REPTILE MAMMAL - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 62
Title: REPTILE MAMMAL
1
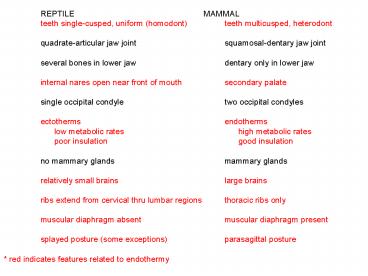
REPTILE MAMMAL teeth single-cusped,
uniform (homodont) teeth multicusped,
heterodont quadrate-articular jaw
joint squamosal-dentary jaw joint several
bones in lower jaw dentary only in lower
jaw internal nares open near front of
mouth secondary palate single occipital
condyle two occipital condyles ectotherms e
ndotherms low metabolic rates
high metabolic rates poor
insulation good
insulation no mammary glands mammary
glands relatively small brains large
brains ribs extend from cervical thru lumbar
regions thoracic ribs only muscular diaphragm
absent muscular diaphragm present splayed
posture (some exceptions) parasagittal
posture red indicates features related to
endothermy
2
(No Transcript)
3
(No Transcript)
4
(No Transcript)
5
Muskox
Lemming
Since insulation is proportional to thickness of
underfur AND to length of guard hairs, little
guys cant be as well insulated as big guys can
6
Some aquatic mammals have extremely thick
underfur to deal with higher thermal conductance
of water
7
Highly or totally aquatic forms give up fur
entirely and rely on thick subcutaneous fat
blubber
8
(No Transcript)
9
Pelycosaur
Therapsid
10
Class Mammalia Subclass Prototheria monotremes
egg- laying mammals (echidna, platypus)
11
Class Mammalia Subclass Theria Infraclass
Metatheria Order Marsupialia
12
Class Mammalia Subclass Theria Infraclass
Eutheria placental mammals
13
Order Insectivora hedgehogs, moles,
shrews
14
(No Transcript)
15
Order Chiroptera Fruit bats (mega), microbats
16
Order Primates prosimian (lemurs, lorises,
indris, bushbaby, tarsier
17
Order Primates
New World monkeys marmosets, spider, squirrel
monkeys
18
Old World Monkeys baboon, macaque, colobus,
langurs, vervet, etc.
19
Order Primates
Apes lesser (gibbon, siamang) and greater
(orang, gorilla, chimp, human)
20
Order Xenarthra (edentates) armadillos,
anteaters, sloths
21
Order Lagomorpha rabbits, pika
22
(No Transcript)
23
Order Rodentia largest of all mammalian orders
24
squirrels
25
Spiny rat
Rattus rattus
Old World rats mice
Mus musculus
26
Cotton rat (Sigmodon hispidus)
New World mice and rats
wood rat (Neotoma floridana)
Peromyscus deer mouse
27
Beaver muskrat aquatic adaptations
28
Gopher, molerats, blesmols digging adaptations
Common mole rat
gopher
Naked mole rat
29
Ords kangaroo rat
Desert rodents
30
Arctic or montane rodents cold adapted
31
Tropical rodents
32
Order Cetacea baleen whales
33
Pilot whale
Order Cetacea toothed whales dolphins
Killer whale
34
cheetah
caracal
leopard
African lion
Order Carnivora felids
snow leopard
tiger
35
Order Carnivora canids
36
Order Carnivora viverrids mongoose, civet,
meerkats, genets, etc.
binturong
meerkat
civet
37
Order Carnivora raccoon, coati, ring-tail,
kinkajou
red panda
kinkajou
raccoon
38
Order Carnivora bears
Malayan sun bear
39
Order Carnivora Mustelids weasels,
mink, otters, skunks, badgers
40
Order Carnivora pinnapeds seals, sealions,
walrus
41
Order Proboscidea elephants
African
Asian
42
Order Sirenia manatee and dugong
43
Order Perissodactyla odd-toed Ungulates
(horse, rhino, tapir)
44
Order Artiodactyla pig, hippo, camels, giraffe
45
Elk
Moose
White-tailed deer
46
Order Artiodactyla cattle
No. American bison
African buffalo
Domestic cattle (Bos taurus)
47
Order Artiodactyla antelope, sheep, goats
Wildebeest
Impala
Big horn sheep
Nyala
Barbary sheep
Pronghorn antelope
48
Tribosphenic teeth
49
Bunodont teeth of omnivores
50
Sectorial teeth of a wolf
51
Order Carnivora all possess a pair of cutting
teeth called carnassials formed from
the expanded upper 4th premolar (PM4) shearing
past the lower 1st molar (M1)
52
badger
weasel
Mustelids have shortened faces so they lose or
reduce the first premolar. They also expand the
first molar laterally to maintain crushing surface
53
bobcat
Cats are the most highly carnivorous of the
Carnivora. They retain only 2 premolars on
the upper jaw, and 2 premolars plus molar 1 on
the lower. Note the lack of crushing surface on
any of the teeth.
54
bear
Some Carnivora secondarily modify their teeth for
new functions. Bears are omnivores, developing
bunodont cheek teeth. Seals sea lions feed on
fishes and have secondarily become homodont for
their cheek teeth.
seal
55
Hypsidont teeth of a rhino
56
horse
Complex enamel ridges (lophs) are typical of
herbivores
bison
57
tapir
Order Perissodactyla these have both upper and
lower Incisors to clip vegetation. Order
Artiodactyla these have procumbent lower
incisors which flare distally (spatulate).
These pin grass against a fibrous pad on the
upper jaw. They pull rather than clip the
leaves.
bison
58
some are hyperlophodont!
Lophodont teeth of rodents (multiple enamel
ridges)
59
Order Rodentia they have enlarged upper and
lower incisors for husking and breaking open
nuts and seeds. Most have pigmented enamel (red,
yellow or orange) on the front surface of the
incisors. How does a small animal keep its teeth
sharp when eating highly abrasive foods?
60
(No Transcript)
61
Musk deer
62
(No Transcript)