Announcements - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Announcements
1
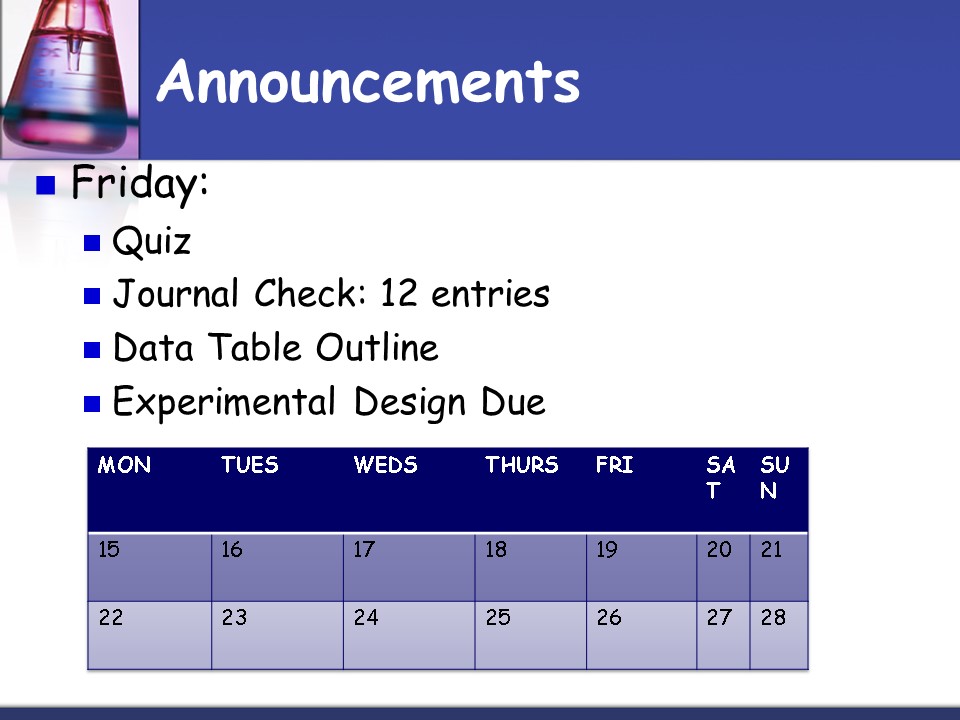
Announcements
- Friday
- Quiz
- Journal Check 12 entries
- Data Table Outline
- Experimental Design Due
MON TUES WEDS THURS FRI SAT SUN
15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22 23 24 25 26 27 28
2
The Periodic Table
- How is the periodic table put together?
3
(No Transcript)
4
What is the Periodic Table?
- It is an organizational system for elements.
- Periodic Table Song ASAPscience
- Periodic Table Song Meet the Elements
Picture from www.chem4kids.com
5
Who created it?
- The quest for a systematic arrangement of the
elements started with the discovery of individual
elements. - By 1860 about 60 elements were known and a
method was needed for organization. - In 1869, Russian chemist Dimitri Mendeleev
proposed arranging elements by atomic weights and
properties. - The table contained gaps but Mendeleev predicted
the discovery of new elements.
6
Mendeleevs Table
7
So how is it arranged?
- The genius of the periodic table is that it is
organized like a big grid. - The elements are placed in specific places
because of the way they look and act. - If you have ever looked at a grid,
- you know that there are rows (left to right)
- and columns (up and down). The periodic table has
rows and columns, too, and they each mean
something different. - quoted from http//www.chem4kids.com/files/elem_pe
rtable.html
8
Periods Rows
- Even though they skip some squares in between,
all of the rows go left to right. When you look
at a periodic table, each of the rows is
considered to be a different period (Get it? Like
PERIODic table.) - quoted from http//www.chem4kids.com/files/elem_pe
rtable.html
9
Across the Periodic Table
- Periods Are arranged horizontally across the
periodic table (rows 1-7) - These elements have the same number of valence
shells.
2nd Period
6th Period
10
Periods Rows
- In the periodic table, elements have something in
common if they are in the same row. - All of the elements in a period have the same
number of atomic orbitals. - Every element in the top row (the first period)
has one orbital for its electrons. All of the
elements in the second row (the second period)
have two orbitals for their electrons. It goes
down the periodic table like that. - quoted from http//www.chem4kids.com/files/elem_pe
rtable.html
11
And you got your groups
- The periodic table has a special name for its
columns, too. When a column goes from top to
bottom, it's called a group. - quoted from http//www.chem4kids.com/files/elem_pe
rtable.html
12
Down the Periodic Table
- Family Are arranged vertically down the periodic
table (columns or group, 1- 18 or 1-8 A,B) - These elements have the same number electrons in
the outer most shells, the valence shell.
