Population Dynamics - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 10
Title:
Population Dynamics
Description:
Title: Human Ecology and Succession Author: Richland School District Two Last modified by: JCS Created Date: 11/9/2005 9:22:54 PM Document presentation format – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:33
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Population Dynamics
1
Population Dynamics
2
Populations
- A population is a group of organisms of the same
species that live in a particular place at one
time. - A population could be a species of plants,
animals, bacteria, or people, living in a given
area (for example, bass living in an isolated
pond).
3
Population Dynamics
- Populations are constantly changing and we need
to keep up with the changes. The study of human
population is demography. Some measures are - Birth Rate Number of births in a given time.
(U.S. 4 million per year) - Death Rate Number of deaths in a given time.
(U.S. 2.4 million per year) - Life Expectancy how long the avg. person lives.
(U.S. men 77, women 80)
4
Age Structure Diagrams
- Distribution of people of different ages (shown
histogram) - Also Shows Sex Ratio number of males to females.
5
Other histograms
6
Population Growth Rate
- Amount by which a pop. changes over a period of
time, depends on 4 processes birth rate, death
rate, immigration, and emigration. - BR immigration - DR emigration growth
- Growth of a population is usually exponential,
only contained by limiting factors (food, water,
space,density)
7
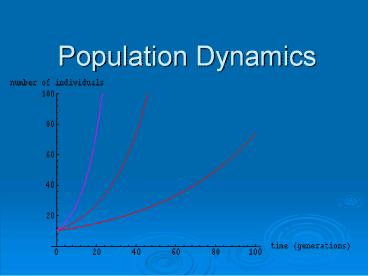
Exponential Growth J-shaped curve. Unlimited
growthex. Humans
8
Logistic Growth S-shaped curve. Pops growth
slows because of a limiting factor (at carrying
capacity) ex. Rabbits in the wild
9
Exponential and Logistical Growth Graph
10
Density Factors
- Density-independent affect all populations in
similar ways regardless of size. Fires,
deforestation, dams, floods, hurricanes etc - Density-dependent factors a limiting factor
that depends on the size of a population. The
more crowded more competition, predation,
parasitism, and disease. CYCLIC