Isolation of Nucleic Acids - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 22
Title:
Isolation of Nucleic Acids
Description:
isolation of a specific type of DNA (or RNA) Types of Methods: ... isopycnic/CsCl (density) DNA ~1.7 g/cm3. protein ~1.3 g/cm3. RNA DNA. ssDNA dsDNA ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:364
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Isolation of Nucleic Acids
1
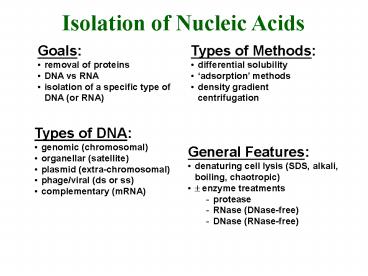
Isolation of Nucleic Acids
- Goals
- removal of proteins
- DNA vs RNA
- isolation of a specific type of DNA (or RNA)
- Types of Methods
- differential solubility
- adsorption methods
- density gradient centrifugation
- Types of DNA
- genomic (chromosomal)
- organellar (satellite)
- plasmid (extra-chromosomal)
- phage/viral (ds or ss)
- complementary (mRNA)
- General Features
- denaturing cell lysis (SDS, alkali, boiling,
chaotropic) - ? enzyme treatments
- protease
- RNase (DNase-free)
- DNase (RNase-free)
2
High MW Genomic DNA Isolation
- Typical Procedure
- Cell Lysis
- 0.5 SDS proteinase K (55o several hours)
- Phenol Extraction
- gentle rocking several hours
- Ethanol Precipitation
- RNAse followed by proteinase K
- Repeat phenol extrac-tion and EtOH ppt
- Phenol Extraction
- mix sample with equal volume of sat. phenol soln
- retain aqueous phase
- optional chloroform/isoamyl alcohol extraction(s)
3
High MW Genomic DNA Isolation
- Typical Procedure
- Cell Lysis
- 0.5 SDS proteinase K (55o several hours)
- Phenol Extraction
- gentle rocking several hours
- Ethanol Precipitation
- RNAse followed by proteinase K
- Repeat Phenol Extrac-tion and EtOH ppt
- EtOH Precipitation
- 2-2.5 volumes EtOH, -20o
- high salt, pH 5-5.5
- centrifuge or spool out
4
Isolation of RNA Special Considerations
- RNAse inhibitors!
- extraction in guanidine salts
- phenol extractions at pH 5-6
- (pH 8 for DNA)
- treatment with RNase-free DNase
- selective precipitation of high MW forms (rRNA,
mRNA) with LiCl - oligo-dT column
5
Adsorption Methods
- nucleic acids selectively absorb to silica or
resins in the presence of certain chaotropic
agents or salts
Plasmid Miniprep Protocol 1. Solubilize bacteria
in alkali solution 2. Neutralize with
Na-acetate 3. Centrifuge, discard pellet 4. Mix
supernatant with resin chaotropic agent 5. Wash
resin 6. Elute DNA with low salt buffer
- applications
- plasmid preps
- fragments after electrophoresis
- PCR templates
6
Density Gradient Centrifugation
- rate zonal/sucrose (size fractionation)
- electrophoresis more common
- isopycnic/CsCl (density)
- DNA 1.7 g/cm3
- protein 1.3 g/cm3
- RNA gt DNA
- ssDNA gt dsDNA
- GC content
7
CsCl Gradients
- Applications
- large scale preparations
- high purity
- satellite DNA
- RNA cushions
CsCl Gradients
8
Using Spectroscopy to analyze DNA
DNA absorbs UV light with a major peak at 260 nm
This absorption is useful because it varies with
the structure of DNA (RNA) i.e. extinction
coefficient depends on the structure
Optical Density
Wave Length
260
dsDNA Low extinction coefficient
ssDNA Higher extinction coefficient
9
Evaluation of Nucleic Acids
- spectrophotometrically
- quantity
- quality
- fluorescent dyes
- gel electrophoresis
10
Agarose Gel Stained with ethidium bromide (EtBR)
to Visualize the DNA
slots where DNA is loaded
1000 bp
700 bp
600 bp
500 bp
Screening PCR products to test for the presence
of specific DNA sequences
molecular weight markers
molecular weight markers
correct PCR product
11
Intercalating Agents Distort the Double Helix
- Several hydrophobic
- molecules containing
- flat aromatic and fused
- heterocyclic rings can
- insert between the
- stacked base pairs
- of DNA. These
- molecules are called
- intercalating agents.
- Intercalating agents
- are potential
- Cancer-inducing
- reagents.
12
(No Transcript)
13
DNA Sequencing
14
Dideoxy Chain Termination
15
DNA sequencing the Sanger (dideoxy) method
Figure 7-29b,c
16
NTP, dNTPs and ddNTPs
17
DNA sequencing the Sanger method
Four separate polymerization reactions are
performed
Figure 7-29a
18
DNA Sequencing
19
(No Transcript)
20
Reading a DNA Sequencing Gel
21
Semi-Automated Sequencing
- thermal cycler
- fluorescent ddNTPs
- unique spectra
- measure intensity of DNA products on gel
è
22
Automated DNA Sequencing with Fluorescent Dyes
Each different ddNTP is coupled to a different
colored fluorescent dye ddTTP is red ddGTP is
black etc.