Circle Scan Conversion - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 7
Title:
Circle Scan Conversion
Description:
Compute Graphics. Circle Scan Conversion. We use D as in the case of line ... D ( 2*xp-2yp 5) Initialization. Dinit=F(1,R-0.5)= E. SE. M. ME. MSE. Opening ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:223
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Circle Scan Conversion
1
Circle Scan Conversion
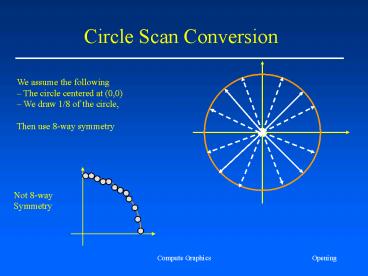
We assume the following The circle centered at
(0,0) We draw 1/8 of the circle, Then use
8-way symmetry
Not 8-way Symmetry
2
Circle Scan Conversion
- We assume (xp, yp) has been correctly
- Selected.
- The slope is between 0 and 1.0
- If the circle passes above M, then
- We select E
- Else
- We select SE
E
M
ME
SE
MSE
We assume The circle centered at (0,0) We
draw 1/8 of the circle, Then use 8-way symmetry
3
Circle Scan Conversion
- We use D as in the case of line
- D F(M) F(xp1, yp-0.5)
- (xp1)2(yp-0.5)2-R2
- If ( D lt 0 ) then
- M is below the arc,
- pixel E is closer to the line.
- If (D gt 0 ) then
- M is above the arc,
- pixel SE is closer to the line.
4
Circle Scan Conversion
- CASE I E is next
- We use D as in the case of line
- Dnew F(ME) F(xp2, yp-0.5)
- (xp2)2(yp-0.5)2-R2
- D ( 2xp3)
- CASE II SE is next
- We use D as in the case of line
- Dnew F(M) F(xp2, yp-1.5)
- (xp2)2(yp-1.5)2-R2
- D ( 2xp-2yp5)
- Initialization
- DinitF(1,R-0.5)
5
Circle Scan Conversion
DrawCircel(int radius, Color clr) int x 0
int y radius int d 1-radius
Plot(x,y, clr) while ( y gt x ) if
( d lt 0 ) // E Selected d 2x 3
else d 2(x-y) 5
y-- x
Plot(x,y, clr)
6
Circle Scan Conversion
- Let us use second order difference
- If E was selected then
- ?Eold 2xp3
- ?Enew 2(xp1)3
- deltaE ?Enew - ?Eold 2
- If SE was selected then
- ?SEold 2xp-2yp5
- ?SEnew 2(xp1)-2yp 5
- deltaSE ?SEnew - ?SEold 4
E
M
ME
SE
MSE
7
Circle Scan Conversion
DrawCircel(int radius, Color clr) int x 0
, y radius int d 1-radius int
deltaE 3, deltaSE -2radius 5
Plot(x,y, clr) while ( y gt x ) if (
d lt 0 ) // E Selected d deltaE
deltaE 2 deltaSE 2
else // SE Selected d
deltaSE deltaE 2 deltaSE
4 y-- x
Plot(x,y, clr)