Date: 9/20/13 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
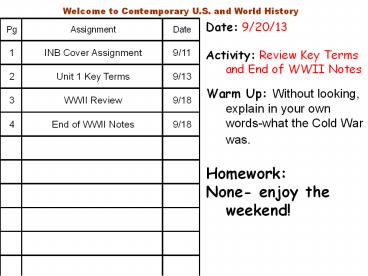
Date: 9/20/13
Description:
Welcome to Contemporary U.S. and World History Date: 9/20/13 Activity: Review Key Terms and End of WWII Notes Warm Up: Without looking, explain in your own words-what ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:98
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Date: 9/20/13
1
Welcome to Contemporary U.S. and World History
- Date 9/20/13
- Activity Review Key Terms and End of WWII Notes
- Warm Up Without looking, explain in your own
words-what the Cold War was. - Homework
- None- enjoy the weekend!
Pg Assignment Date
1 INB Cover Assignment 9/11
2 Unit 1 Key Terms 9/13
3 WWII Review 9/18
4 End of WWII Notes 9/18
2
World War II Review
- European Entry into the war
- -Germany invaded Poland
- American Entry into the war
- -Pearl Harbor
Direct Causes
Indirect Causes
- Nationalism
- Treaty of Versailles too harsh and Hitler
violated it - Policy of Appeasement failed
- League of Nations failed
- Imperialism (expansion) and militarism
(aggression) of Axis powers - Democratic nations were passive
3
World War II Review
- Britain
- France
- Soviet Union
- USA
- (Plus many other smaller nations)
Allies
Axis
- Germany
- Japan
- Italy
- (Plus Hungary, Bulgaria and Romania)
4
World War II Review
Leaders
- Allies
- - United Kingdom
- Winston Churchill
- France
- Charles deGaulle
- -Soviet Union
- Joseph Stalin
- -USA
- Franklin D. Roosevelt,
- Harry S. Truman
Axis - Germany Adolf Hitler - Italy Benito
Mussolini - Japan Hideki Tojo
5
World War II Review
New Technology
- Atomic Bomb
- Blitzkrieg Warfare
- Radar and sonar, as well as rubber coating to
protect against sonar - Jet engines
- Bomb sight
- Computers and code breaking
- Aircraft carriers
- Amphibious landing vehicles (D-Day)
- Canned food
- Gas chambers
- Jeep
- Radio-direction finders
6
World War II Review
Key Battles
- Battle of Britain
- Pearl Harbor
- Battle of Coral Sea
- Battle of Midway
- Invasion of Sicily
- Battle of Stalingrad
- El Alemen
- Leningrad
- Normandy
- Battle of the Bulge
- Iwo Jima
- Okinawa
- Nagasaki/Hiroshima
7
World War II Review
Holocaust
- 11 million people killed
- 6 million of those people were Jewish
- 2/3 of the Jews in Europe were exterminated
- Nuremberg laws, Kristallnacht and Ghettos were
just the beginning - Concentration and Extermination camps
- Gas chambers, among many other unimaginable
atrocities against human beings
8
World War II Review
Outcomes
- Allies defeated Axis powers
- U.S. Emerges as a Superpower
- Division of Communist/Capitalist Nations led to
the Cold War
9
Unit 1 Key Terms
- Cold War
- The state of hostility, without direct military
conflict, that developed between the U.S. and the
U.S.S.R. after WWII.
10
Unit 1 Key Terms
- Communism
- An economic and political system based on
one-party government and state ownership of
property and production. Goal of communism is to
share the wealth
11
Unit 1 Key Terms
- NATO
- North Atlantic Treaty Organization a defensive
military alliance formed in 1949 by ten (10)
Western European countries, the U.S. and Canada.
- Warsaw Pact
- A military alliance formed in 1955 by the Soviet
Union and its Eastern European satellites.
12
Unit 1 Key Terms
- United Nations
- An international peacekeeping organization to
which most nations in the world belong, founded
in 1945 to promote world peace, security, and
economic development .
13
Unit 1 Key Terms
- Containment
- The blocking of another nations attempts to
spread its influence especially in the efforts
of the U.S. to block the spread of Soviet
influence during the late 1940s and early 1950s.
