Geologic Time Scale - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
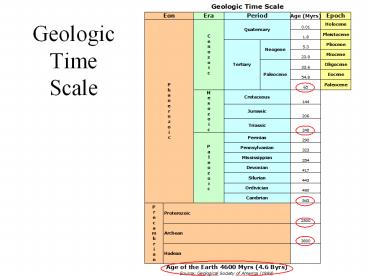
Geologic Time Scale
Description:
Geologic Time Scale – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:195
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Geologic Time Scale
1
GeologicTimeScale
2
Scientific Method
- Raise question
- Gather data
3
Scientific Method
- Raise question
- Gather data
- Form hypothesis
- Test and modify hypothesis
4
Peer-Reviewed Journals
5
Science Magazines
6
Scientific Method
- Scientific Theory
- Scientific Law
Le château des Pyrénées (Castle in the
Pyrenees) (1961)
7
(No Transcript)
8
Stuff of the Universe
- The Raw Materials for Planets, Rocks and Life
9
Matter Energy
10
Phases of Matter
Determined by temperature and pressure
Gas
Solid
Liquid
11
(No Transcript)
12
Rock
13
Atomic Particles
Atoms (Elements)
Compounds (Minerals, Organic Compounds)
Rocks
Living Things
Earth
Biosphere
14
Atomic StructureWhat are atoms made of?
Particle Charge Weight (amu)
Proton (p) 1
Electron (e) - 0
Neutron (n) 0 1
15
Atomic Structure
16
Atomic NumberNumber of Protons
Importance of Protons
17
Elements
Carbon
Iron
Gold
18
Periodic Table of the Elements
19
The most abundant element in the universe
Hydrogen
Large Magellanic Cloud
20
Abundance of the Elements (wt. )Solid Earth
- Crust Whole Earth
- Oxygen(O) 46.3 29.5
- Silicon (Si) 28.2 15.2
- Aluminum (Al) 8.2 1.1
- Iron (Fe) 5.6 34.6
- Calcium (Ca) 4.1 1.1
- Sodium (Na) 2.4 0.6
- Potassium (K) 2.1 0.1
- Magnesium (Mg) 2.3 12.7
- All others 0.5 5.1
21
Abundance of the Elements (wt.)Living Things
- Human Alfalfa Bacteria
- Oxygen(O) 62.8 77.9 73.7
- Carbon (C) 19.4 11.3 12.1
- Hydrogen (H) 9.3 8.7 9.9
- Nitrogen (N) 5.1 0.8 3.0
- Phosphorous (P) 0.6 0.7 0.6
- Sulfur (S) 0.6 0.1 0.3
22
AtomicWeight number of protons neutrons
Importance of Neutrons
23
Quiz - Lithium
3 7
Atomic Number Atomic Weight
24
Isotopes
25
Atoms vs. Ions
Importance of Electrons
(atomic weight 23)
X
Charge 0
26
Positive Ions
Importance of Electrons
10e
Sodium Ion
(atomic weight 23)
Charge 1
27
Ions
Importance of Electrons
9e
Chlorine
(atomic number 9)
(atomic weight 18)
9p 9n
Charge 0
28
Negative Ions
Importance of Electrons
10e
Chlorine Ion
(atomic number 9)
(atomic weight 18)
9p 9n
Charge -1
29
Atomic Particles
Atoms (Elements)
Compounds (Minerals, Organic Compounds)
Rocks
Living Things
Earth
Biosphere
30
Determine how atoms bond to formCompounds
Importance of Electrons
31
Organic Compounds
Carbon is found in all organic compounds
32
Minerals - Inorganic Compounds
33
Minerals andCrystalline Structure
34
Graphite
35
Atomic Particles
Atoms (Elements)
Compounds (Minerals, Organic Compounds)
Rocks
Living Things
Earth
Biosphere
36
Energy
- Types
- Kinetic
- Mechanical
- Electromagnetic
- Electricity
- Heat
- Potential
- Chemical
37
Electromagnetic Spectrum
38
EnergyQuality
Low Quality High Quality (disorganized
concentrated)
39
Rules of the Universe
- Conservation of Matter
- 1st Law of Thermodynamics(Conservation of
Energy) - 2nd Law of Thermodynamics(Degradation of Energy)
- You cant thrown anything away
- You cant get something for nothing
- In fact, you cant even break even
40
Earth Open or Closed System?
41
EarthMatter does not come and go
So matter is constantly recycled on Earth
Earth is a Closed System to Matter
42
Biogeochemical CyclesReservoirs Pathways
Atmosphere
Biosphere
Lithosphere
Hydrosphere
43
Some Major Cycles of Matter
- Water Cycle
- Rock Cycle
- Chemical Cycles
- Carbon
- Nitrogen
- Phosphorous
- Sulfur
44
Carbon Cycle
Atmosphere
Biosphere
Lithosphere
Hydrosphere
45
Carbon Cycle Reservoirs
Atmosphere
1x ( 7.3x1017 grams carbon)
Biosphere
3x
55x
35,000x
Lithosphere
Hydrosphere
46
Carbon Cycle
Atmosphere
Biosphere
Lithosphere
Hydrosphere
47
Carbon TransferBiosphere Atmosphere
Photosynthesis (Atmosphere to Biosphere)
Carbon Dioxide Water Sunlight --gt Sugar
Oxygen
Respiration (Biosphere to Atmosphere)
Sugar Oxygen --gt Carbon Dioxide Water Energy
48
Carbon Cycle
Atmosphere
Biosphere
Lithosphere
Hydrosphere
49
Carbon Cycle
Human Impacts
Atmosphere
Biosphere
Net Effect Increase in Carbon in Atmosphere
Lithosphere
Hydrosphere
50
Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide
northern winter
northern summer
51
Impact
52
EarthEarth constantly gains loses energy
Heat
Earth is a Open System to Energy
Sunlight
53
Earth Open or Closed System?
Mostly Open to Energy
Mostly Closed to Matter