Hypersensitive PowerPoint PPT Presentations
All Time
Recommended
Hypersensitivity (Type III) Hypersensitivity (Type IV) Huan-Yao Lei, Ph.D. Department of Microbiology & Immunology College of Medicine National Cheng Kung University
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Hypersensitivity ( ) Jianzhong Chen Institute of Immunology Zhejiang University School Of Medicine chenjianzhong@zju.edu.cn Type II hypersensitivity ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Cuatro tipos de hipersensibilidad seg n el tipo de respuesta ... comienzo minutos despu s de la exposici n al ant geno ... incidence decreases after ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Adaptive immunity is important against microbial infections, ... Cetirizine (Zyrtec) -Desloratadine (Clarinex) -Fexofenadine (Allegra) -Loratadine (Claritin) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
ITS ABNORMAL BODY RESPONSE AGAINST AN ATIGEN THAT CAN BACTERIA, VIRUSES, TOXINS,BUT SUCH REACTION MAY BE DANGEROUS AGAINST OUR OWN BODY
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Type IV Delayed Hypersensitivity. Antigen : Chemical , Bacteria , Virus ,Fungus. Antibody : ... Cell death ( tissue necrosis ) Lymphokines * Chemotactic factor ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Type III Arthus or Immune complex. Type IV Delayed hypersensitivity ... House dust : mite - Pollen - Animal dander - Microorganisms - Serum protein/Animal protein ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
'Non-specific coordinated response by vascularized living tissue to injury' ... May be due to bee, wasp or ant stings, drugs (penicillin) or food (nuts) 17. Mast Cell ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: Chapter 13 Hypersensitivity Author: Persson Last modified by: walkinnet Created Date: 6/19/2005 6:48:49 AM Document presentation format
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Hypersensitivity reactions Hypersensitivity reactions excessive undesirable (damaging, discomfort producing and sometimes fatal) reactions produced by the normal ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Dentine Hypersensitivity Dr. F J Shaini PhD, M Dent Sci, BDS
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Title: Hypersensitivity type I Author: Michael Jackson Last modified by: acadpm01 Created Date: 4/17/2006 1:32:05 PM Document presentation format
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
DENTIN HYPERSENSITIVITY
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Dentin Hypersensitivity Zhang Qi Wuhan University School of Stomatology Introduction Definition: Characteristic Stimuli Etiology Two phases of development of dentin ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: PowerPoint Presentation Author: Gamal Ahmed Last modified by: Jihan Abdelmenam Created Date: 1/1/1601 12:00:00 AM Document presentation format
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Hypersensitivity and Autoimmunity * Type IV hypersensitivity the three forms Patch testing for contact hypersensitivity Summary or hypersensitivity reactions ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Pigeon, turkey, duck, parrots, cannaries, doves, chickens, geese, owls ... Decreased frequency in pigeon fanciers. TNF-2 -308 polymorphism of TNF-alpha promoter gene ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Type I hypersensitivity Immediate IgE mediated Localized ... peanuts and penicillins Type II hypersensitivity Cytotoxic Transfusion reactions Hemolytic ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Topics Type III hypersensitivity Type IV hypersensitivity Type III hypersensitivity Immune complex mediated Activates complement Inflammation Type IV ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
The reaction may take 3 - 10 hours after exposure to the antigen (as ... endogenous (non-organ specific autoimmunity: e.g., systemic lupus erythematosus, SLE) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Automobile, train, bicycle. Mobile telephone (GSM, C2000) Power tools ... Exploitation of pool of instruments for renting. Website www.electroallergie.org ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Type I Hypersensitivity Definition of Hypersensitivity An immunologic reaction which produces tissue damage on reexposure to antigen. Gell and Coombs Classification ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
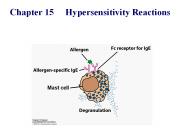
Chapter 15 Hypersensitivity Reactions Mast cell Although the word hypersensitivity implies an increased response, the immune response of a hypersensitivity ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Title: Hypersensitivity type I Author: Michael Jackson Last modified by: acadpm01 Created Date: 4/17/2006 1:32:05 PM Document presentation format
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Types of hypersensitivity diseases The type of immune response and immunologic mechanisms that causes tissue injury The nature and location of the antigen that is the ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
A subsequent exposure to the same allergen cross links the cell-bound IgE and ... Intradermal skin test with multiple positive allergen responses ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Differentiate CD4 helper cell to TH1 cell. Induces IFN ? secretion by T cells & NK cell ... molecules (B7-1) & secretion of IL-12 to generate TH1 T cells ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Allergy and Hypersensitivity I. Introduction A. Definitions Allergy Immune-mediated response to innocuous environmental antigen Can be humoral or cell-mediated ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Lecture 20 Hypersensitivity Reactions Immune responses that result in tissue injury
