CELL DIVISION - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
CELL DIVISION
Description:
Title: No Slide Title Author: Hillel Foundation Last modified by: Maggie Created Date: 7/28/2002 11:14:58 PM Document presentation format: On-screen Show – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:147
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: CELL DIVISION
1
CELL DIVISION
2
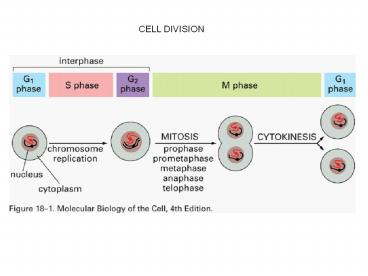
Stages of mitosis (animal cell) prophase -
chromosomes condense (replicated in S phase) -
centrosomes separate (duplicated in S
phase) prometaphase - nuclear envelope breaks
down - MTs contact chromosomes, spindle forms
3
metaphase - chromosomes align at spindle
equator (metaphase plate) anaphase - sister
chromatids separate - chromosomes move to poles -
poles move apart telophase - nuclear envelope
reforms - chromosomes decondense - interphase
array of MTs reforms cytokinesis - contractile
ring pinches cell in two
4
Centrosome cycle (animal cell) - centrosome
(centriole) duplication begins at the start of S
phase - remains as one complex until M phase In
early embryonic cells, the centrosome cycle can
operate without a nucleus - egg cell extracts
5
Mediators of mitotic chromosome structure -
cohesins deposited along the length of sister
chromatids as the DNA is replicated - hold
sisters together - condensins coil DNA - mediate
chromosome condensation
6
Structure of a spindle 3 classes of MTs
(polar MTs)
How does a spindle form, and how does it work to
separate chromosomes?
7
Prophase changes in MT dynamics - more MTs
nucleated from centrosome - shorter, more dynamic
MTs
Quantifying MT dynamics - inject fluorescent
tubulin - bleach with laser - measure recovery
(newly formed MTs) - t1/2 time to 50 recovery
8
MT dynamics regulated by MAPs vs. catastrophins
centrosomes incubated in Xenopus egg extracts
higher catastrophe rates shorter MTs
9
Spindle formation in vitro mitotic extracts
DNA centrosomes - abnormal spindles form when
ratio of MAPscatastrophins is perturbed
no MAP (MTs are too short)
10
Centrosome separation in prophase is driven by
plus-end motors (KLPs) - balanced by minus-end
motors
11
(No Transcript)
12
Yeast mutants identification and
characterization of spindle motors
(-) ()
13
Prometaphase kinetochores capture MTs (mechanism
of attachment??)
14
Forces that drive chromosomes to metaphase
plate - kinetochores pull chromosomes to poles
(-)end directed motors? - astral ejection force
()end directed motors on chromosome arms
15
Metaphase - chromosomes continue to oscillate
at metaphase plate (vertebrate cells) - MTs
undergo poleward flux (function?)
16
- poleward flux of metaphase MTs can be measured
with caged fluorescein
17
Dynamics of individual MTs can be measured with
fluorescence speckle microscopy - poleward flux
of metaphase MTs occurs in kinetochore and
overlap MTs but not in astral MTs
18
Anaphase A - kinetochore MTs shorten -
chromosomes move to poles Fluorescent tubulin
injections show locations of MT growth,
depolymerization
19
Two models for kinetochore movement along MTs
20
Anaphase B - poles separate - overlap MTs
lengthen
21
Model for motor protein activity in anaphase B
22
Bipolar spindles can assemble without
centrosomes or chromosomes
23
(No Transcript)
24
Cytokinesis (animal cell)
25
What determines the position of the cleavage
furrow? - signal from asters to cortex - signal
from central spindle - chosen before mitosis
(position of spindle from previous mitosis)
26
Contractile ring of actin and myosin red
actin, green myosin II
27
Cytokinesis in plants
28
(No Transcript)