
- Na2S
16
An Easier Way
- For ionic compounds, always made up of ionsa
metal and a nonmetal - Find the charge of each ion
- Cross the charge of each to make the subscript of
the other ion - Lose the charges and write the formula!
- Na Cl-
17
Crossing the Charges
- Na1 Cl1-
- NaCl final formula
1
1
18
Crossing the Charges
- Li1 S2-
- Li2S final formula
2
1
19
Crossing the Charges
- Ca2 S2-
- Ca2S2 --if both subscripts are
- divisible by the same
number, then reduce to lowest
terms - CaS final formula
20
Try These!!
- Ca and Cl
- Mg and F
- Mg and S
- Ca and N
- Mg and O
21
Here are the answers!
- Ca and Cl CaCl2
- Mg and F MgF2
- Mg and S MgS
- Ca and N Ca3N2
- Mg and O MgO
22
Naming Ionic Compounds
- Name the first element(the metal), name the
second element, but change the ending to ide - NaCl sodium chloride
- CaCl2 calcium chloride
- SrO strontium oxide
23
Try these!!
- CaCl2
- MgF2
- MgS
- Ca3N2
- MgO
24
Answers!
- CaCl2 calcium chloride
- MgF2 magnesium fluoride
- MgS magnesium sulfide
- Ca3N2 calcium nitride
- MgO magnesium oxide
25
Now, write the formulas from the names
- Calcium oxide
- Barium nitride
- Sodium sulfide
- Potassium phosphide
- Strontium chloride
26
Answers!
- Calcium oxide CaO
- Barium nitride Ba3N2
- Sodium sulfide Na2S
- Potassium phosphide K3P
- Strontium chloride SrCl2
27
Write the names from the formulas!
- CaCl2 KCl
- MgF2 SrO
- MgS MgI2
- Ca3N2 BaS
- MgO Li2N
28
The answers!
- CaCl2 Calcium chloride KCl Potassium chloride
- MgF2 Magnesium fluoride SrO Strontium oxide
- MgS Magnesium sulfide MgI2 Magnesium iodide
- Ca3N2 Calcium nitride BaS Barium sulfide
- MgO Magnesium oxide Li2N Lithium nitride
29
Lewis Dot Diagrams--show number of valence
electrons
30
You try some!
- Ca
- H
- Br
- P
- I
- Sr
- F
31
(No Transcript)
32
Making Compound Lewis Dot Diagrams
33
Examples
34
MOLECULE LEWIS DIAGRAMS
- 1. Find the total number of electronsTabulate
the total number of outer energy level electrons
for all atoms in the molecule. For each atom,
read the group number.2. Draw a first tentative
structure The element with the least number of
atoms is usually the central element. Draw a
tentative molecular and electron arrangement
attaching other atoms with single bonds as the
first guess. Single bonds represented with a line
represent 2 electrons
35
- 3. Add electrons as dots to get octets around
atomsWhen counting electrons for the octet
around an atom, count both electrons in a bond
for each atom and any lone pair electrons.
Hydrogen, of course, gets only 2 electrons.4.
Count the total number of electrons in the final
structure to see if the total agrees with the
number tabulated in step 1. If not, then move a
lone pair of electrons into a double bond. Or add
more lone pairs of electrons.5. Cycle through
steps 3 and 4 several times until you get it
right by trial and error.
36
Covalent Bonding
- Atoms share electrons to achieve an octet like
the noble gasses!! - Made up of 2 nonmetals
- Ex CO2 NO3
37
Naming Covalent Compounds
- Name the first element. If it has a subscript of
more than one, use a prefix to tell how many of
that atom there are. - Name the second elementalways use the
appropriate prefix, even if it is a one! Then
change the ending to ide!
38
Prefixes for Covalent compounds
- 1 - mon(o)
- 2 - di
- 3 - tri
- 4 - tetr(a)
- 5 - pent(a)
- 6 - hex(a)
- 7 - hept(a)
- 8 - oct(a)
- 9 - non(a)
- 10 - dec(a)
39
Examples
- CO2 carbon dioxide
- NO3 nitrogen trioxide
- H20 dihydrogen monoxide
40
Try these!
- H2S
- CO
- H2O2
- N2O3
- NO4
41
Answers!
- H2S Dihydogen monosulfide
- CO Carbon monoxide
- H2O2 Dihydrogen dioxide
- N2O3 Dinitrogen trioxide
- NO4 Nitrogen tetroxide
42
How many atoms share?