13
Groups Columns
- The elements in a group have the same number of
electrons in their outer orbital. - Every element in the first column (group one) has
one electron in its outer shell. Every element on
the second column (group two) has two electrons
in the outer shell. As you keep counting the
columns, you'll know how many electrons are in
the outer shell. - There are some exceptions to the order when you
look at the transition elements, but you get the
general idea.
14
What do all the numbers mean ?
From www.science-class.net
15
Periodic Table Metallic arrangement
- Layout of the Periodic Table Metals vs.
nonmetals
Nonmetals
Metals
16
Other than periods and groups, the table is
divided into families.
From www.science-class.net
17
9.16 WARM UP
- What are 3 ways the periodic table is organized?
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
18
Announcements
- See front board
- Experimental Design hard copy
- Bring science fair journals on Friday
- Quiz Friday
19
9.16 WARM UP
- What are 3 ways the periodic table is organized?
- 1. Atomic number
- 2. Properties and characteristics
- 3. Valence electrons
- 4. State of Matter
- 5. Metal Properties
20
Getting to know the families
- Groups will discuss each family
- Find
- 3 characteristics
- 2 common examples
- Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals, Transition
Metals, Rare Earth Metals, Other Metals,
Non-Metals, Metalloids, Halogens, Noble Gases
21
- Alkali Metals 120
- Alkaline Earth 121
- Transition Metals 122
- Lanthanides 122
- Actinides 124
- Metalloids 135
- Carbon Family 130
- Nitrogen Family 131
- Oxygen Family 132
- Halogen Family 133
- Noble Gases 134
- Hydrogen 134
22
ALKALI METALS
- very reactive metals that do not occur freely in
nature - malleable, ductile, good conductors of heat and
electricity. - can explode if they are exposed to water
From www.science-class.net
23
ALKLINE EARTH METALS
- metals
- very reactive
- not found free in nature
From www.science-class.net
24
TRANSITION METALS
- ductile and malleable, and conduct electricity
and heat - iron, cobalt, and nickel, are the only elements
known to produce a magnetic field.
From www.science-class.net
25
RARE EARTH ELEMENTS
- many are man-made
From www.science-class.net
26
OTHER METALS
- are ductile and malleable
- are solid, have a high density,
From www.science-class.net
27
METALLOIDS
- have properties of both metals and non-metals
- some of the metalloids are semi-conductors. This
means that they can carry an electrical charge
under special conditions. This property makes
metalloids useful in computers and calculators
From www.science-class.net
28
NON-METALS
- not able to conduct electricity or heat very well
- very brittle
- Do not reflect light.
From www.science-class.net
29
HALOGENS
- "halogen" means "salt-former" and compounds
containing halogens are called "salts" - exist in all three states of matter
From www.science-class.net
30
NOBLE GASES
- do not form compounds easily
- Happy/Inert Elements (Full outer shells)
From www.science-class.net
31
Trends
32
Trend 1. Electron Configuration
- Top has fewer electrons, bottom (NE corner) has
the most - Electrons increase as you move across and down
33
2. Trend in Atomic Radius
- Atomic Radius
- The size of the atom as determined by the
boundaries of the valence e-. Largest atomic
species are those found in the SW corner since
these atoms have the largest n
34
3.Trend in Ionization Potential
Ionization potential The energy required to
remove the valence electron from the atom.
Largest toward NE corner of PT since these atoms
hold on to their valence e- the tightest.
35
4. Trend in Electron Affinity
Electron Affinity The energy release when an
electron is added to an atom. Most favorable
toward NE corner of PT since these atoms have a
great affinity for e-. (Likelihood to gain an
electron)
36
Trends on a graph
3. Ionization Energy Largest toward NE of PT 4.
Electron Affinity Most favorable NE of PT
2. Atomic Radius Z Largest toward SW corner
of PT
37
5. Trends with Metals
- Becomes less metal-like from left to right
- More metallic from top to bottom
38
Secret Words
- Saying is
- _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
- _ _ _ _ _ happy.