3.1 Human population growth - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 42
Title:
3.1 Human population growth
Description:
World Population Dynamics – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:443
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: 3.1 Human population growth
1
3.1 Human population growth
2
The Population Explosion Exponential Growth
3
The Population Clock
- Population Clock
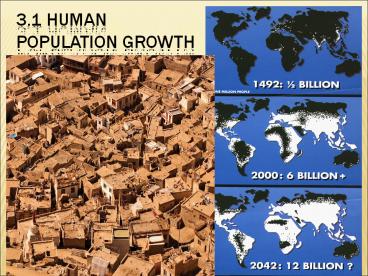
- http//www.census.gov/main/www/popclock.html
- The global population reached 6 billion in fall
of 1999
4
Reasons for population explosion
- Expansion of habitat
- Increased capacity in existing habitats
- Importing resources
- Improved sanitation and medicine
- Increase in agricultural technology
5
Limiting factors of population
- Availability of food and water
- Invasion of parasites, pathogens, or disease
- Over-crowding
- Sudden Climate changes
- Pollution of air, soil and water
- If we do not take steps to control population it
is likely one of these factors will forcibly
reduce our population for us!!
6
Population, population change, growth rates
- Population number of persons
- Population change increase in the number of
persons (per year) - Growth rates rate of change (per year) includes
births, deaths and immigration, and emigration
7
measuring POPULATION Growthuse International
Data Base http//www.census.gov/ipc/www/idbnew.htm
l, then Online Demographic Aggregation
- Crude Birth Rate (CBR) number of births per 1000
population - 1990 24 Today 21.3
- Crude Death Rate (CDR) number of deaths per 1000
population - 1990 9 Today 8.93
- Rate Natural Increase is growth rate without
migration - RNI (crude birth rate crude death rate)
10 - 1990 1.5 Today 1.4
- growth rates have come down
8
Doubling Time
- Number of years in which a population doubles its
size - Doubling time can be approximated using growth
rates and the rule of 70 - Doubling time (T) ___70_____
- growth rate
- Calculate Doubling Time Below
- rate 1.4 doubling time 50 years
- rate 2.0 doubling time ______ years
- rate 0.5 doubling time _______ years
- rate -0.5 doubling time _______years
9
Growth Rate
- Human Population Growth Per Year 1.4
- LEDC (least economically developed country)1.7
- MEDC (more economically developed country) 1.0
10
Rate of Population Increase
11
Special Kinds of Fertility and Mortality Rates
- TFR (total fertility rate)
- number of children born to a woman during her
reproductive years (or life time) - 1990 3.1 2000 2.8
- IMR (infant mortality rate)
- infant deaths per 1000 live births (infant lt 1
yr) - Used as overall indicator of health
- 1990 62 2000 56 (1900 200)
12
Total Fertility Rate
13
Infant Mortality rate
14
(No Transcript)
15
Calculating Future population
- Use Ne(rt) formula
- N Current population
- e constant 2.71828
- r growth rate as a decimal!!!
- t time in years
- Example 2010 data reports that a population of
2,350,000 has a growth rate of 1.2. What will
the population be in 2025?
16
Carrying Capacity
- The maximum population that can be sustainably
supported without running out of resources.
17
3.1.3 Population Pyramids
18
Characteristics of MEDC/LEDC
MEDCs LEDCs
industrialized little or no industry
high GDP (gross domestic product) low GDP
relatively rich population provide raw materials but few processed or manufactured goods
access to education and health care limited access to education and health care
high resource use per capita fewer resources consumed per person
low population growth rates most have high population growth rates
19
Population Pyramids
- Graphic device bar graph
- Shows the age and gender composition of a region
- Horizontal axis gender
- male left-hand female right-hand
- absolute number of people or
- Vertical axis age
- 5-year or 10-year age groups
- Three population categories
- Pre Reproductive- (0-14)
- Reproductive- (15-44)
- Post Reproductive- (45 )
20
Example from Ukraine
21
Why a population Pyramid?
- Helps to determine specifics of potential future
populations - Shape of pyramid indicates future growth
- Can point to future changes in social conditions
of a country
22
Population Pyramids
23
3.1.4 Demographic Transition Model
24
Stages of Demographic Transition Model
Stage Pre-industrial (Stage 1) LEDC (Stage 2) Wealthier LEDC (Stage 3) MEDC (Stage 4) MEDC (Stage 5)
Birth rate High High Declining Low Very low
Death rate High Moderate Low Low Low
Life expect Short Medium Long Long Long
Popl growth Slow Rapid Slowing Stable Shrinking
25
Five Stages of the Demographic Transition
- Birth rates, death rates and growth rates
systematically change through time as societies
change - Modernize, urbanize
- Gain access to new technology
- Births, deaths, migration
- Fertility rates play huge role
26
Factors affecting fertility Rates
- Urbanization
- Importance of children in workforce
- Cost of raising a child
- Education/Employment for women
- Average age of marriage
- Availability of abortion
- Availability of birth control
- Religious beliefs, traditions and culture
27
Stage 1
- High birth rates, high death rates, low growth
rates - Stage for much of human history, traditional
societies - Practically no country today
28
Stage 2
- High birth rates, declining death rates, rising
growth rates - Improvements in sanitation (water) and medicine
- Europe during Industrial Revolution
- LEDC countries since the 1950s
- Much of Africa today, some countries of Asia
(Afghanistan, Nepal)
29
Stage 3
- Continued decline of death rates, declining birth
rates, growth rates decline from high to lower
levels - Change in behavior adaptation to lower death
rate, in particular infant mortality rate - Economic change urbanization (incentive to have
fewer children) - Mexico today
30
Stage 4 5
- Stage 4 low birth rates, low death rates, low
growth rates - United States today
- Stage 5 low birth rates, rising death rates,
declining growth rates (if birth rates drop below
death rates negative growth rates) - Western Europe, Japan
31
Population Pyramid with young cohorts
32
Population Pyramid and Demographic Transition
- Stage 2 wide base
33
Population Pyramid and Demographic Transition
- stage 3 wide middle
34
Population Pyramid and Demographic Transition
- stage 4 slender
35
Population Pyramid and Demographic Transition
- stage 5 narrow base
36
Demographic Transitions in China
37
(No Transcript)
38
(No Transcript)
39
China Population Pyramid 2005
40
(No Transcript)
41
(No Transcript)
42
Models for Predicting Population growth
- Computer simulations
- Can be highly accurate with many variables
- Cant include unforeseen events (i.e. natural
disaster, terrorist strike, warfare)? - Statistical and/or demographic tables
- Include actual field measurements based on past
trends. - Past trends may not always predict future trends.
- How large/representative are the sample
populations? - Age/sex pyramids (
- see above)
- Population curves
- Mathematical extrapolation from graphs based on
real data - Less complex than computer models