The Human Brain - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 27
Title: The Human Brain
1
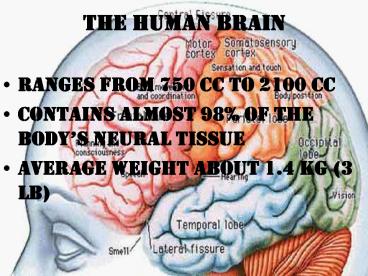
The Human Brain
- Ranges from 750 cc to 2100 cc
- Contains almost 98 of the bodys neural tissue
- Average weight about 1.4 kg (3 lb)
2
(No Transcript)
3
Can You Label the Brain?
Motor Cortex
Sensory Cortex
1
2
3
Parietal Lobe
4
Frontal Lobe
5
Occipital Lobe
Temporal Lobe
Cerebellum
6
7
Reticular Activating System
8
Spinal Cord
9
4
three layers of meninges around the brain and
spinal cord.
5
- 1. Cerebrum
- Largest part of brain
- Controls higher mental functions
- Divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres
- Surface layer of gray matter (neural cortex)
- Neural Cortex
- Also called cerebral cortex
- Folded surface increases surface area
- Elevated ridges (gyri)
- Shallow depressions (sulci)
- Deep grooves (fissures)
6
- 2. Cerebellum
- Second largest part of brain
- Coordinates repetitive body movements
- 2 hemispheres
- Covered w/ cerebellar cortex
- 3. Diencephalon
- Located under cerebrum and cerebellum
- Links cerebrum with brain stem
4. Mesencephalon Also called midbrain Processes
sight, sound, and associated reflexes Maintains
consciousness
7
The Diencephalon
- Thalamus, epithalamus, and hypothalamus
- Integrates sensory information and motor commands
- Pineal Gland in posterior epithalamus
- Secretes hormone melatonin
- Thalamus Post Office
- Filters ascending sensory information for primary
sensory cortex
Figure 145a
8
thalamus(80 of diencephalon), hypothalamus,
epithalamus.
9
Brain Structure Hindbrain
- Hindbrain (Old Brain)
- (Reptilian Brain)
- Spinal cord, lower brain stem, and cerebellum
- Medulla Oblongata
- Located where the spinal cord enters the skull
- Breathing, posture
10
Brain Structure Hindbrain
- Cerebellum
- Extends from rear of hindbrain
- Motor control
- Pons
- Bridge in hindbrain
- Sleep and arousal
11
Brain Structure Midbrain
- Midbrain
- Between midbrain forebrain
- Relays information between the brain and
eyes/ears - Reticular Activation System
- RAS
- Stereotyped patterns of behavior
- Walking, sleeping, automatic functions
Basal ganglia Starting and stopping voluntary
movements
12
Brain Structure Limbic SystemInstinctual Brain
- Limbic system
- Plays an important role in both memory and
emotion - Amygdala
- Discrimination of objects and emotion Angry Amy
- Hippocampus
- Storage of memories
- BIG Campus Library!
13
Brain Structure
- Hypothalamus
- Monitors eating, drinking, sex, temperature
- Helps direct the endocrine system through the
pituitary gland - Involved in emotion, stress, and reward
14
8 Functions of the Hypothalamus
- Provides subconscious control of skeletal muscle
- Controls autonomic function
- Coordinates activities of nervous and endocrine
systems
- Secretes hormones ADH(Antidiuretic) OT
(Oxytocin)
- Produces emotions and behavioral drives
- the feeding center (hunger)
- the thirst center (thirst)
- Coordinates voluntary and autonomic functions
- Regulates body temperature
- Controls circadian rhythms (daynight cycles)
15
Sensory Areas
- Postcentral gyrus of parietal lobe
- receives somatic sensory information (touch,
pressure, pain, vibration, taste, and
temperature) - Primary sensory cortex
- surface of postcentral gyrus
Central sulcus separates motor and sensory areas
- Visual cortex
- information from sight receptors
- Auditory cortex
- information from sound receptors
- Olfactory cortex
- information from odor receptors
- Gustatory cortex
- information from taste receptors
16
(No Transcript)
17
Neocortex..NEWBRAIN
- Occipital lobe ..SIGHT
- Back of the head
- Vision
- Temporal lobe
- Just above the ears
- Hearing,Speech
18
Neocortex
- Frontal lobe
- Behind the forehead
- Purposeful control of voluntary muscles
- Intelligence, Cognition
- Parietal lobe
- Top of the head, toward the rear
- Processing bodily sensations
- Motor Cortex
- Somatosensory Cortex
19
Right Hemisphere Radical, Religious, Random,
Roundabout ways
Left Hemisphere Language, Linear, Logical
Corpus Callosum
20
(No Transcript)
21
Brain Protection and Support
- Physical protection
- bones of the cranium
- cranial meninges
- cerebrospinal fluid
- Biochemical isolation
- bloodbrain barrier
- Cranial Meniges - 3 layers
- dura mater
- arachnoid mater
- pia mater
- Is continuous with spinal meninges
- Protects the brain from cranial trauma
22
4 Breaks in the BBB
- Portions of hypothalamus
- secrete hypothalamic hormones
- Posterior lobe of pituitary gland
- secrete hormones ADH and oxytocin
- Pineal glands
- pineal secretions
- Choroid plexus
- where special ependymal cells maintain bloodCSF
barrier
23
Brain Damage
Phineas Gage
- Plasticity
- The brains capacity to modify and reorganize
itself following damage - Collateral sprouting
- Axons of healthy neurons adjacent to damaged
cells grow new branches - Substitution of function
- Damaged regions function is taken over by
another area, or areas, of the brain
24
(No Transcript)
25
Studying the Brain
- Electroencephalograph (EEG)
- Records the electrical activity of the brain
- Computer-assisted axial tomography (CAT scan)
- 3D imaging obtained from X rays of the head
- Magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)
- Magnetic field around the body
- PET Positron Emission Tomograpy
- Color images of hot cold actions
26
The Endocrine System
- Endocrine Glands
- Release their chemical products, called
hormones, directly into the bloodstream - Pituitary gland
- Controls growth and regulates other glands
- Adrenal glands
- Play an important role in our moods, energy
level, and ability to cope with stress - Thyroid Gland Growth
- Gonads Sex Characteristics
27
Autonomic nerves (in blue)--sympathetic and
parasympathetic--regulate much of the body
without our conscious knowledge. Sympathetic
nerves branch from spinal nerves (in white) and
form a chain of ganglia that sends fibers to the
organs. Parasympathetic nerves, including the
important vagus, usually reverse the action of
sympathetic ones.