WELCOME BACK! In Question: Copy - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 47
Title: WELCOME BACK! In Question: Copy
1
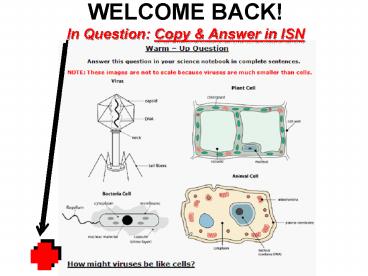
WELCOME BACK!In Question Copy Answer in ISN
2
Lets Review handout from last class Venn
Diagram (Glue it in ISN)
3
Use this Class Set to complete the Virus Notes
Page for..TEKS 4C
- 4C Compare the structure of viruses to cells,
describe viral reproduction, and describe the
role of viruses in causing diseases such as human
immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and influenza
4
Welcome to the Wonderful World of
Viruses!
5
What type of cell is this?
6
What type of cell is this?
7
What type of cell is this?
8
What type of cell is this?
9
The Common Cold What causes it?
A common cold is an illness caused by a virus
infection located in the nose.
10
What is a virus?
- Viruses are particles of nucleic acid, protein,
and sometimes lipids. They can only reproduce by
infecting living cells.
11
What does a virus look like?
- They differ widely in size and structure.
- Size
- 1/100 of smallest bacteria
- - can only be seen with a powerful
- electron microscope
- Structure
- inner core of DNA or RNA
- A capsid or protein coat, surrounds the virus
12
(No Transcript)
13
(No Transcript)
14
Virus Structure
Human Influenza
Chicken Pox
DNA
Protein coat or head
Tail sheath
Tail Fibers
Rabies Virus
HIV
15
Soare viruses alive?
- Viruses have one thing in common. They ALL
reproduce by - Entering living cells, then use the cells
machinery to produce more viruses. - So.does it make them biotic or abiotic
organisms?
16
- Viruses are not alive!
- Not made of cells
- Cant grow
- Do not metabolize nutrients
- Cant reproduce without a host
- Antibiotics cant kill them because theyre not
alive to begin with
17
Origin? Ancient or Recent?
- Yet they are like living things because after
infecting living cells, they can reproduce and
even evolve. - Possibly escaped nucleic acid that developed
parasitic relationship with host cell - Viruses more closely related to host cell than
other viruses
18
Why We NEED Viruses
- VACCINATIONS
- A vaccine is an immunity-producing substance
formed from weakened, dead, or parts of viruses. - The Flu Shot is a weakened version of the flu
virus. When injected, the vaccine triggers an
immune response inside of your body so you will
be prepared for the real thing.
19
Why We NEED Viruses
- POPULATION CONTROL
- Introducing viruses specific to one kind of
organism is a natural mechanism for population
control. - Rabbits are not native to Australia and in the
1940s European rabbits were introduced to the
Australian environment. - These rabbits caused significant amounts of
damage to farmland and devastated the
agricultural economy
20
Why We NEED Viruses
- POPULATION CONTROL CONTINUED
- Since the rabbits had no natural predators in
Australia, scientists needed another way to
control the population boom without introducing
another foreign organism. - In 1950, biologists from Europe imported the
Myxoma virus which was lethal in 99.8 of the
infected rabbits. - The agricultural economy bounced back and the
rabbit population has leveled out.
21
How Viruses are HARMFUL
- ILLNESS
- There are many illnesses caused by viruses. Some
examples are - HIV and AIDS
- Common Cold
- Flu
- Herpes
- Chicken Pox
- Viral illnesses are often highly contagious and
they can be spread easily through sexual contact,
inhalation, or physical contact
22
How Viruses are HARMFUL
- ILLNESSES CONTINUED
- Can a viral infection (cold, flu) be cured by
taking antibiotics used to combat bacterial
infections? - Since a virus is not alive, antibiotics used to
fight living bacteria will not be effective on
viral illnesses - Should you still take an antibiotic just in
case or to help relieve your symptoms? - This will lead to antibiotic resistance of your
immune system, causing the antibiotic to lose
effectiveness and you will to get sicker in the
future
23
Diseases caused by Viruses
Common Cold
- ___________________
- 200 kinds of Viruses
Symptoms include nasal discharge, obstruction of
nasal breathing, swelling of the sinus membranes,
sneezing, sore throat, cough, and headache.
