The Modern Mediterranean - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
The Modern Mediterranean
Description:
Title: No Slide Title Author: Wheeler High School Last modified by: install Created Date: 9/22/1997 2:22:44 AM Document presentation format: On-screen Show (4:3) – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:83
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Modern Mediterranean
1
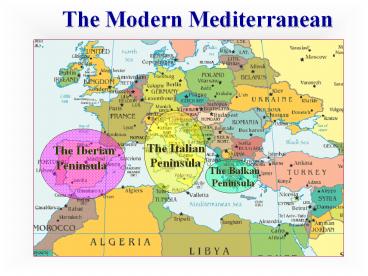
The Modern Mediterranean
The Italian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula
The Balkan Peninsula
2
The Ancient Mediterranean
3
The Geography of Rome
4
The Role of Geography in Ancient Rome
5
The Role of Geography in Ancient Rome
6
The Role of Geography in Ancient Rome
Mountains Two Major Ranges - Alps and Apennines
impact Italy
- Alps to the north separate Italy from the rest of
Europe. They offer some but not total protection
from invasion because of natural passes. - Apennines run the length of Italy but do not
hinder trade or travel.
Effects
Trade and contact with other civilizations was
possible but invasion was also a constant threat,
thus a strong military developed.
7
Northern Italy The Alps
8
Northern Italy The Apennines
9
The Role of Geography in Ancient Rome
Seas Adriatic Sea lies to the East and
Mediterranean to south and west
- Long coastlines with fewer natural harbors than
Greece. - Rivers are generally short and shallow. Poorly
suited for travel and transportation.
Effects
- People turned inland for trade rather than to the
sea as the Greeks had. - The long coastlines made invasion easier.
10
The Seas The Italian Riviera
11
The Role of Geography in Ancient Rome
Land, Soil and Vegetation Most of land is
foothills and mountains except in the valleys of
the north.
- Most soil is sandy and easily erodes. Best suited
for grazing. - Northern valleys are fertile enough for grains.
- Most other areas are good for vegetable, grapes,
olives, and citrus fruits.
Effects
- The Romans were mostly self-sufficient in early
history but turned to trade to supplement food
supply as empire grew.
12
The Land Central Italy
13
Northern Italy - Tuscany
14
Italian Farmland
15
The Role of Geography in Ancient Rome
- Climate Mediterranean Climate
- Mild temperatures and plentiful winter
precipitation. - Suitable for citrus, grapes, olives, and
vegetables.
Effects
- Like the Greeks, Romans spent much time outdoors
socializing and trading ideas. - Citrus, grapes, and olives were major exports for
trade.
16
Mild Mediterranean Climate
17
The History of Ancient Italy
Early Settlers
18
Italy in 750 BC
Three Groups of Early Settlers in Italy Latins
1000 B.C. Etruscans 900 B.C. Greeks 750 B.C.
19
The Latins
- Arrived around 1000 B.C.
- Settled in area known as Latium.
- Primarily farmers who lived in villages along the
Tiber River. - Established the city of Rome around 753 B.C.
- Considered to be the first Romans
The Ancient City of Rome Built on Seven
Hills Along the Tiber River
20
The Etruscans
- Arrived around 900 B.C.
- Settled in area known as Etruria in northern
Italy. - Skilled metal workers and advanced in
engineering. Developed the arch. - Had a writing system which was adopted by the
Romans and became the basis of Latin. - Influenced early Roman religion.
21
The Greeks in Italy
- Began establishing colonies in southern Italy
between 750 and 600 B.C. - Greek cities became prosperous and spread trade
contacts throughout Italy. - Introduced Romans to Greek culture.
- Had a strong influence on Roman trade,
architecture, politics, and religion. - Romans adopted Greek religion and gods.
22
The Mythical Founding of RomeRomulus Remus
23
Early Rome Before the Republic
- The Latins and Etruscans began to merge and
became known as Romans. - Around 600 B.C. an Etruscan was elected king of
Rome and established the Tarquin dynasty. - Rome began emerging into a major city with
impressive engineering and architecture. - Great temples and the forum were built during
this time. - In 509 B.C. a harsh and unjust Tarquin king was
overthrown by the Romans. The Romans declared
they would never again be ruled by a king. - The Romans established a republic that would last
for nearly 500 years. This began Romes climb to
glory and world prestige.
24
The Roman Republic 509 BCE - 27 BCE
25
ANCIENT ROMAN HISTORY THE REPUBLIC
Neolithic Culture
3000 BC
1000 BC
Latin Settlement
EARLY PERIOD
Etruscan Settlement
900 BC
750 BC
Greek Colonization
600 BC
Etruscan Rule of Rome
509 BC
Establishment of the Republic
264 BC
Punic Wars
THE RUPUBLIC
146 BC
Spartacus Slave Revolts
73 BC
First Triumvirate Formed
60 BC
44 BC
Assassination of Julius Caesar
26
Ancient Roman Society
(Early Republic)
Patricians (Aristocrats)
- Plebeians
- Farmers
- Merchants
- Artisans
Freedmen
- Slaves
- City Slaves
- Household Slaves
27
Patricians vs. Plebeians
- The Patricians were wealthy landowners and held
most of the power. - They inherited their power and social status and
claimed to be descendants from the original
Romans.
28
Patricians vs. Plebeians
3. Plebeians were the common people and made up
the majority of Romans. 4. Plebeians were
citizens, could vote but couldnt hold powerful
government office. 5. Eventually Plebeians gained
the right to appoint tribunes to protect their
rights.
6. Around 450 B.C. the Plebeians began writing
down Romes laws and posting them. These were
known as the Twelve Tables.
29
The Twelve Tables, 450 BCE
- Provided political and socialrights for the
plebeians. - Established the idea that all free citizens had a
right to protection by the law.
30
Early Settlements in Italy
















![READ[PDF] An Introduction to the Modern Middle East: History PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10117900.th0.jpg?_=202409020510)

![[DOWNLOAD]PDF️ Foolproof Fish: Modern Recipes for Everyone, Everywhere PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10066494.th0.jpg?_=20240627016)
![[DOWNLOAD]⚡️PDF✔️ Foolproof Fish: Modern Recipes for Everyone, Everywhere PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10066990.th0.jpg?_=20240628011)










![READ [PDF] Super Quick, Easy & Complete Mediterranean Air Fryer Cookbook for Beginners: 2 PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10064288.th0.jpg?_=202406260112)