Sec. 1.4 Measure and Classify Angles - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 14
Title:
Sec. 1.4 Measure and Classify Angles
Description:
1.4 Measure and Classify Angles. An angle consists of two different rays with the same endpoint. ... Matching arcs are used to show that angles are congruent. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:965
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Sec. 1.4 Measure and Classify Angles
1
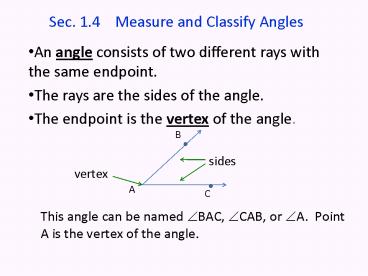
Sec. 1.4 Measure and Classify Angles
- An angle consists of two different rays with the
same endpoint. - The rays are the sides of the angle.
- The endpoint is the vertex of the angle.
This angle can be named ?BAC, ?CAB, or ?A. Point
A is the vertex of the angle.
2
EXAMPLE 1
Name angles
3
- A protractor can be used to approximate the
measure of an angle. - An angle is measured in units called degrees
- (ex 90).
We write the measure of an angle as m?ABC 90
4
Classifying Angles
- Angles can be classified as acute, right, obtuse,
and straight.
5
EXAMPLE 2
Measure and classify angles
Use the diagram to find the measure of the
indicated angle. Then classify the angle.
SOLUTION
A protractor has an inner and an outer scale.
When you measure an angle, check to see which
scale to use.
6
EXAMPLE 2
Measure and classify angles
7
for Examples 1and 2
GUIDED PRACTICE
1. Name all the angles in the diagram above.
Which angle is a right angle?
8
Postulate 4 Angle Addition Postulate
If P is in the interior of ?RST, then m?RST
m?RSP m?PST Very similar to which postulate?
- Two angles are congruent angles if they have the
same measure.
Angles are congruent ?A ? ?B
Angle measures are equal m?A m?B
9
Find angle measures
EXAMPLE 3
Angle Addition Postulate
Substitute angle measures.
145 6x 7
Combine like terms.
Subtract 7 from each side.
138 6x
Divide each side by 6.
23 x
10
EXAMPLE 3
11
Given that ?EFG is a right angle, find m ?EFH
and m ? HFG.
GUIDED PRACTICE
Combine like terms.
Subtract 3 from each side.
Divide each side by 3.
12
- An angle bisector is a ray that divides an angle
into two angles that are congruent.
13
EXAMPLE 5
Double an angle measure
SOLUTION
14
Homeworkp. 28-314-26 even, 30-38 all, 40,53,54