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Types of hypersensitivity diseases The type of immune response and immunologic mechanisms that causes tissue injury The nature and location of the antigen that is the ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Local erythema - H1 (and some H2)-mediated arteriolar dilatation ... Skin: erythema, induration, burning ... Nose/eyes: erythema, congestion, burning ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Urticaria (hives, wheal & flare response) Clinical Manifestations of Type I ... If the patient is allergic a wheal & flare response occurs ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: Hypersensitivity type I Author: Michael Jackson Last modified by: acadpm01 Created Date: 4/17/2006 1:32:05 PM Document presentation format
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Early IL-4 response promotes Th2 development that drives B cell class switching to IgE ... on hand of patient with poison ivy contact dermatitis (a type IV reaction) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis is an immune system disorder causing lungs to become inflamed due to allergic reactions to inhaled microorganisms, plant and animal proteins, or chemicals. In this presentation "Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis" has been described including their Causes, Diagnosis, Management, etc. For more information, please contact us: 9779030507.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Allergies Hugh B. Fackrell Hypersensitive Reactions Assigned Reading Content Outline Performance Objectives Key terms Key Concepts Short Answer Questions Assigned ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Hypersensitivity Types II-V Type II: Cytotoxic (ITH) Type III: Toxic Complex (ITH) Type IV: T Cell-Mediated (DTH) Type V: Stimulatory Cytotoxic Hypersensitivity (Type ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Dust Mite. What are the characteristics of allergens? ... The enzymatic activity of a dust mite fecal protein allows it to penetrate ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
SEQUENCE OF SPECIFIC PHYSIOLOGICAL BEHAVIORS. THAT OCCUR IN ... A. LABILE Capable of lifelong regeneration. B. STABLE Tissue can regenerate when stimulated ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Presentation on anti fibrotic drugs
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
HLA Haplotype and Abacavir HSR. Differences in incidence between ethnic groups and report of familial ... HLA = human leukocyte antigens (major ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Localized: Hives or asthma from contact or inhaled antigens ... Involve IgG or IgM antibodies and complement ... Drug-induced Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Figure 19.5 ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: Chronic stress, sensory hypersensitivity, anxiety-induced hyperalgesia. Author: Your User Name Last modified by: Summers, Cliff Created Date
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Most common allergies: Asthma prevalence: 7% of population. Atopic ... Cause of increasing prevalence of allergies. Hygiene hypothesis. Shift from Th1 to Th2 ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Global cough hypersensitivity syndrome size is expected at $13.51 Bn by 2028 at a growth rate of 6.9% and trends by The Business Research Company.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Mineral Dust Pneumoconiosis Fibrogenic Asbestosis Silicosis Berylliosis Coal worker s pneumoconiosis * * * * Title: Slide 1 Author: user Last modified by:
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Introduction to Lab Ex. 24: Hypersensitivity Response to antigens (allergens) leading to damage Require sensitizing dose(s) Type I (Anaphylactic) Reactions Involve ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Type III Hypersensitivity Immune Complex Mediated Reaction Type III: Immune Complex Mediated Reaction *When antibodies (Ig G ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Alpha, beta and gamma chains. Alpha chain. Two Ig like domains; extracellular. Gamma chain. Homodimer; two intracytoplasmic tails ... Fc gamma RIII receptors ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
After the exposure ceases the reaction disappeares in 3-4 months. ... Symptoms mild to severe, ceasing when no exposure. Symptoms milder than in allergic alveolitis ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
... Anti-Sm or antiphospholipid antibodies Antinuclear antibody Systemic Sclerosis A seronegative spondyloarthropathy because of lack of rheumatoid factor a ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
IgG and IgM based immunopathological reaction (reaction of hypersensitivity type II). = antibody-dependent antibodies produced by the immune response bind to antigens ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
... Lung biopsy Objective testing to establish work-relatedness: ... myalgia 4-8 hours after exposure - chronic disease: dyspnea in ... health care: information ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Prevalence of Asthma - Overlap with Chemical Hypersensitivity. 14.1% of American Population. Report being Diagnosed with Asthma ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Type III Hypersensitivity ( Arthus reaction or Immune complex ) ... Pigeon breeder disease. Antibody Fungal spore Pneumonitis. Organic material Pneumonitis ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Normally, auto-antigens in this site are not exposed to the immune system ... About half of all cases are classified as 'idiopathic,' meaning the cause is unknown. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view