See class handout - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 22
Title:
See class handout
Description:
contains old and newly formed stars. spiral arms = newly formed, luminous, massive stars ... Composed of old, low mass stars and globular clusters. Globular cluster ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:196
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: See class handout
1
See class handout
2
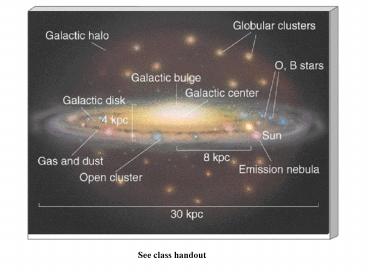
The Milky Way Galaxy
- In broad brush form, our galaxy is composed of
three distinct structures (see handout) - The central nucleus and bulge
- spherical distribution of stars about GC Dia 4
Kpc - The disk
- contains old and newly formed stars
- spiral arms newly formed, luminous, massive
stars - gas and dust of the interstellar medium
- about 30 Kpc in diameter and 1 Kpc in thickness
- The halo
- Composed of old, low mass stars and globular
clusters
3
Globular cluster
Circular orbits of stars in galactic disc
Inclined, eccentric orbits of Halo stars and
globular clusters
4
The Suns location
Question How far away is the Sun from the
galactic center ? Answer Look at the
distribution of globular clusters
- Harlow Shapleys method (c. 1915)
- Determine distances to many globular clusters
- use 5 star formula and standard candle method
- Then calculate the distance to the center of the
globular cluster distribution Suns distance
from GC
5
A globular cluster Composed of old low mass
stars N(stars) 105 - 106 Diameter 10 pc
6
Globular cluster
Many globular clusters
Few globular clusters
Disk
Sun
Nucleus
7
The mass of the galaxy
- 1917 Harlow Shapley
- Finds that the Sun is some 8000 pc away from the
galactic center - Also,
- Studies of star velocities indicate that the Sun
has an orbital speed of 220 km/s about GC - Hence, known radius and velocity ? orbital period
time to circle GC 2 p 8000 pc / 220 km/s 240
Myr
Sun has been 19 times around GC since it formed
8
A real corker of a result
- From speed and position of Sun from GC, Keplers
3rd law tells us - Mgalaxy a3 / P2
- where a 8000 pc and P 240 million years
- Mgalaxy 1011 M?
9
Galaxy classification
- Observations
- Three main types of galaxies are observed
- Spiral galaxies S and SB types
- a type large nucleus, tightly wound spiral arms
- c type small nucleus, loose, open spiral arms
- Elliptical galaxies E type
- Irregular galaxies Irr type
10
Hubbles tuning fork diagram
Sa
Sc
Irr
E0
E7
SBa
SBc
Openness of arms
Gas and dust
Nucleus / disk ratio
11
- Spiral galaxies
- bright nucleus
- spiral arms mapped out by bright stars
- many regions of active star formation
- Two types of spiral galaxy
- normal spiral
- arms radiate from a central spherical nucleus
- barred spiral
- arms radiate from a bar that extends either side
of the nucleus
12
- Irregular galaxies
- no obvious structure
- large quantities of gas and dust
- many regions of active star formation
- Elliptical galaxies
- football shaped
- no regions of active star formation
- very little gas and dust
- old, low mass stars only
13
Galaxy collisions
- Separation of stars tens of millions of star
diameters - Separation of galaxies a few galaxy diameters
- Hence
- Stars virtually never collide, but galaxies do
collide quite often - During galaxy collision
- Large ISM clouds become compressed and star
formation is triggered
14
The Hubble flow
Edwin Hubble and Milton Humason (1920s) studied
distant galaxies
- Observations
- distances from standard candles
- velocities from Doppler shift
Milton Humason (1891 1972)
15
Assume all elliptical galaxies are the same size
V from Doppler shift, d from standard ruler method
16
Galaxy data V(km/s) vs d(Mpc)
Velocity (km/s)
Slope H 75 km/s/Mpc
Distance (Mpc)
17
- Result - recall lab 5
- All distant galaxies have redshifts
- (i.e., are moving away from us)
- Hubbles law (1929) for galaxy recession
velocities (another 5 star general!!) - velocity H x distance ()
- H Hubbles constant
OOTETK
18
km/s/Mpc
19
An astounding result
- Hubbles law tells us that
- The Universe is expanding uniformly
- NB The galaxies are not moving into space but
are moving with space - it is, in fact, space
that is expanding carrying the galaxies along
with it
20
- Faintest
- galaxies in the
- image are some
- 1000 Mpc distant
- 10 day exposure
- over a 2 arc min. by 2 arc min.
- region of the sky
- Some 1500 galaxies
- have been
- identified in the
- image
- 55 billion
- galaxies in the observable universe
21
The cosmological principal
- Hubble (again) 1936 in his book
- The Realm of the Nebulae
- Observations imply
- On the large scale ( 100 Mpc) the Universe is
homogeneous (the same everywhere) and isotropic
(the same in all directions) - in other words there is nothing special about our
specific location in the Universe
22
- The Cosmological Principal in essence
- completes the Copernican Revolution
- 1543 Copernicus removes the Earth from the
center of the Solar System - 1917 Harlow Shapley removes the Sun from the
center of the galaxy - 1936 Edwin Hubble removes the Milky Way galaxy
from center of the Universe