Current - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Current
Description:
Electrical Circuits An electric circuit is composed of 3 elements Conductor, potential difference, closed loop An electrical circuit without a load that has some ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:66
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Current
1
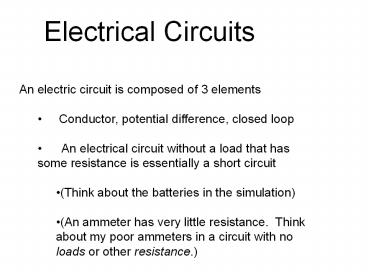
Electrical Circuits
- An electric circuit is composed of 3 elements
- Conductor, potential difference, closed loop
- An electrical circuit without a load that
has some resistance is essentially a short
circuit - (Think about the batteries in the simulation)
- (An ammeter has very little resistance. Think
about my poor ammeters in a circuit with no loads
or other resistance.)
2
Electrical Circuits
In a series electric circuit all of the electrons
must flow through the same elements In a
parallel electric circuit electrons may flow
through different circuit elements
3
Electrical Circuits
In a series electric circuit, the voltage drops
as it flows through each resistive circuit
element
4
Resistors in Series Building Analogy
R1 Lamp
6 steps
R1
R2 Lamp
Elevator (battery)
11 steps
R3 Lamp
R2
3 steps
To go from the top to the bottom floor, all
people must take the same path. So, by
definition, the staircases are in series. With
each flight people lose some of the potential
energy given to them by the elevator, expending
all of it by the time they reach the ground
floor. So the sum of the V drops across the
resistors the voltage of the battery. People lose
more potential energy going down longer flights
of stairs, so long stairways correspond to high
resistance resistors. The double waterfall is
like a pair of resistors in series because there
is only one route for the water to take. The
longer the fall, the greater the resistance.
5
Diagramming circuits
6
Ohms Law Ohm's Law says that, for many
materials under a wide range of conditions, the
voltage, V, and current, I, are linearly related,
which implies resistance, R, is independent of V
and I.
- When does it not apply? (Most important case)
7
Ohms Law Mnemonic
8
Resistance and Ohms Law
- Resistance is the impedance to the flow of charge
- Resistance is defined as the ratio of potential
difference to current - R V/I Unit is the Ohm, O
- A device is said to obey Ohms Law if its
resistance is independent of the Voltage
9
First, fill in all values of V and I. After
review, fill in values of R
I1 1
V2
R2
V1 9
V
V
10
First, fill in all values of V and I. After
review, fill in values of R. Assume all light
bulbs have the same resistance.
I2
R4
V3
V4
V
V
I3 2
V5 2
R5
V
V
11
First, fill in all values of V and I. After
review, fill in values of R. Assume all light
bulbs have the same resistance.
I4 1
R7
V7
V6
V
V
I5
V8 3
R8
V
V
I6
R9
V
V
V9
12
We will work this one out together. Assume all
light bulbs have the same resistance.
I4
R7 1
V7
V
V
R7 2
V7
V6
V
V
I5
V8 6
R8 3
V
V
I6
R9 4
V
V
V9
13
We will work this one out together
I4
VT V1 V2 V3
R7
V7 3
V
V
RT R1 R2 R3
R8 2
V8
V6
V
V
I5
V9 5
R9
IT I1 I2 I3
V
V
I6
R10 4
V
V
V10 4
14
Questions
- What happens if we greatly increase the
resistance? - When else, besides electricity, do we see things
like this? - - Think about the effects on voltage (pressure),
current (flow), and resistance (blockage)
15
(No Transcript)
16
(No Transcript)
17
(No Transcript)
18
(No Transcript)
19
Tell me about heart bypassess
20
Tell me about heart bypassess
21
Parallel Circuit
- More than one path for the flow of charge
- More room for the flow of charge so Resistance
goes down - Voltage must stay the same since all sections
have the same drop
22
Kirchoffs Junction Rule
- Conservation of charge
23
Kirchoffs Loop Rule
- Conservation of Energy
- The sum of the changes in potential around any
closed path (loop) of a circuit must be zero.
24
- Parallel Circuit
- Voltmeters are parallel to the circuit
How do the sum of I1, I2, and I3 relate to
IT? Hint What is current? What is it made up
of?
