Levels of Analysis - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Levels of Analysis
Description:
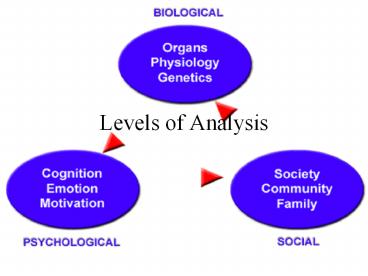
Levels of Analysis Biological Influences Natural selection of adaptive traits Genetic predispositions responding to environment Brain mechanisms Hormonal influences ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:83
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Levels of Analysis
1
Levels of Analysis
2
Biological Influences
- Natural selection of adaptive traits
- Genetic predispositions responding to environment
- Brain mechanisms
- Hormonal influences
3
Psychological Influences
- Learned fears and other learned expectations
- Emotional responses
- Cognitive processing and perceptual
interpretations
4
Social-Cultural Influences
- Presence of others
- Cultural, societal, and family expectations
- Peer and other group influences
- Compelling models (such as the media)
5
Modern Approaches/Perspectives
- Evolutionary
- Biological
- Cognitive
- Behavioral
- Psychoanalytical
- Humanistic Approach
- Social-Cultural
6
Evolutionary Approach
- Focus How nature selects traits that promote
the perpetuation of ones genes. Survival. - Influenced by Charles Darwin
7
Psychoanalytical Approach
- Focus How behavior springs from unconscious
drives and conflicts - Early Childhood
- Dreams
- Sigmund Freud
8
Biological Approach
- Focus How the body and brain create emotion,
memories, and sensory experiences. - Brain structures, blood chemistry, neural
communication. - Roger Sperry, Michael Gazzaniga, Paul Broca
9
Cognitive Approach
- Focus How we encode, process, store, and
retrieve information. - Jean Piaget, Elizabeth Loftus, Hermann Ebbinghaus
10
Behavioral Approach
- Focus Learning based on how a behavior is
rewarded or punished. - John Watson, B.F. Skinner, Ivan Pavlov
11
Humanistic Approach
- Focus Emphasizes that we have great freedom in
directing our future, a large capacity for
growth, intrinsic worth, and self-actualization. - Abraham Maslow
- Carl Rogers
12
Social-Cultural Approach
- Focus How behavior and thinking vary across
situations and cultures. - Albert Bandura, Phillip Zimbardo
13
Which Perspective??
- Dr. A is interested in studying the different
attitudes about the elderly among North American
and Japanese adults. Dr. A has found that the
Japanese show more respect and responsibility
toward elderly parents, and wishes to understand
the cultural norms that contribute to these
attitudes.
14
Which Perspective??
- Prof. B studies the attention process involved
when people search for specified objects by
measuring the amounts of blood flow to various
portions of the brain while a participant engages
in a letter detection task.
15
Which Perspective??
- Dr. C tries to help a client stop smoking by
understanding the unconscious reasons for the
clients need to smoke. Dr. C encourages the
client to talk about his childhood conflicts with
his parents.
16
Which Perspective??
- Dr. Dre tries to help a client stop smoking by
telling her to keep a careful record of the
number of cigarettes smoked and the particular
people or situations who are a part of her
smoking behavior. She keeps these records as a
way of uncovering the factors that reward her for
smoking, so that she may later remove those
rewards.
17
Which Perspective??
- Prof. E studies the factors that help or hinder
students in memorizing information from
textbooks. The professor systematically varies
task characteristics such as textbook difficulty
in an effort to understand the underlying memory
processes involved in reading a textbook.
18
Which Perspective??
- Dr. F is working to help a seriously depressed
man become a productive member of society again.
She points out to her client his potential for
personal growth and his obvious love for his
family, and reminds him of his many successes in
professional and personal activities.
19
Subfields/jobs that conduct basic research
- Biological links between brain and mind
- Development changing abilities from the womb to
tomb - Cognitive how we think, perceive and solve
problems - Educational studying influence on teaching and
learning - Personality investigating our persistent traits
- Social explore how we view and affect one
another
20
Subfields/jobs that conduct applied research
- Industrial-organization psychologists use
psychology concepts and methods in the workplace
to help organizations and companies select and
train employees, , boost morale and productivity,
design products, and implement systems - Human factors psychologists focus on the
interaction of people, machines, and physical
environments - Counseling psychologists help people to cope
with challenges and crises and to improve their
personal and social functioning - Clinical psychologists assess and treat mental,
emotional, and behavior disorders - Psychiatrists medial doctors licensed to
prescribe drugs and otherwise treat physical
causes of psychological disorders
21
Where Do Psychologists Work?
- 49 Private Practice-Therapy Setting-Clinical
Psychologist - 28 Academic Setting- Research (Basic/Applied,
Professor) - 13 Variety (Social Work, Group Home
Coordinator) - 6 Industrial/Organization Setting (Production
Manager) - 4 Secondary Schools-(School Psychologist/Counselo
r)