III Manipulating DNA - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 21
Title:
III Manipulating DNA
Description:
Title: Biology Last modified by: John Furin Document presentation format: On-screen Show (4:3) Company: Laura Baselice Other titles: Arial MS P BIO3b ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:71
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: III Manipulating DNA
1
III Manipulating DNA
2
The Tools of Molecular Biology
- The Tools of Molecular Biology
- How do scientists make changes to DNA?
3
The Tools of Molecular Biology
- Scientists use different techniques to
- extract DNA from cells
- cut DNA into smaller pieces
- identify the sequence of bases in a DNA molecule
- make unlimited copies of DNA
4
The Tools of Molecular Biology
- In genetic engineering, biologists make changes
in the DNA code of a living organism.
5
The Tools of Molecular Biology
- DNA Extraction
- DNA can be extracted from most cells by a simple
chemical procedure. - The cells are opened and the DNA is separated
from the other cell parts.
6
The Tools of Molecular Biology
- Cutting DNA
- Most DNA molecules are too large to be analyzed,
so biologists cut them into smaller fragments
using restriction enzymes. - Which type of molecule is an enzyme?
7
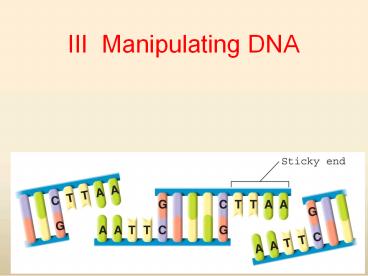
The Tools of Molecular Biology
- Each restriction enzyme cuts DNA at a specific
sequence of nucleotides.
Recognition sequences
DNA sequence
Restriction enzyme EcoR I cuts the DNA into
fragments
Sticky end
8
The Tools of Molecular Biology
- Separating DNA
- In gel electrophoresis, DNA fragments are placed
at one end of a porous gel, and an electric
voltage is applied to the gel.
9
The Tools of Molecular Biology
Power source
DNA plus restriction enzyme
Longer fragments
Shorter fragments
Mixture of DNA fragments
Gel
Gel Electrophoresis
10
The Tools of Molecular Biology
DNA plus restriction enzyme
- First, restriction enzymes cut DNA into
fragments. - The DNA fragments are poured into wells on a gel.
Mixture of DNA fragments
Gel
Gel Electrophoresis
11
The Tools of Molecular Biology
Power source
- An electric voltage is applied to the gel.
- The smaller the DNA fragment, the faster and
farther it will move across the gel.
12
The Tools of Molecular Biology
Power source
Longer fragments
Shorter fragments
Gel Electrophoresis
13
Using the DNA Sequence
- Making Copies
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique
that allows biologists to make copies of genes. - Small amounts of DNA can be multiplied making it
easier to analyze. - Made possible by an enzyme found in a bacterium
living in hot springs in Yellow Stone National
Park.
14
Using the DNA Sequence
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
DNA heated to separate strands
DNA polymerase adds complementary strand
DNA fragment to be copied
PCR cycles
1
2
3
4
5 etc.
DNA copies
1
2
4
8
16 etc.
15
Quiz
16
- Restriction enzymes are used to
- extract DNA.
- cut DNA.
- separate DNA.
- replicate DNA.
17
- During gel electrophoresis, the smaller the DNA
fragment is, the - more slowly it moves.
- heavier it is.
- more quickly it moves.
- darker it stains.
18
- The DNA polymerase enzyme found in bacteria
living in the hot springs of Yellowstone National
Park illustrates - genetic engineering.
- the importance of biodiversity to biotechnology.
- the polymerase chain reaction.
- selective breeding.
19
- A particular restriction enzyme is used to
- cut up DNA in random locations.
- cut DNA at a specific nucleotide sequence.
- extract DNA from cells.
- separate negatively charged DNA molecules.
20
- During gel electrophoresis, DNA fragments become
separated because - multiple copies of DNA are made.
- recombinant DNA is formed.
- DNA molecules are negatively charged.
- smaller DNA molecules move faster than larger
fragments.
21
END OF SECTION