24
Polio
2. ________________
- Poliomyelitis is a crippling disease of spinal
nerve cells caused by poliovirus infection. - The disease can strike non-immune persons of any
age but affects mainly children under the age
of three, and causes paralysis in one case of
every 200 to 1000 infections. - Preventable by vaccination.
25
Tobacco Mosaic
3. ______________________
Symptoms induced can include mosaic, mottling,
necrosis, stunting, leaf curling, and yellowing
of plant tissues.
26
Tulip Mosaic
- Causes streaks on white in a normally red tulip.
27
AIDS/HIV
___________
STD
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, is caused by
the human immunodeficiency virus, or HIV. HIV
destroys the body's ability to fight infections
by attacking cells of the immune system.
28
Transmission a. Sexual Contact b.
Needles/Syringes c. Mother to Infant
- blood
- semen
- vaginal fluid
- breast milk
- other body fluids containing blood
29
Rabies
______________
The vast majority of cases reported to the
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
each year occur in wild animals like raccoons,
skunks, bats, and foxes. Infects the central
nervous system, causing encephalopathy and
ultimately death.
30
Chicken pox
6. ______________ (Herpes simplex )
31
Shingles
7. _____________
An acute infection caused by a ractivation of the
varicella zoster virus, which also causes chicken
pox.
It usually occurs during adulthood after exposure
to chicken pox in childhood. The chicken pox
virus remains dormant in the body.
32
Smallpox
11. _____________
Small pox is a disease caused by poxvirus
variola. Includes a three day prodromal illness
characterized by fever, headache, backache, and
vomiting.
33
Measles
8. _____________
Most infected children will have a rash, high
fever, cough, runny nose, and watery eyes. For
every 1,000 children who get it, 1 or 2 will die
from it Spreads so easily that any child who is
not immunized will probably get it, either now or
later in life.
34
Warts
9. ___________
Non-cancerous skin growths caused by a viral
infection in the top layer of the skin. Viruses
that cause them are called human papillomavirus
(HPV).
STD
35
STD
Herpes
10. _______________
HSV-2 usually produces only mild symptoms or
signs or no symptoms at all. However, HSV-2 can
cause recurrent painful genital sores in many
adults, and HSV-2 infection can be severe in
people with suppressed immune systems.
Regardless of severity of symptoms, genital
herpes frequently causes psychological distress
in people who know they are infected.
36
Ebola
12. _____________
37
The Common Cold What causes it?
A common cold is an illness caused by a virus
infection located in the nose.
38
Viral Reproduction Handout
39
Retroviruses
- Virus that contains RNA, is lysogenic, and
therefore mutates frequently so that vaccination
is impossible.
HIV
40
How viruses cause disease
Viruses disrupt the bodys normal equilibrium by
causing cells to lyse or break apart.
41
Infections
- Viruses Infect Plants, Animals, Bacteria
- Bacterial Virus- Bacteriophage
- 2 types Lytic Lysogenic (p.481)
42
Viral Reproduction Handout
43
(No Transcript)
44
PROJECT
- Viral Disease Foldable
- DUE TODAY!!!
45
GIZMO VIRAL LYTIC CYCLE (6th pd only)
- Get a Computer
- Log-in to www.explorelearning.com
- Click Launch GIZMO
- Read each question on the handout and complete
the GIZMO as you answer the questions. - Turn-In your work
- DUE IN 20 MIN. !!!
46
OUT Exit Ticket
- What are bacteriophages?
- What are retroviruses?
47
Understanding Viruses Video
- PART 1 (FRONT SIDE)
- PART 2 (BACK SIDE)
- Answer the Pre-Viewing questions on your own as
you discuss them with your table.
- Answer the Post-Viewing questions while watching
the video with the help of a video buddy as
needed.