Lecture 19 Modifications of the Basic Gravity Model - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 9
Title:
Lecture 19 Modifications of the Basic Gravity Model
Description:
19-1 The Distance-Decay Parameter (Cont.) Example of Chicago's Beta value change over time: ... 19-1 The Distance-Decay Parameter (Cont. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:163
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Lecture 19 Modifications of the Basic Gravity Model
1
Lecture 19 Modifications of the Basic Gravity
Model
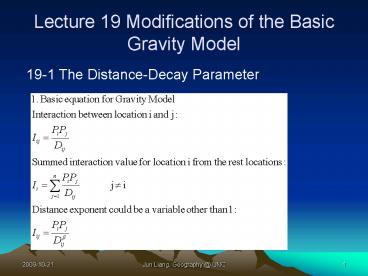
19-1 The Distance-Decay Parameter
2
19-1 The Distance-Decay Parameter (Cont.)
- How to decided the distance exponent?
- Recall the example of Chicago phone calls, truck
traffic, and air traffic. - Variations in the distance exponent itself have
become the subject of empirical study - Different time (years, months, days, or weeks.)
- Different types of travel
- Different commodities shipped
- Different regions
3
19-1 The Distance-Decay Parameter (Cont.)
- Example of Chicagos Beta value change over time
- The decline in Chicagos distance exponent
represents the declining friction of distance in
air transport as technological and economic
changes that took place in latter part of the
twentieth century.
4
19-1 The Distance-Decay Parameter (Cont.)
5
19-1 The Distance-Decay Parameter (Cont.)
- Changing parameters in spatial interaction models
Negative relationships VS. Positive
relationships. See figure 7.24.
6
19-1 The Distance-Decay Parameter (Cont.)
7
19-1 The Distance-Decay Parameter (Cont.)
- Surface transportation shows greater sensitivity
to distance than does air transportation. - Distance exponents for the truck flows (Chicago)
are approximately 2.0 - British road and rail transport 2.5
- Air transport exponents are closer to 1.0
- The study of changes in the Chicago air exponent
suggests a value of less than one for large
gateway cities
8
19-2 Complementarity Attractive and Propulsive
Forces
Distance
Variances for the dependent variable Airline
traffic, Phone calls, etc.
Population
Functionalities
Complementairty
Other attractive forces
9
19-2 Complementarity Attractive and Propulsive
Forces (Cont.)
- Complementairty will increase interaction between
destinations and origins. Example Ullmans
agriculture surplus and deficit example. - Basic Gravity model works for general cases, and
it is hardly exist. It is important to look for
other forces.