*Gregor Johann Mendel 1822-1884 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 12
Title:
*Gregor Johann Mendel 1822-1884
Description:
Pisum sativum-Why study (or experiment with) the garden pea?-Mendel followed several visible features: The Monohybrid Cross -Example: X Tall Dwarf P1 F1 all Tall ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:151
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: *Gregor Johann Mendel 1822-1884
1
Chapter 3 Mendelian Genetics
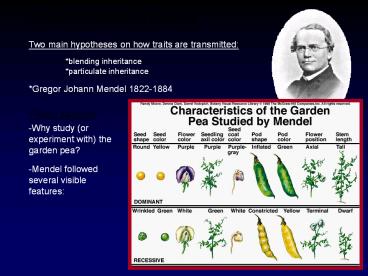
Two main hypotheses on how traits are
transmitted blending inheritance
particulate inheritance
Gregor Johann Mendel 1822-1884
Pisum sativum
-Why study (or experiment with) the garden pea?
-Mendel followed several visible features
2
The Monohybrid Cross
-Example
F2
P1
X
Tall
Dwarf
F1 all Tall
3
Mendels Principles of Inheritance
unit factors
1. Unit factors occur in pairs
P1
Tall
Dwarf
Factors
DD dd Dd
4
Mendels Principles of Inheritance cont
2. Dominance/Recessiveness
P1
X
Tall
Dwarf
DD dd
F1 all Tall
Tall
Dd
5
Mendels Principles of Inheritance cont
3. Segregation
P1
X
Tall
Dwarf
DD dd
F1 all Tall
Tall
Dd
6
Mendels Principles of Inheritance cont
What about the F2?
Tall
Tall
Self cross F1
D
d
D
d
7
The Test Cross One Character
-How to distinguish DD or Dd genotype?
Test cross
8
Punnett Squares
Tall
Tall
Self cross F1
X
Dd Dd
Gamete formation
9
CH3 Problem 2
2. Albinism in humans is inherited as a simple
recessive trait. Determine the genotypes of the
parents and offspring for the following families.
When two alternative genotypes are possible, list
both. (A) Two non albino (normal) parents have
five children, four normal and one albino. (B) A
normal male and an albino female have six
children, all normal.
10
Mendelian inheritance is based on probability
Example- coin toss
11
The Rule of Addition
12
Chi-Square Analysis
p value (probability) consider as a percentage
(i.e. 0.05 5)



















![Gregor Johann Mendel (July 20, 1822[1] PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/6267679.th0.jpg?_=20150314042)