IT
IT
I2 I3
I1
R3
R1
R2
V2
V3
V1
V
V
V
V
V
V
IT
25
- Parallel Circuit
- Voltmeters are parallel to the circuit
IT I1 I2 I3 by Conservation of charge
(conservation of matter)
IT
IT
I2 I3
I1
R3
R1
R2
V2
V3
V1
V
V
V
V
V
V
IT
26
- Parallel Circuit
- Follow the current
- Now map the current flow for circuit 2
IT
R5
R6
R4
V2, I2
V3, I3
R1
R2
V1, I1
R3
IT
Circuit 2
Circuit 1
27
- Parallel Circuit
- Follow the current
- How does circuit 1 differ from circuit 2?
IT
R5
R6
R4
V2, I2
V3, I3
R1
R2
V1, I1
R3
IT
28
R1 100 Ohms
VT 120V
R2 200 Ohms
V1
VT
V2
RT
V2, I2
V
V
V1, I1
R1
R2
IT
IT
I1
I2
29
R1 100 Ohms
VT 120V
R2 200 Ohms
V1
R3 150 Ohms
V2
VT
RT
V3
V2, I2
V3, I3
V
V
R3
V1, I1
R1
R2
IT
IT
I1
I2
I3
30
R1
VT 120V
Rwire 1 Ohms
R2
V1
R3
V2
VT
RT
V3
V2, I2
V3, I3
V
V
R3
V1, I1
R1
R2
IT
IT
I1 5A (600W)
I2 5A
I3 5A
31
(No Transcript)
32
Resistance of an object
- What would we expect it to depend on?
- (Resistance is the impedance to the flow of
charge)
33
Resistance of an object
- What would we expect it to depend on?
- (Resistance is the impedance to the flow of
charge)
L
A
34
Find Resistance of a material
- Depends on four factors
- R 8 Temp
- R 8 RHO (?) resitivity
- R 8 Length
- R 8 A-1 (cross-sectional Area)
35
Low resistance
- Short
- Fat
- cold
36
High Resistance
- Long
- Thin
- Hot
37
Series and Parallel Circuits
L
Series Single Path, high effective resistance
a
L
A
Parallel Multiple Paths, low effective
resistance
38
Resistivities at 20C Resistivities at 20C
Material Resistivity
Aluminum 2.82 108
Copper 1.72 108
Gold 2.44 108
Nichrome 150. 108
Silver 1.59 108
Tungsten 5.60 108
From Reference tables
39
Electrical Power
- P IV Poison Ivy
40
Electrical Power
- Power is the rate at which work is done or energy
is expended. - Unit is Watt Joule / second
- (James Watt worked on steam engines and launched
the industrial revolution) - Electrical Energy Power Time VIt
41
Electrical Power
- Electrical Power is priced in kWh
- One kiloWatt 1000 Watts
- One kWh One kW for one hour
42
(No Transcript)
43
Monthly Service Charge is 18 Monthly Service Charge is 18
Central Hudson Variable Costs Central Hudson Variable Costs Central Hudson Variable Costs
0.047
0.002
-0.007
0.004
0.001
0.003
0.001
0.004
0.065
0.014
Total 0.134
44
Monthly Charges Monthly Charges Monthly Charges (Includes the effect of Schedules 59, 91, 93)
6.00 Basic Charge, Basic Charge, plus
0.06850 0.06850 per Kwh for the first per Kwh for the first per Kwh for the first 600 Kwhs
0.07933 0.07933 per Kwh for the next per Kwh for the next per Kwh for the next 700 Kwhs
0.09260 0.09260 per Kwh for all additional Kwhs per Kwh for all additional Kwhs per Kwh for all additional Kwhs per Kwh for all additional Kwhs
Example - Example -
If you used 1450 1450 Kwhs of electricity, your bill would be calculated like this Kwhs of electricity, your bill would be calculated like this Kwhs of electricity, your bill would be calculated like this Kwhs of electricity, your bill would be calculated like this Kwhs of electricity, your bill would be calculated like this Kwhs of electricity, your bill would be calculated like this
Basic Charge 6.00
0.06850 0.06850 x 600 Kwhs 41.100
0.07933 0.07933 x 700 Kwhs 55.531
0.09260 0.09260 x 150 Kwhs 13.890
Charge for 1450 1450 Kwhs 116.52 (franchise fees not included) (franchise fees not included)