Memory Hierarchy - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 22
Title:
Memory Hierarchy
Description:
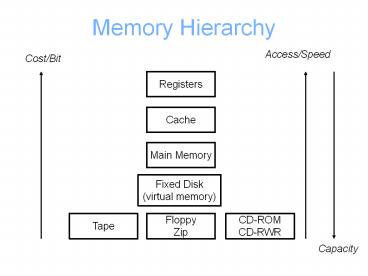
Memory Hierarchy Access/Speed Cost/Bit Registers Cache Main Memory Fixed Disk (virtual memory) Tape Floppy Zip CD-ROM CD-RWR Capacity Connection of memory to the ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:146
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Memory Hierarchy
1
Memory Hierarchy
Access/Speed
Cost/Bit
Registers
Cache
Main Memory
Fixed Disk (virtual memory)
Tape
Floppy Zip
CD-ROM CD-RWR
Capacity
2
Connection of memory to the Processor
Memory Up to 2k addressable locations Word
length n bits
K-bit address bus
MAR
N-bit data bus
MDR
Control lines R/W, IRQ,IE, etc
3
Control Connections
Addresslog2(K)-10
DataN-10
MEM
CS
OE
WE
Chip Select must be asserted before Memory will
respond to read or write operation. If negated,
data bus is high impedance. May have more than
one if so, all must be asserted. OE Asserted
for read operation, Memory will drive data lines.
WE Asserted for a write operation (Memory
inputs data from data pins, processor writes to
memory). There may only be one control line (R/W)
4
Main Memory Characteristics
- Semiconductor Chips
- Housed in DIP Packages
- DIP Packages Mounted on SIMM, DIMM Circuit
Boards - Characteristics
- Access Times (read,write,erase)
- Faster is Better (varies from minutes to a few
ns) - Volatility
- Ability to Retain Data After Power is Removed
- Power Consumption
- Less is Better (mW to nW typical)
- Density
- Larger is Better (bits/sq. micron or
transistors/bit) - Cost
- Less is Better
5
Timing Characteristics
- Memory Access Time
- The time from a valid address being placed on the
address bus until valid data appears on the data
bus. - Memory Write Time
- The time from when a valid address is placed on
the address bus until the value on the data bus
is captured by memory. - Faster is Better!!!!
6
Address/Data Connections
K x N
DataN-10
Addresslog2(K)-10
MEM
K locations, N bits per location Address bus has
log2(K) address lines, data bus has N data
lines. Address pins labeled An-1 A 0 where A0
is least significant Data pins labeled Dn-1 D0
where D0 is least significant
7
Memory Chips
- Most devices are 8-bits wide (Byte-addressable)
some are 16-bits, others 1 bit wide. - Listing refer to memory locations x bits/location
- 1Kx8, 16Kx8
- Often classified by total bit capacity
- 1Kx8 (8K device)
- 64Kx4 (256K device)
8
Pentium Memory System 4G capacity 64 bit
data bus, 32 bit Address Bus
Can see use of CS, W and OE signals.
9
Semiconductor Memory Device Architecture
Storage Cell Array
2?4 Decoder
A1
A0
Buffers
D3
D2
D1
D0
D4
10
DECODER REVIEW
- n2n Device
- n encoded inputs
- 2n decoded outputs
2?4 Decoder
D3
A1
D2
D1
A0
D0
A1
A0
D3
D2
D1
D0
- 0 0
- 0 1
- 0
- 1 1
0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0
0 0
11
Buffers
- Single-Ended Amplifier
- Gain Av
- 1 input voltage, 1 output voltage referenced to
common ground
Av
Vin
Vout Av Vin
- Differential Amplifier
- Gain Av
- 2 input voltages, 1 output voltage referenced to
common ground
V1
Av
Vout Av (V1-V2)
V2
-
12
ROM
- ROM Read Only Memory - a type of memory that
cannot be written, can only be read. Contents
determined a manufacture time. - ROM is non-volatile contents remain even when
power is off. - PROM Programmable ROM a type of memory whose
contents can be programmed by the user - OTP One Time Programmable, a PROM is OTP if
contents can be programmed only once. - EEPROM Electrically Erasable PROM contents
can be erased electrically by the user. - Memory is not alterable under normal operation.
13
4x5 PROM Organization
1-Bit Storage Cell
14
Basic Types of RAM
- RAM Random Access Memory
- memory that can be both read and written during
normal operation. - Contents are non-volatile, will be lost on power
off. - Static RAM
- Fast access time (used for off-processor cache)
- Does not have to be refreshed
- Dynamic RAM
- Slower access time
- Must be refreshed
- much more dense
15
Static RAM
- Fastest access time of memory types. Typically
the type of RAM used primarily in Level -2 cache. - Read, Write operations take equal amounts of
time. - Access to any random location takes same amount
of time. - Basic memory cell is a latch, takes 6 transistors
per memory bit. - SRAM static - high speed memory that does not
require a refresh operation. Much faster than
dynamic RAM, with speeds between 8-12 nsec. - PBSRAM pipeline burst - static RAM that has
been enhanced by the use of burst technology.
Multiple requests can be collected together and
sent as a single pipelined request. Bus speeds of
75MHz or higher.
16
Static RAM Cell
17
Dynamic RAM
- Must be refreshed within less than a millisecond
- Most main memory is dynamic RAM (least expensive)
- FPO Fast Page Mode Can only match speed of
30MHz data bus - EDO Extended Data Out 66MHz motherboards or
less - BEDO burst enhanced data-out
- SDRAM Synchronous dynamic operates
synchronously with system clock and data bus.
Can handle 100MHz or more - DDR Double Data Rate can transmit data on
both edges of the clock - RD Rambus operates in a serial fashion rather
than
18
SIMMS and DIMMS
- Mount Memory Device Packages on Circuit Boards
to Conserve Space - 30-Pin SIMM First Single Byte Access
- Used in Pairs Since in x86 1 Word16 bits
- 72-Pin SIMM Four Byte (32 bit) Access
- Need Pairs for Pentium Since 64 bit Data Bus
- 168-pin DIMM Eight Byte (64 bit) Access
- SIMM Single In-Line Memory Module
- DIMM Dual In-Line Memory Module
19
8M x 32 (32MB) SIMM
20
Flash Memory
- Hybrid of RAM/ROM
- Have basically replaced EEPROMs
- Memory parts can be electrically erased and
reprogrammed without removing the chip. - The entire chip (or block) must be erased at one
time. Individual byte erasure is not possible. - Silicon Hard Disks PCMCIA (Personal Computer
Memory Card International Association) credit
card size - ROM BIOS, Font cards for printers, automotive
industry diagnostic codes, modems, Ethernet cards
21
Flash Memory Examples
- Computer BIOS Memory
- Compact Flash (In Digital Cameras)
- Smart Media (Digital Cameras)
- Memory Stick (Digital Cameras)
- PCMCIA Type I and Type II (solid state disks in
laptops) - Memory Cards for video game consoles
22
Main Memory Technologies
Main Memory Technologies 1.(12) Match each of
the phrases below with one or more of the
following memory technologies.