CSCI 6900/4900 Special Topics in Computer Science - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
CSCI 6900/4900 Special Topics in Computer Science
Description:
CSCI 6900/4900 Special Topics in Computer Science Automata and Formal Grammars for Bioinformatics Bioinformatics problems sequence comparison pattern/structure search – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:117
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: CSCI 6900/4900 Special Topics in Computer Science
1
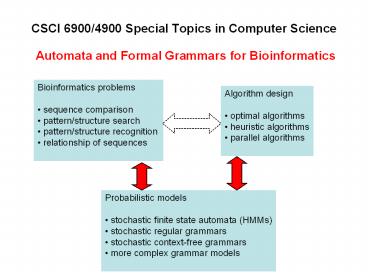
CSCI 6900/4900 Special Topics in Computer Science
- Automata and Formal Grammars for Bioinformatics
- Bioinformatics problems
- sequence comparison
- pattern/structure search
- pattern/structure recognition
- relationship of sequences
- Algorithm design
- optimal algorithms
- heuristic algorithms
- parallel algorithms
- Probabilistic models
- stochastic finite state automata (HMMs)
- stochastic regular grammars
- stochastic context-free grammars
- more complex grammar models
2
Probabilistic modeling and algorithms
- M modeling a family of sequences (e.g. RNA) to
capture certain properties - Q1, Q2, .
- Each sequence x possesses a property Qk(x) with
probability Pk(x) - (2) A probability distribution for each sequence
x over the properties, - i.e., ?k Pk(x) 1 for each given x
- (3) The most likely property Q(x) is one with
the highest probability, - i.e., Q(x) arg maxk Pk(x)
- (4) Algorithms are designed to find the most
likely property for given sequences. But how?
D (sample, training data)
assigning probs
Computational linguistic systems can describe
desired properties of bio sequences
Modeling mechanism
3
Outline for the course
- Part 0 molecular biology basics and review of
probability theory - Part 1 pairwise alignment, HMMs, profile-HMMs,
gene finding, and multiple alignment (chapters
1-6) - potential research projects efficient HMM
algorithms, gene finding - Part 2 RNA stem-loops, SCFG, secondary structure
prediction, structural homology search (chapters
9-10) - potential research projects efficient SCFG
algorithms, pseudoknot prediction, protein
secondary structure prediction - Part 3 phylogeny reconstruction, probabilistic
approaches (chapters 7-8) - potential research projects grammar
modeling of evolution
4
The ways this course is to be conducted
- To learn new concepts and techniques
- Lectures (by the instructor and students)
- To apply learned knowledge to research
- Research discussions (lead by students and
the instructor) - To demonstrate learning effectiveness
- Presentations of research results (by
students)
5
The central dogma of molecular biology
6
Building blocks of DNA
- Nucleotides
- Purines
- Adenine,
- Guanine
- Pyrimidines
- Cytosine,
- Thymine
7
Double helix of DNA
8
DNA replication
9
- Genetic code
10
Mutations
(1) synonymous
(2) Missense
(3) nonsense
(4) frame-shift
11
RNA synthesis
12
RNA synthesis (cont)
13
RNA can fold to itself
14
Protein synthesis
15
Biological information flow
Introns Exons
Gene sequence
Protein sequence
Protein structure
Genome AGACGCTGGTATCGCATTAACTAACGGGTTACTCGGATATTA
CCTTACTATAGGGCGCTATCGCGCGTTAATCTGGTATC
Regulatory DNA sequence
Sequence family
Structure family
Protein-DNA interactions
Protein-protein interactions
Gene regulation
Gene expression
Protein function
Protein abundance
Cellular role
16
What bioinformatics is NOT
- Not just using a computer to speed up biology
- Not just applying computer algorithms to biology
- Not just the accountant of genomic data
What bioinformatics is then
- The creative use of computers to define and solve
central biological puzzles - The computer becomes an hypothesis machine,
making predictions to be tested at the bench.