Energy Resources - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 55
Title:
Energy Resources
Description:
Energy Resources By Vaibhavi Apte Geothermal Energy Energy by Tapping the Earth s Internal Heat Geothermal heat pumps Hydrothermal reservoirs Steam Hot water Deep ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:567
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Energy Resources
1
Energy Resources
- By
- Vaibhavi Apte
2
Energy Resources A natural resource that can
be converted by humans into forms of energy in
order to do useful work!
3
Evaluating Energy Resources
- About three-quarters of the worlds commercial
energy comes from nonrenewable fossil fuels, and
the rest comes from nonrenewable nuclear fuel and
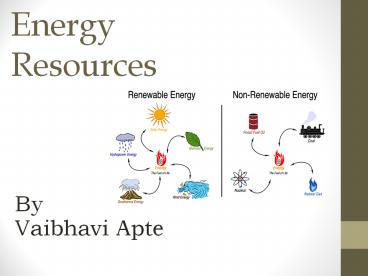
renewable sources. - Energy resources are classified as
- NONRENEWABLE
- RENEWABLE
4
Non Renewable Energy
- These are energy resources that cannot be
replaced after they have been used or need
thousands to millions of years to be replaced.
5
Coal, Petroleum, And Natural Gas
- Coal, petroleum, and natural gas are considered
nonrenewable because they can not be replenished
in a short period of time. These are called
fossil fuels.
6
How Are Oil And Gas Made ???
7
How Is Coal Made ???
8
Coal facts.
- Was formed 255-350 million years ago
- 4 types of coal Anthracite ,Bituminous ,Lignite
,Peat - India has high coal deposits in Bokaro, Jharia,
Raniganj, Singrauli, Godavari Valley, Chandrapur.
- Coal Is in abundance But Dirty Fuel
- Used in electricity production
- Worlds most abundant fossil fuel
- U.S. reserves should last about 250 years
- Sulfur and particulate pollutants ,Mercury and
radioactive pollutants
9
- Heat produced by burning pulverized coal in a
furnace boils water to produce steam that spins a
turbine to produce electricity. - The steam is cooled, condensed, and returned to
the boiler for reuse. - Waste heat can be transferred to the atmosphere
or to a nearby source of water. - The largest coal-burning power plant in the
United States, located in Indiana, burns three
100-car trainloads of coal per day
10
Petroleum or Crude Oil
- Also called light oil
- Trapped underground or under ocean with natural
gas - Crude oil is the single largest source of
commercial energy in world and U.S. - Proven oil reserves
- Can be extracted profitably at todays prices
with modern technology - Its a mixture of
- hydrocarbons needs
- to be purified and
- refined before use
11
(No Transcript)
12
Natural gas
- Natural Gas Is a Useful and Clean-burning Fossil
Fuel - Compressed natural gas
- Synthetic natural gas
- Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG)
- Less carbon dioxide emitted per unit of energy
than with crude oil, tar sand, shale oil - World supply of conventional natural gas 62-125
years
13
Nuclear Energy
- Nuclear fission uses uranium to create energy.
- Nuclear energy is a nonrenewable resource because
once the uranium is used, it is gone!
14
NUCLEAR FISSION AND NUCLEAR FUSION
15
Facts
- Tremendous potential
- Disaster if leakage happens
- Energy potential high but not highly exploited in
India - 4 plants currently Capacity 2005 MW
- Tarapur
- Kota
- Kalpakkam
- Narora
16
Renewable Energy
- Renewable resources are natural resources that
can be replenished in a short period of time. - Solar
- Geothermal
- Wind
- Biomass
- Hydro-power
- Tidal energy
17
Solar Energy
- Sustainability mostly depends on solar
energyDirect form from the sun - Nuclear fusion reactions occur inside the sun and
release tremendous energy - 1.4 kilojoules second/m2
18
Solar devices
- Solar heat collectors
- Solar cells
- Solar cooker
- Solar water heater
- Solar furnace and Solar power plants
19
Using Solar Energy to Heat Buildings and Water
- Passive solar heating system
- Active solar heating system
20
(No Transcript)
21
(No Transcript)
22
(No Transcript)
23
Photovoltaic (PV) or solar cells can provide
electricity for a house or building using solar
cell roof shingles, as shown in this house in
Richmond Surrey, England. Solar-cell roof systems
that look like a metal roof are also available.
In addition, new thin-film solar cells can be
applied to windows and outside walls.
24
(No Transcript)
25
(No Transcript)
26
Wind Energy
- Freely available source of energy
- Minimum wind speed required 15 km/hr
- Worlds second fastest-growing source of energy
- Indias Potential is
- 20,000 MW
- Vast potential
- Land
- Offshore
27
(No Transcript)
28
(No Transcript)
29
(No Transcript)
30
Hydro Power Producing Electricity from Flowing
Water
31
(No Transcript)
32
Facts..
- Hydropower
- Leading renewable energy source
- Much unused capacity
- Dams and reservoirs
- Turbines generate electricity
- Eventually fill with silt
- Micro-hydro generators
- Potential of India 4 X 10 11KW-hours
33
(No Transcript)
34
Geothermal Energy
- Energy by Tapping the Earths Internal Heat
- Geothermal heat pumps
- Hydrothermal reservoirs
- Steam
- Hot water
- Deep geothermal energy
- New Zealand, U.S.A have successful working plants
35
(No Transcript)
36
(No Transcript)
37
Tidal Energy
- Tidal power, also called tidal energy, is a form
of hydropower that converts the energy of tides
into useful forms of power - mainly electricity. - Although not yet widely used, tidal power has
potential for future electricity generation. - Tidal stream generators (or TSGs) make use of the
kinetic energy of moving water to power turbines,
in a similar way to wind turbines that use wind
to power turbines.
38
Tidal barrages make use of the potential energy
in the difference in height (or head) between
high and low tides. Barrages are essentially dams
across the full width of a tidal estuary.
39
Ocean Thermal Energy
40
Biomass Energy
- Biomass
- Wood
- Agricultural waste
- Plantations
- Charcoal
- Animal manure
- Common in developing countries
- Carbon dioxide increase in atmosphere
41
Converting Plant Matter to Liquid Biofuel
- Biofuels
- Ethanol and biodiesel
- Crops can be grown in most countries
- Sustainability
42
Liquid fuel from Corn
43
(No Transcript)
44
Biogas
- Mixture of Methane, Carbon dioxide, hydrogen etc
- Produced by anaerobic degradation of animal waste
in presence of water - Non polluting, clean and low cost fuel
- Two types of biogas plants
- Floating dome type
- Fixed dome type
45
Process
46
Types of Biogas Plant
47
Installed float type
48
Hydrogen as Fuel
- Hydrogen is environmentally friendly
- Thermal dissociation, photolysis or electrolysis
of water - Problems
- Net energy yield is negative
- Fuel is expensive
- Air pollution depends on production method
- Storage
49
(No Transcript)
50
(No Transcript)
51
- A Fact
Recycling just one aluminum can saves enough
energy to run a television set for four hours!
52
REDUCE , REUSE, RECYCLE
53
Transition to a More Sustainable Energy Future?
54
Solutions
- Decentralized power system in which electricity
is produced by a large number of dispersed,
small-scale micropower systems. - Some would produce power on site others would
feed the power they produce into a modern
electrical distribution system. - Over the next few decades, many energy and
financial analysts expect a shift to this type of
power system, largely based on locally available
renewable energy resources.
55
THANK YOU