nucleic acids DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 15
Title:
nucleic acids DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides
Description:
nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) are polymers of nucleotides ... isopycnic/CsCl (density) DNA ~1.7 g/cm3. protein ~1.3 g/cm3. RNA DNA. ssDNA dsDNA ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:219
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: nucleic acids DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides
1
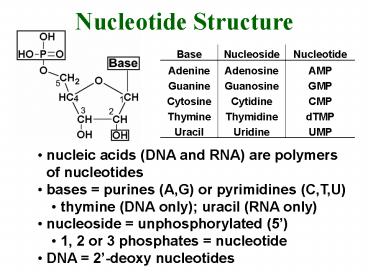
Nucleotide Structure
- nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) are polymers of
nucleotides - bases purines (A,G) or pyrimidines (C,T,U)
- thymine (DNA only) uracil (RNA only)
- nucleoside unphosphorylated (5)
- 1, 2 or 3 phosphates nucleotide
- DNA 2-deoxy nucleotides
2
(No Transcript)
3
The Central Dogma
- cells make exact copies of DNA
- RNA is transcribed from a DNA template
- proteins are translated from RNA template
4
DNA/RNA Synthesis
- the DNA strands are separated
- each strand serves as template
- complementary strands are synthesized (5'?3')
- yields 2 identical DNA molecules
- carried out by DNA polymerase
- RNA synthesis is similar
- RNA polymerase
- single template
- U/T and 2'-O
- processing
retrovirus/reverse transcriptase
5
RNA Processing
- ? addition of caps and tails to primary
transcript - some genes have regions of non-coding sequence
(introns) which are removed - messenger RNA (mRNA)
6
Translation
carried out by ribosomes
triplet code (tRNA)
7
The Central Dogma
- information about proteins contained in DNA and
RNA - sequencing DNA relatively simple
- cloning and manipulating genes is possible
8
Isolation of Nucleic Acids
- Goals
- removal of proteins
- DNA vs RNA
- isolate specific type of nucleic acid
- Types of Methods
- differential solubility
- adsorption methods
- density gradient centrifugation
- Types of DNA
- genomic (chromosomal)
- organellar (satellite)
- plasmid (extra-chromosomal)
- phage/viral (ds or ss)
- complementary (mRNA)
- General Features
- denaturing cell lysis (SDS, alkali, heating,
chaotropic) - ? enzyme treatments
- protease
- RNase (DNase-free)
- DNase (RNase-free)
9
High MW Genomic DNA Isolation
- Typical Procedure
- Cell Lysis
- 0.5 SDS proteinase K (55o several hours)
- Phenol Extraction
- gentle rocking several hours
- Ethanol Precipitation
- RNAse followed by proteinase K
- Repeat phenol extrac-tion and EtOH ppt
- Phenol Extraction
- mix sample with equal volume of sat. phenol soln
- retain aqueous phase
- optional chloroform/isoamyl alcohol extraction(s)
10
High MW Genomic DNA Isolation
- Typical Procedure
- Cell Lysis
- 0.5 SDS proteinase K (55o several hours)
- Phenol Extraction
- gentle rocking several hours
- Ethanol Precipitation
- RNAse followed by proteinase K
- Repeat Phenol Extrac-tion and EtOH ppt
- EtOH Precipitation
- 2-2.5 volumes EtOH, -20o
- high salt, pH 5-5.5
- centrifuge or spool out
11
Isolation of RNA Special Considerations
- RNAse inhibitors!
- extraction in guanidine salts
- phenol extractions at pH 5-6
- (pH 8 for DNA)
- treatment with RNase-free DNase
- selective precipitation of high MW forms (rRNA,
mRNA) with LiCl - oligo-dT column
12
Adsorption Methods
- nucleic acids selectively absorb to silica or
diatomaceous earth in presence of certain
chaotropic agents or salts
Plasmid Miniprep Protocol 1. Solubilize bacteria
in alkali solution 2. Neutralize with
Na-acetate 3. Centrifuge, discard pellet 4. Mix
supernatant with resin chaotropic agent 5. Wash
resin 6. Elute DNA with low salt buffer
- applications
- plasmid preps
- fragments after electrophoresis
- PCR templates
13
Density Gradient Centrifugation
- rate zonal/sucrose (size fractionation)
- electrophoresis more common
- isopycnic/CsCl (density)
- DNA 1.7 g/cm3
- protein 1.3 g/cm3
- RNA gt DNA
- ssDNA gt dsDNA
- GC content
14
CsCl Gradients
- Applications
- large scale preparations
- high purity
- RNA cushions
- satellite DNA
Cesium Chloride Gradients
15
Evaluation of Nucleic Acids
- spectrophotometrically
- quantity
- quality
- fluorescent dyes
- gel electrophoresis