14
Unit 1 Key Terms
- Totalitarian
- Characteristic of a political system in which the
government exercises complete control over its
citizens lives.
15
Unit 1 Key Terms
- Reparations
- The compensation paid by a defeated nation for
the damage or injury it inflicted during a war.
16
Unit 1 Key Terms
- Subjugation
- the act, fact, or process of subjugating, or
bringing under control enslavement
17
Unit 1 Key Terms
- Self Determination
- the determining by the people of the form their
government shall have, without reference to the
wishes of any other nation, especially by people
of a territory or former colony
18
Unit 1 Key Terms
- Truman Doctrine
- A U.S. policy, announced by President Harry S.
Truman in 1947, of providing economic and
military aid to free nations threatened by
internal or external opponents.
19
Unit 1 Key Terms
- Marshall Plan
- The relief package offered to European Nations to
help recovery after WWII to help they stay
democratic.
20
The Wars Aftermath
Main Idea
Important Details
Questions? Important Key Terms to remember?
The victorious Allies held crime trials to punish
Axis leaders and occupied Axis countries to bring
democracy and ensure peace in the world.
- Allies learned the full extent of the inhumanity
of the Holocaust at the end of the war and put
Nazis on trial for their war crimes in the
Nuremberg Trials. - Most important purpose of the trials was to
show that political and military leaders COULD BE
HELD ACCOUNTABLE for wartime actions AND
discredited totalitarian ideologies. - Japanese atrocities also took place throughout
Asia. - In order to ensure tolerance and peace, the
Allies wanted to strengthen democracy abroad. - Allies occupied Germany and Japan and created
democratic constitutions
Nuremberg War Crime Trials Japanese occupation
21
Establishing the United Nations
Main Idea
Important Details
Questions? Important Key Terms to remember?
The UN was established to replace the League of
Nations in the role of peacekeeper, but went
beyond by taking on many world problems such as
hunger and disease
- The UN was drafted in San Francisco
- Each member nation has a vote in the General
Assembly - The Security Council is made up of 5 permanent
members US, Britain, France, China and Soviet
Union (Russia today) - Any member of the Security council can veto a
vote by the Assembly, and therefore differences
between the US and USSR often rendered the UN
ineffective.
General Assembly Security Council
22
The Alliance Breaks Apart
Main Idea
Important Details
Questions? Important Key Terms to remember?
US and USSR rose as the two new superpowers after
WWII, but their conflicting ideologies and mutual
distrust caused a tense conflict which came to be
known as the Cold War.
- Cold War was a state of tension and hostility
between the US (and its allies) and the USSR (and
its allies), without armed conflict between the
major rivals - Stalins goal for Eastern Europe was to spread
communism and create a buffer zone - Although Stalin promised free elections in
Eastern Europe, by 1948 he broke his promise and
communist nations were in place throughout
Eastern Europe.
Differences between USSR and US Meetings
(Potsdam, Yalta) Cold War
23
New Conflicts Develop
Main Idea
Important Details
As Stalin was attempting to continue his
aggressiveness in Europe, the US was attempting
to counter him by building stronger democracies
so weakened countries wouldnt feel the need to
give in to communism.
- Truman Doctrine Military and economic aid sent
to Greece and Turkey to withstand communist
threat - -rooted in the idea of containment (which would
limit communism to areas already under communist
control) and guided our foreign policy for years - Marshall Plan massive aid package offered to
European nations who were war torn- offered in an
attempt to strengthen democratic governments (so
they wouldnt give in to communism) - Germany was divided into 4 parts (US, Britain,
France and USSR) - -US, Britain and France united their parts as
Western Germany (democratic) - -USSR was communist
- Berlin (Germany capitol) was located inside of
USSR portion of Eastern Germany, but was also
split in 4 sections. - -Berlin Airlift- USSR blockaded entry into West
Berlin and Allies airlifted food for over a year
to help them survive - NATO alliance of democratic nations
- Warsaw Pact alliance of Eastern European,
Soviet dominated communist nations
24
Welcome to Contemporary U.S. and World History
- Date 9/23/13
- Activity Results of WWII
- Warm Up What policy did the US adopt after WWII
and what was the purpose of this policy? - Homework
- Finish the back of page 5 (read and answer
questions) for tomorrow
Pg Assignment Date
1 INB Cover Assignment 9/11
2 Unit 1 Key Terms 9/13
3 WWII Review 9/18
4 End of WWII Notes 9/18
5 Results of WWII ppt Notes 9/23
25
Class Notes Results of WWII
- DISCUSS PREVIEW
- HOW MIGHT A COUNTRYS EXPERIENCES
DURING THE WAR AFFECT ITS VIEWS FOR
THE POST-WAR WORLD?
