Steps in the Risk Management Process - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 46
Title:
Steps in the Risk Management Process
Description:
Understand the methods used by a risk manager to set up clean-up goals and objectives. ... Preservation of Wilderness. Quality of Life. Choosing an Option ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:84
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Steps in the Risk Management Process
1
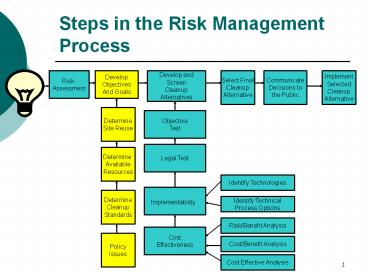
Steps in the Risk Management Process
Risk Assessment
Develop Objectives And Goals
Develop and Screen Cleanup Alternatives
Select Final Cleanup Alternative
Communicate Decisions to the Public
Implement Selected Cleanup Alternative
Determine Site Reuse
Objective Test
Legal Test
Determine Available Resources
Identify Technologies
Determine Cleanup Standards
Identify Technical Process Options
Implementability
Risk/Benefit Analysis
Cost Effectiveness
Policy Issues
Cost/Benefit Analysis
Cost Effective Analysis
2
Session Objectives
- Understand the methods used by a risk manager to
set up clean-up goals and objectives. - Understand how site redevelopment and available
resources impact a projects clean-up goals. - Understand how environmental policy may impact
goals and objectives.
3
Clean-up Goals and Objectives Defined
- Clean-up goal cleanup levels that are expected
to be achieved. - Clean-up objective provides a description of
what the cleanup will accomplish.
4
Clean-up Objectives
- Provide media specific objectives.
- Form the basis for development of cleanup
options. - Should not be too restrictive so as to limit
alternative development. - Specify acceptable cleanup concentrations for
each contaminant of concern, medium, and route
of exposure.
5
Clean-up Objectives
- Reexamined prior to cleanup alternative
development. - Address all risks during all phases of cleanup
action. - May change if site conditions change.
- May change if site technical or non-technical
information changes.
6
Example of a Clean-up Objective
- Prevent ingestion of or direct contact with soil
contaminated with lead at levels above 500 parts
per million by on-site workers and visitors in t
he wood treatment and storage area. - Prevent migration of lead that would result in
groundwater contamination in excess of 50 parts
per billion for lead.
7
Factors to Consider When Developing Clean-up Goals
- Environmental policies
- Site reuse and its possible impacts
- Economics
- Other factors (politics, public perception, legal
considerations)
8
Environmental Policy Defined
- Policy is a broad course of action, guiding
principles, or procedure, considered to be
expedient, prudent, or advantageous.
9
Impact of Site Reuse
- May affect the level of cleanup at a site.
- May affect the selection of a cleanup option or
alternative. - May affect the selection of a cleanup technology.
10
Economics
- Availability of Funding
- Available cleanup funds may limit the scope of
site cleanup. - Impact of the potential cleanup option on the
local economy. - Impact of the selected cleanup option on the
national economy. - The intrinsic value of a resource.
11
Other Factors to Consider
- Technical factors.
- Availability
- Feasibility
- Implementability
- Non-technical factors
- Politics
- Legal issues
- Public perception
- Society's values
12
Session Summary
- Develop initial cleanup goals and objectives
- Revise cleanup goals and objectives
- Consider technical factors
- Consider non-technical factors
13
Steps in the Risk Management Process
Risk Assessment
Develop Objectives And Goals
Develop and Screen Cleanup Alternatives
Select Final Cleanup Alternative
Communicate Decisions to the Public
Implement Selected Cleanup Alternative
Determine Site Reuse
Objective Test
Legal Test
Determine Available Resources
Identify Technologies
Determine Cleanup Standards
Identify Technical Process Options
Implementability
Risk/Benefit Analysis
Cost Effectiveness
Policy Issues
Cost/Benefit Analysis
Cost Effective Analysis
14
Session Objectives
- Understand how clean-up alternatives are
developed - Understand how clean-up alternatives are screened
- Understand how a clean-up alternative is selected
15
Selection of Clean-up Alternatives
16
Examples of General Clean-up Alternatives
- Treatment
- Engineering Controls
- Collection and Discharge
- Institutional Controls
- No Action
17
Selection of Clean-up Alternatives
18
Technology AlternativesElements to Evaluate
- Site specific data
- Technical information
- A technology type needs to be identified for each
general cleanup alternative
19
Clean-up Alternative Technology Selection
- Technical Factors to Be Considered
- Availability
- Feasibility
- Implementability
20
Clean-up Alternative Technical Information
- Risk Reduction Data
- Impact of remedy on risk
- Short-term
- Long-term (performance)
21
Selection of Clean-up Alternatives
22
Identification of Technology Process Options
- Identify the types of technologies that may be
appropriate for a remedial alternative. - Define specific process for each technology type.
