Periodic Trends - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 9
Title:
Periodic Trends
Description:
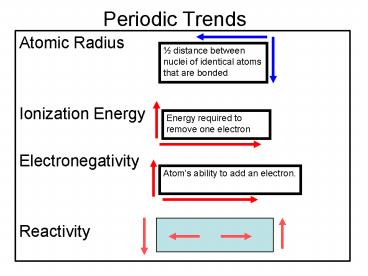
Periodic Trends Atomic Radius Ionization Energy Electronegativity Reactivity distance between nuclei of identical atoms that are bonded Energy required to remove ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:224
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Periodic Trends
1
Periodic Trends
- Atomic Radius
- Ionization Energy
- Electronegativity
- Reactivity
½ distance between nuclei of identical atoms that
are bonded
Energy required to remove one electron
Atoms ability to add an electron.
2
Atomic Radii p.140
- Period trends
- Trend to larger radii
- because proton pull is less
- on e- of same energy level
- less p and less e- bigger radii
- Group trends
- Trend to larger atoms
- because e- are added to NEXT energy level
- farther away from nucleus.
Larger
Larger
Which has largest atomic radii? Mg, Cl, Na, P,
Na
Which has largest atomic radii? Ca, Be, Ba, Sr?
Ba
Which has smallest atomic radii? Li, O, C, F ?
F
3
88888 Octet rule P. 168
- Chemical compounds tend to form so that each atom
has an octet of electron in its highest occupied
energy level. - .atoms will try to get a group of 8 electrons in
its outer orbit. - Either by gaining,
- losing,
- sharing .electrons
4
- Ion an atom or group of bonded atoms that have
a or charge. - If they have lost an electron they become
postiveNa called cation - If they have gained an electron they become
negativeCl- called anion. - Do oxidation numbers here
5
Radii of Ions
- Positive Cations lost e- .
- Lost therefore radii smaller
- Negative Anion gained e- .
- gained therefore radii larger.
- Describe the ion radii of the following as
increase or decrease. - Chlorine, nitrogen, calcium, copper, sulfur,
sodium,
6
Ionization energy p.143 energy required to
remove one electronenergy required to make it a
cation
- Period trends
- Increases across period because more protons
pull greater on e- in same energy level
- Group trends
- Increases going up group. Electrons are closer
to nucleus so protons can pull electrons
tighter. therefore takes more energy to take an
e-.
Measured in k/joules
7
- Ionization energy energy required to remove one
electron - 2nd ionization energy required to remove a 2nd
electron - 3rd ionization energy required to remove a 3rd
electron. - numbers will increase
- Turn to p.146 in book
- which would lose e- easier?
- Arrange the following in increasing ionization
energy. - Li, O, C, K, Ne, F
- K,Li,C,O,F,Ne
- Which would least likely form?
- Sr2, Al3, K2
- K2
8
Electronegativityability to gain
electronsability to become an anion
- Period
- Ability to gain electrons
- increases across period
- Group
- Ability to gain electrons
- increases going up the
- Group slightly
Which element would gain e- easier? Br, I, Cl, F
F
Which element is most electronegative? C, N, O,
Se, S
9
- Reactivity
- Which would react easier with chlorine?
- Sodium or Potassium
- How about Sodium and Magnesium?
- What would happen if you put Lithium and
Potassium in a beaker? - What would happen if you then put in Bromine?