Integumentary System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 30
Title: Integumentary System
1
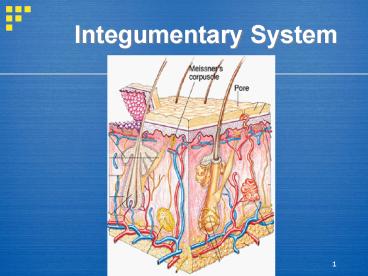
Integumentary System
2
Integumentary System
- Consists of two components
- Skin
- Skin Derivatives (accessory structures) sweat
and oil glands hair nails
3
Functions
4
Integumentary System
- Skin has two layers a subcutaneous layer
- a. Epidermis
- b. Dermis
- c. Hypodermis
5
(No Transcript)
6
Epidermis
7
(No Transcript)
8
(No Transcript)
9
Dermis
10
(No Transcript)
11
Dermal Layers
- 1. Papillary layer- loosely woven mat of fibers,
rich blood supply, dermal papillae (fingerprints) - 2. Reticular layer- dense irregular CT, dense
bundles of collagen fibers, cleavage lines
12
Subcutaneous Layer
13
(No Transcript)
14
Skin Color
- Melanin- made from tyrosine, yellow ?
reddish-brown?black, color differences due to
type amount of melanin produced - freckles moles local accumulation of melanin,
- protects DNA from UV photodamage, albino-
individuals without tyrosinase
15
Skin Color
- 2. Carotene- yellow to orange pigment, found in
carrots etc, accumulates in fat and stratum
corneum (palms and soles), seen when diet rich in
carotene - 3. Hemoglobin- RBCs in dermal capillaries shown
in light skin
16
Appendages of the Skin
- 1. Hair
- 2. Nails
- 3. Sudoriferous or sweat glands
- 4. Sebaceous (oil) glands
17
(No Transcript)
18
Arrector Pili Hair Root Plexus
- Arrector pili- bundle of smooth muscle associated
with each hair follicle, hair raising goose
bumps - Hair root plexus sensory nerve endings
sensitive to touch
19
So... do you know...
what causes goose bumps?
20
Hair Functions
- Warms
- Senses-
- Protects- on head from trauma, sun
- 4. Shields- eyelashes
- 5. Filters- nose hair
21
Nails
- Scale-like modification of epidermis hard,
keratinized cells that form a clear protective
covering - 2. Act as tools, to help pick up objects
22
(merocrine)
Modified sweat glands
23
(No Transcript)
24
(No Transcript)
25
Functions of Skin
- 1. Protection
- 2. Temperature regulation
- 3. Cutaneous sensation
- 4. Metabolic Functions Excretion
26
Cutaneous Sensation
- 1. Meissners corpuscles- light touch receptors,
just below epidermis - 2. Pacinian receptors- mechanoreceptors, deep
pressure touch receptors deep in the dermis - 3. Root hair plexi
- 4. Bare nerve endings- pain receptors
27
Metabolic Functions
- 1. Break down carcinogens that penetrate skin
- 2. Collagenase- aids in turnover of collagen and
helps prevent wrinkles
28
Excretion
- 1. Limited nitrogen wastes in sweat
29
Life-span changes
- Skin repair processes take longer due to reduced
number and activity of stem cells. - Skin forms wrinkles and becomes less resilient.
- Skins immune responsiveness is diminished.
- Skin becomes drier due to decreased sebaceous
gland activity. - Sweat production diminishes.
- Blood supply to the dermis is reduced --gt
impaired thermoregulation. - Hair thinning and loss.
- Development of skin cancers
30
All this info is making ...
my epithelium crawl !