26
WARTIME CONFERENCES
- THE ALLIES MADE PLANS FOR THE END OF THE WAR IN A
SERIES OF WARTIME CONFERENCES - CAIRO (NOV. 1943)
- TEHRAN (NOV. DEC. 1943)
- YALTA (FEB. 1945)
- POTSDAM (JULY-AUG. 1945)
27
THE BIG THREE
- ROOSEVELT (LATER TRUMAN) USA
- CHURCHILL BRITAIN
- STALIN USSR
28
Different Goals
FDR
Stalin
Churchill
Wanted help to beat Japan and wanted to establish
the UN and wanted help in Japan
unified Germany and free elections throughout
Europe
Harsh treatment and division of Germany.
29
NEGOTIATIONS AT YALTA
30
Yalta Conference
- What was actually agreed to at Yalta
- Stalin agreed to help end the war in Japan
- Stalin agreed to help establish the UN
- Churchill and FDR agreed to divide Germany into
four zones temporarily, as long as Stalin kept
free elections throughout Europe.
31
OTHER MAJOR DECISIONS
- AXIS LEADERS TO BE TRIED AS WAR CRIMINALS
- WAGING AGGRESSIVE WAR
- TREATMENT OF POWs
- BEHAVIOR TOWARD CIVILIANS
- NUREMBERG TRIALS HELD IN GERMANY
- TOKYO TRIALS IN JAPAN
- THOUSANDS CONVICTED SOME EXECUTED
32
SET PRECEDENT FOR TREATMENT OF WAR CRIMINALS
- MOST FORMER NAZIS DEFENDED THEIR ACTIONS BY
CLAIMING THEY WERE JUST FOLLOWING ORDERS - 12 OF THE 24 WERE SENTENCED TO DEATH, MOST OF THE
REMAINING WENT TO PRISON - IN LATER YEARS OVER 200 MORE NAZIS WERE TRIED FOR
THEIR RESPECTIVE ROLES IN THE HOLOCAUST - ESTABLISHED THE IMPORTANCE OF INDIVIDUAL
RESPONSIBILITY IN INTERNATIONAL LAW - INDIVIDUALS ARE RESPONSIBLE FOR THEIR OWN
ACTIONS, EVEN IN TIMES OF WAR
33
OTHER MAJOR DECISIONS (CONTD)
- NOT ONLY WOULD GERMANY BE DIVIDED INTO 4
OCCUPATION ZONES - USA
- BRITAIN
- FRANCE
- USSR
- . . . BUT BERLIN (WITHIN SOVIET ZONE) WOULD BE
DIVIDED INTO 4 ZONES AS WELL
34
OTHER MAJOR DECISIONS (CONTD)
- OCCUPATION OF JAPAN BY USA
- LASTED 7 YEARS
- EMPHASIZED LAND REFORM DEMOCRACY
GEN. MACARTHUR EMPEROR HIROHITO
35
REBUILDING JAPAN
- TOJO AND SIX OTHER JAPANESE LEADERS WERE TRIED
FOR CRIMES AGAINST HUMANITY AND EXECUTED - MACARTHUR INTRODUCED FREE-MARKET CAPITALISM,
WHICH LED TO A REMARKABLE ECONOMIC RECOVERY - THE MACARTHUR CONSTITUTION ALSO TRANSFORMED
JAPANS GOVERNMENT INTO A MODERN DEMOCRACY,
COMPLETE WITH BASIC FREEDOMS AND WOMENS SUFFRAGE - THE EMPEROR WAS KEPT IN POWER, BUT ONLY AS A
FIGURE-HEAD