Electrophilic substitution in pyrrole, furan and thiophene - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
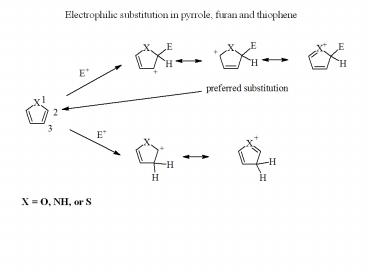
Electrophilic substitution in pyrrole, furan and thiophene
Description:
Electrophilic substitution in pyrrole, furan and thiophene X = O, NH, or S Examples: Furan is able to act as a diene in the reactions of cycloaddition The Fisher ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:2123
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Electrophilic substitution in pyrrole, furan and thiophene
1
Electrophilic substitution in pyrrole, furan and
thiophene
X O, NH, or S
2
Examples
3
Furan is able to act as a diene in the reactions
of cycloaddition
The Fisher synthesis of indoles
4
4. Chemistry of pyridine
Electrophilic substitution in pyridine
Pyridine is less active, than benzene toward
electrophilic agents, because nitrogen is more
electronegative, than carbon and acts like an
electron withdrawing substituent, including the
meta-directing effect. Example
5
Nucleophilic substitution in pyridine
The presence of nitrogen enables pyridine to
react with nucleophilic agents, like an electron
withdrawing substituents enables benzene to
participate in such reactions, including the
ortho-directing effect.
6
Another example
These reactions require very strong nucleophiles
and heat, because H- is a very weak leaving
group. In ortho- or para-substituted pyridines
nucleophilic substitution proceeds much easier.
7
Tautomerism of 2-pyridones
Unlike phenol, 2-hydroxypyridine prefers the
carbonyl form (2-pyridone), because the
isomerisation does not break aromaticity.
However, 2-aminopyridine is the preferred isomer
due to the strong conjugation between electron
donating amino-group and electron withdrawing
pyridine ring and weaker conjugation
in 2-pyridoneimine
8
Pyridinium salts