MRP Systems - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 8
Title:
MRP Systems
Description:
MRP Systems. Thus far, planned order releases were based solely ... What if setup costs are significantly greater than carrying inventory? ... ( Rheem example) ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:436
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: MRP Systems
1
MRP Systems
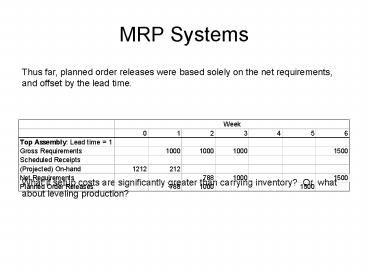
Thus far, planned order releases were based
solely on the net requirements, and offset by the
lead time. What if setup costs are
significantly greater than carrying inventory?
Or, what about leveling production?
2
MRP Systems
EOQ strategy Ex. 8.5 Setup cost (A)
100 Holding cost (h) .10/unit/week The
following MPS Demand 117 145 175
128 211 74 242 1092 units
/ 10 weeks
3
MRP Systems
Recalling the Economic Order Quantity Equation
(EOQ) Using the EOQ results in the
following planned order release.
4
MRP Systems
Another common strategy is to produced at
periodic intervals. This strategy uses a
periodic order quantity (POQ). In the previous
example, using the EOQ, an order was placed about
every 4 weeks. Therefore using a 4 week POQ,
orders will be placed in week 1, 5, and 9 as
follows Week 1 145 175 128 111
337 Week 5 211 74 285
5
MRP Systems
- Necessary conditions for a successful MRP system
- Feasible master production schedule if
capacity not available, lead times will not be
met resulting in part shortages for higher level
assemblies. - Accurate bill of materials BOMs evolve over
time, careful coordination between Engineering
change orders and material handling required.
(Rheem example). - Accurate and current inventory records very
difficult to maintain accuracy when reporting of
scrap or counts are inaccurate. - Known and constant lead times variability in
lead times are typcially handled with safety
stock, increasing WIP levels.
6
MRP Systems
- Necessary conditions for a successful MRP system
cont. - Employee discipline employees must stick to
the schedule and not deviate from the amount or
the ordering. - Batch withdrawals MRP assumes all parts of a
batch must be in place before withdrawals and
begin. While in practice, withdrawals may begin
as soon as parts arrive. Therefore, the MRP will
result in unnecessarily large buffer inventory.
7
MRP Systems
Structural Limitations of MRP Discrete time
buckets - MRP assumes all parts that will be used
in a time period must be available at the start
of the time period. In reality, parts will be
consumed throughout the time period. Therefore
if time buckets are large then WIP is increased.
If time buckets are small, lead time variability
may hamper the ability to complete orders in
time.
8
MRP Systems
Structural Limitations of MRP cont. Lead time
variability lead time in practice are variable.
To account for this variation, order sizes are
increased as a safety factor, thus leading to
increased WIP. Accurate data MRP systems
require accurate inventory levels. Because
counts are difficult to maintain, cycle counters
are required to periodically count inventory and
adjust the MRP system accordingly. This adds
labor cost.