- Identify representative examples of process
options within a technology.
23
Example of Screening Criteria
- Implementability
- Effectiveness
- Economic
- Political Issues
- Public Concern Issues
- Benefit Analysis
24
Implementability
- Technically and Administratively Feasible
- Reliability, complexity, resources, etc.
- Technology is appropriate for site location
25
Effectiveness
- Meets goals and objectives?
- Risks to receptors during implementation or
construction of the technology? - Reliability (track record)?
26
Economic Issues
- Cost to implement
- Direct Capital
- Indirect Capital
- Operation and Maintenance
- Returning site to economic reuse
27
Political Issues
- Objections to certain technologies
- Incentives for certain technologies
- Concern about cost and cost effectiveness
28
Public Concern Issues
- Impact on community
- Noise
- Traffic
- Hazards
- Emissions
- Property values
- Time (how long will clean-up last?)
- Future of the site (redevelopment)
29
Benefit Analysis
- Benefit analysis involves the comparison of
- Effects on Environmental Protection
- Costs
- Measure of Confidence
30
Types of Benefit Analysis
- Risk Benefit Analysis
- Cost Benefit Analysis
- Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
31
Evaluating Intangibles
- Consider Intangibles Subjectively
- Such as
- Preservation of Wilderness
- Quality of Life
32
Choosing an Option
- Calculate cost per unit of benefit
- Factor in the intangibles
- Consider the overall affordability
- Cost/Benefit Cost of Clean-up Alternative
- Benefits
33
Example of Option Selection
- Option 1 Groundwater Extraction with Off-site
Treatment to Contain Pollution from Facility - Cost Per Unit Benefit
- 1 acre of wetland saved for every 1,000 spent.
- Intangibles
- Public acceptance,
- Wildlife Preserved,
- Localized depletion of groundwater resources
leading to less water available for
residential/industrial use nearby.
34
Example of Option Selection
- Option 2 Insitu Soilwashing and Groundwater
Bioremediation - Cost Per Unit Benefit
- 2 acres of wetlands saved for every 1,000 spent
- Intangibles
- Public unsure of long-term affects and success of
remedy - Timeframe for cleanup of groundwater is long -
greater than 10 years. - Overall Affordability
- Within the cost of available funding
35
Example of Option Selection
- Option 3 Placement of a Contaminant Barrier
(slurry wall) - Cost per unit benefit
- 4 acres of wetlands saved for every 1,000 spent.
- Intangibles
- Public uncertainty over effectiveness,
- Time frame for remediation is less short.
- Long-term effectiveness (greater than 15 to 20
years) is unknown
36
Cost Effectiveness Analysis
37
How to Measure Effectiveness
- Reduction in Toxicity
- Reduction in Volume
- Reduction in Mobility
38
Asymptotic Curve
- Diminishing returns (risk reduction) on the
investment (money) over time
39
Calculating Costs and Effectiveness
- A simple cost-effectiveness comparison might look
like this
Option 1 is the most cost effective however, in
the scenario, 12.5 additional miles of river
could be cleaned-up for only 9,000, which might
be selected based on policy goals.
40
Session Summary
- Alternative Screening
- Risk Benefit Analysis
- Cost Benefit Analysis
- Cost Effectiveness Analysis
- Selection of pre-final clean-up alternative
- Alternative Selection
41
Steps in the Risk Management Process
Risk Assessment
Develop Objectives And Goals
Develop and Screen Cleanup Alternatives
Select Final Cleanup Alternative
Communicate Decisions to the Public
Implement Selected Cleanup Alternative
Determine Site Reuse
Objective Test
Legal Test
Determine Available Resources
Identify Technologies
Determine Cleanup Standards
Identify Technical Process Options
Implementability
Risk/Benefit Analysis
Cost Effectiveness
Cost/Benefit Analysis
Cost Effective Analysis
42
Session Objectives
- Familiarity of and utilization with the
procedures to select a remedial option. - Understanding of the importance of communicating
the selected remedy to the public.
43
Selecting the Remedy
- Questions to consider
- Will a clean-up alternative meet risk management
objectives? - Is the remedy legal?
- Is the remedy technically and administratively
implementable? - Will the remedy be effective over time?
44
Selecting the Remedy (continued)
- Questions to consider
- Will the clean-up cause more harm then good?
- What is the opinion of the public and other
stakeholders? - Is the remedy cost-effective?
- Are resources available to design and implement
the remedy?
45
Documenting the Decision
- Purpose of Decision
- Public awareness and input
- Engineering use
- Legal record
- Decision record
46
Session Summary
- Risk Management Decision Process
- Evaluation of Clean-up Alternatives
- Selection of Final Site Remedy
- Documentation to the Public