4
- Carbon needs ___ more electrons to have an
octet. - Oxygen needs ____ more electrons to have an
octet. - So. Carbon will share 2 electrons with O and 2
oxygens will share 2 each with carbon
2
C
O
O
C
O
43
(No Transcript)
44
(No Transcript)
45
Making Compound Lewis Dot Diagrams
- H2
46
Polyatomic Ionsatoms that are covalently bonded
that have a charge and act like a single ion
- hydroxide ion, OH-
- Nitrite ion, NO2-
- nitrate ion, NO3-
- acetate ion, C2H3O2-
- carbonate ion, CO32-
- sulfate ion, SO42-
- phosphate ion, PO43-
- ammonium ion, NH4
47
Polyatomic ions make ionic compounds with other
ions
- Na and OH-
- make NaOH sodium hydroxide
- K and SO42-
- Make K2SO4 potassium sulfate
- Ca2 and PO43-
- Make Ca3(PO4)2 calcium phosphate
48
Formulas and Names of Compounds with Polyatomic
Ions
- Formulastake the charges and cross them to
become subscripts just as in binary ionic
compounds - Namingif the polyatomic ion comes second--name
the metal and the polyatomic ion just as they
areNO ide ending! - --if the polyatomic ion comes first, name
it, then put an ide ending on the nonmetal ion
49
Examples
- Li and SO42-
- Li2SO4
- Lithium sulfate
- Ba2 and OH-
- Ba(OH)2
- Barium hydroxide
50
Try these!!
- NH4 and Cl
- Mg and CO32-
- Li and C2H3O2-
- NH4 and N
- Ba and PO43-
51
Answers!!
- NH4Cl Ammonium chloride
- MgCO3 Magnesium carbonate
- LiC2H3O2 Lithium acetate
- (NH4)3N Ammonium nitride
- Ba3(PO4)2 Barium phosphate
52
Chemical Reactions
- Chemical reactionwhen 2 substance react and
their atoms are rearranged to form a new
substance - Ex
- NaCl LiBr NaBr LiCl
53
5 Types of Chemical Reactions
- 1) Combustion when oxygen combines with another
compound to form water and carbon dioxide. - --are exothermic-- they produce heat.
- Example-- burning of methane
- CH4 2O2 ---gt CO2 2 H2O
54
- 2) Synthesis when two or more simple compounds
combine to form a more complicated one - A B ---gt AB
- Na Cl ---gt NaCl
55
- 3) Decomposition opposite of a synthesis
reaction - a complex molecule breaks down to make
simpler ones. - AB ---gt A B
- 2 H2O ---gt 2 H2 O2
56
- 4) Single replacement when one element trades
places with another element in a compound. - A BC ---gt AC B
- 2Mg 2HCl ---gt 2MgCl H2
57
- 5) Double replacement when two different
molecules switch places, forming two entirely
different compounds. - AB CD ---gt AD CB
- Ca(NO3)2 2 KI ---gt CaI2 2 KNO3
58
Try these!!
- 1) NaOH KNO3 --gt NaNO3 KOH
- 2) CH4 2 O2 --gt CO2 2 H2O
- 3) 2 Al 6 NaBr --gt 2 AlBr3 6 Na
- 4) CaSO4 Mg(OH) 2 --gt Ca(OH) 2 MgSO4
59
- 5) NH4OH HBr --gt H2O NH4Br
- 6) Sr O2 --gt SrO2
- 7) Na2CO3 --gt Na2O CO2
60
Try these for a quiz!
- Cu AgNO3 ---gt Ag Cu(NO3) 2
- KOH H2SO4 ---gt K2SO4 H2O
- Mg O2 ---gt MgO
- C6H12O6 O2 ---gt CO2 H2O
61
Parts of a Chemical Equation
Yields
- 2H2 O2 ---gt 2H2O
Product(s)
Reactant(s)
62
Parts of these?
- 1) NaOH KNO3 --gt NaNO3 KOH
- 2) CH4 2 O2 --gt CO2 2 H2O
- 3) 2 Al 6 NaBr --gt 2 AlBr3 6 Na
Product(s)
Reactants
Reactant(s)
Product(s)
Reactant(s)
Product(s)
63
Balancing Chemical Reactions
- Law of Conservation of Matter
- NaOH KNO3 --gt NaNO3 KOH
- 2 Al 6 NaBr --gt 2 AlBr3 6 Na
- Atoms are not created or destroyedwe must finish
our chemical reaction with as many atoms of each
element as when we started
64
Lets balance these!
- H2 O2 ---gt H2O
- N2 H2 ---gt NH3
- S8 O2 ---gt SO3
- N2 O2 ---gt N2O
65
The Seven Diatomic Substances (plus two friends)
- Hydrogen H2 Nitrogen N2 Oxygen O2 Fluorine F2
Chlorine Cl2 Bromine Br2 Iodine I2 - I Bring Clay For Our New Houseand Swimming
Pool - In addition to the above, phosphorous is P4 and
sulfur is S8.
66
Organic Compounds
- All organic compound
- contain carbon
- come from living things
- Ex CH4 organicprod by organisms
- CO2 inorganicnot from organism
- Contain Hydrogen and Carbonalso called
hydrocarbons
67
Hydrocarbon formulas
- All Carbon and hydrogen atoms
- Carbon likes to make 4 bonds
- Hydrogens around the outside
- All single bonds saturated hydrocarbons
- Not all single bonds unsaturated
- CH4 C4H10 C2H2
68
Number of carbons and prefix
- 1 meth- 6 hex-
- 2 eth- 7 hept-
- 3 prop- 8 oct-
- 4 but- 9 non-
- 5 pent- 10 dec-
- Kind of bonds suffix
- All single -ane
- A double -ene
- A triple -yne
69
How many hydrogens?
- All single -ane C x 2 2 H
- A double -ene C x 2 H
- A triple -yne C x 1 H