Physics of Light - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 23
Title:
Physics of Light
Description:
Speed of Light ALL electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light (Radio, TV, Gamma, Ultraviolet and Infrared. . . See Reference Table) Dual Nature of Light Light ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:726
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Physics of Light
1
Physics of Light
2
Light
- Electromagnetic wave
- Needs NO medium to travel
- Transverse wave.
- Speed of Light 3.00 x 108 m/s
- (In air and in a Vacuum)
3
Speed of Light
- ALL electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of
light - (Radio, TV, Gamma, Ultraviolet and Infrared. . .
See Reference Table)
4
(No Transcript)
5
Dual Nature of Light
- Light sometimes behaves like a particle
- Light sometimes behaves like a wave
6
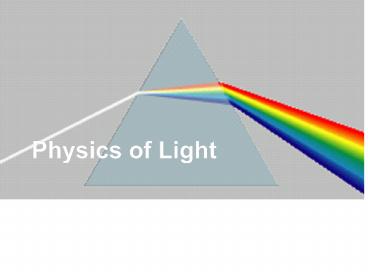
White Light
- The light that comes from the sun and other
artificial means is called white light or visible
light. - White Light is composed of the colors of the
rainbow.
7
Visible Light
- ROY G. BIV
8
Light Energy
- Luminous Objects Objects that generate their
own light - Illuminated Objects Objects that are capable of
reflected light
9
Light Reflection
- Regular Reflection
- Diffuse Reflection
10
Refraction of Light
11
Refraction of Light
- Speed of light is dependent on the medium it is
traveling through - Optical density (How well light can pass through)
12
Index of Refraction
- Index of Refraction Number that tells how
optically dense an object is based on the speed
of light through it.
13
Index of Refraction Value
- Ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the
speed of light in the material. - n index of refraction
- c speed of light (m/s)
- v velocity (m/s)
14
(No Transcript)
15
Snells Law
- As light speeds up, it bends AWAY from the normal
- As light slows down, it bends TOWARDS the normal
16
- Using Snells Law and the values for n in the
diagram below, draw arrows to show the path
through the layers of different materials.
Air (1.0)
Flint Glass (1.61)
Water (1.33)
Diamond (2.42)
17
Diffraction
- Bending of a wave around an obstacle
- Single Slit Diffraction
18
Diffraction
- Double Slit Diffraction
19
Diffraction
- Size of opening and wavelength affect the
diffraction pattern - Greatest diffraction pattern occurs with a long
wavelength and narrow opening
20
Polarization
- Unpolarized light Light waves which are
vibrating in more than one plane (Sun, lamps,
candle) - Polarized Light Light waves in which the
vibrations occur in a single plane
21
Polarization
- Polarization process of transforming
unpolarized light into polarized light. - Uses - Sunglasses
22
WARM-UP
- The speed of light in Lucite is _________?
- The speed of light in goop is 2.56x108 m/s. What
is the index of refraction of goop?
23
Lab 17 and 18
- Lab 17
- Problem How are the angle of incidence and the
angle of reflection related? - Lab 18
- Problem How are the angle of incidence and the
angle of refraction related?













![L 34 Modern Physics [1] PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/7125701.th0.jpg?_=20150905079)


![L 33 Modern Physics [1] PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/7602675.th0.jpg?_=201602121011)












