Leaves - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 19
Title:
Leaves
Description:
Leaves Tissues of leaves and their function Palisade mesophyll consists of densely packed cylindrical cells with many chloroplast. This is the main photosynthetic ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:104
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Leaves
1
Leaves
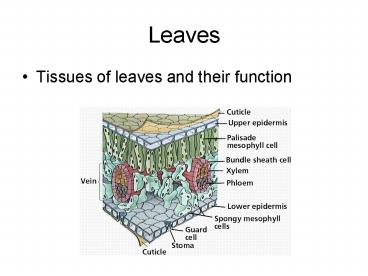
- Tissues of leaves and their function
2
- Palisade mesophyll consists of densely packed
cylindrical cells with many chloroplast. This is
the main photosynthetic tissue and is positioned
near the upper surface where the light intensity
is highest
3
(No Transcript)
4
- Upper epidermis a continuous layer of cells
covered by a thick waxy cuticle. Prevents water
loss from the upper surface even when heated by
sunlight. Lower epidermis is in a cooler
position and has a less thick waxy covering
5
- Note stomata on epidermis. The stomata is a pore
that allow carbon dioxide for photosynthesis to
diffuse in and oxygen out
6
- Xylem brings water to replace losses due to
transpiration
7
- Phloem transports products of photosynthesis
out of leaf. - Both xylem and phloem are called the vascular
system of plants. The vein is centrally located
to be close to all cells.
8
phloem
9
Transport in phloem
- Phloem is located inside leaves. Used to
transport sugars, amino acids, and other organic
compounds from photosynthesis. - Structures called sieve tubes do the
transporting. - This is an active process requiring ATP
- High concentration in sieve tubes of solute cause
water to move in by osmosis
10
- This creates a high enough pressure for movement
where ever the plant needs these products. - The transport of any biochemical (includes
sprayed on chemicals) in phloem is called
translocation. - Sugar Transport in Plants
11
Transpiration
- Flow of water from the roots, through the stems
to the leaves of plants (transpiration) - Starts with evaporation of water from the cell
walls of spongy mesophyll. - Water is replaced with water from the xylem
12
Xylem and transport of water
- Google Image Result for http//www.phschool.com/sc
ience/biology_place/labbench/lab9/images/xylem.gif
13
Structure of xylem
14
Factors which affect transpiration
- Light closed guard cells in stomata in darkness
- Temperature high temp increase rate of diffusion
through air spaces in spongy mesophyll - Humidity movement by osmosis requires water
potential gradient. Low humidity increases
transpiration - Wind blows saturated air away from leaf thus
increasing transpiration
15
Food storage in plants
- The excess products of photosynthesis may be
stored in storage area called tubers.
16
Roots
17
- Roots absorb mineral ions and water from the soil
- Anchor the plant and are sometimes used for food
storage - Plants Transport and Nutrition - Water Movement
18
Mineral uptake by roots
- Plants absorb potassium, nitrate and other
mineral ions - Concentration is lower than inside roots
- active transport
- Root hairs provide surface area for ion uptake
19
(No Transcript)